Collaboration & Governance

Business Process Governance & Business Process Collaboration

Throughout all phases of your program (content development, training, change management, ongoing updates and improvements), collaboration, communication and business process governance is key to success. The Enterprise Process Center® provides team members with a centralized reusable repository that can be worked on by several individuals in-parallel without the risk of duplicating content nor over-writing someone else’s work.
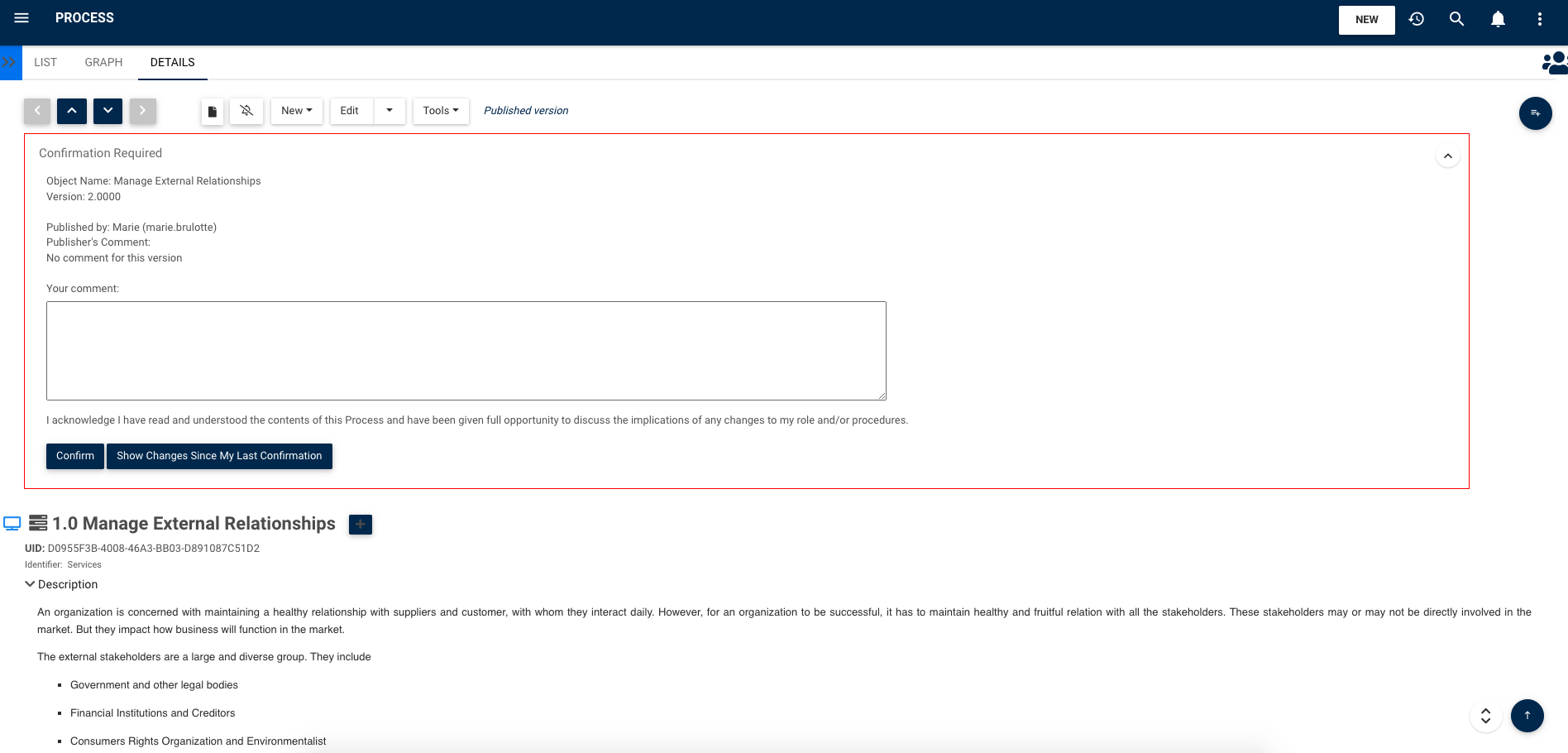
Employees are notified of newly published versions, need to confirm they read and understand changes, and have a user-friendly forum to raise improvement requests or discuss issues as they arise. Empowering employees with tools to collaborate is of great importance for success; and as much so is enforcing ongoing accountability and governance.
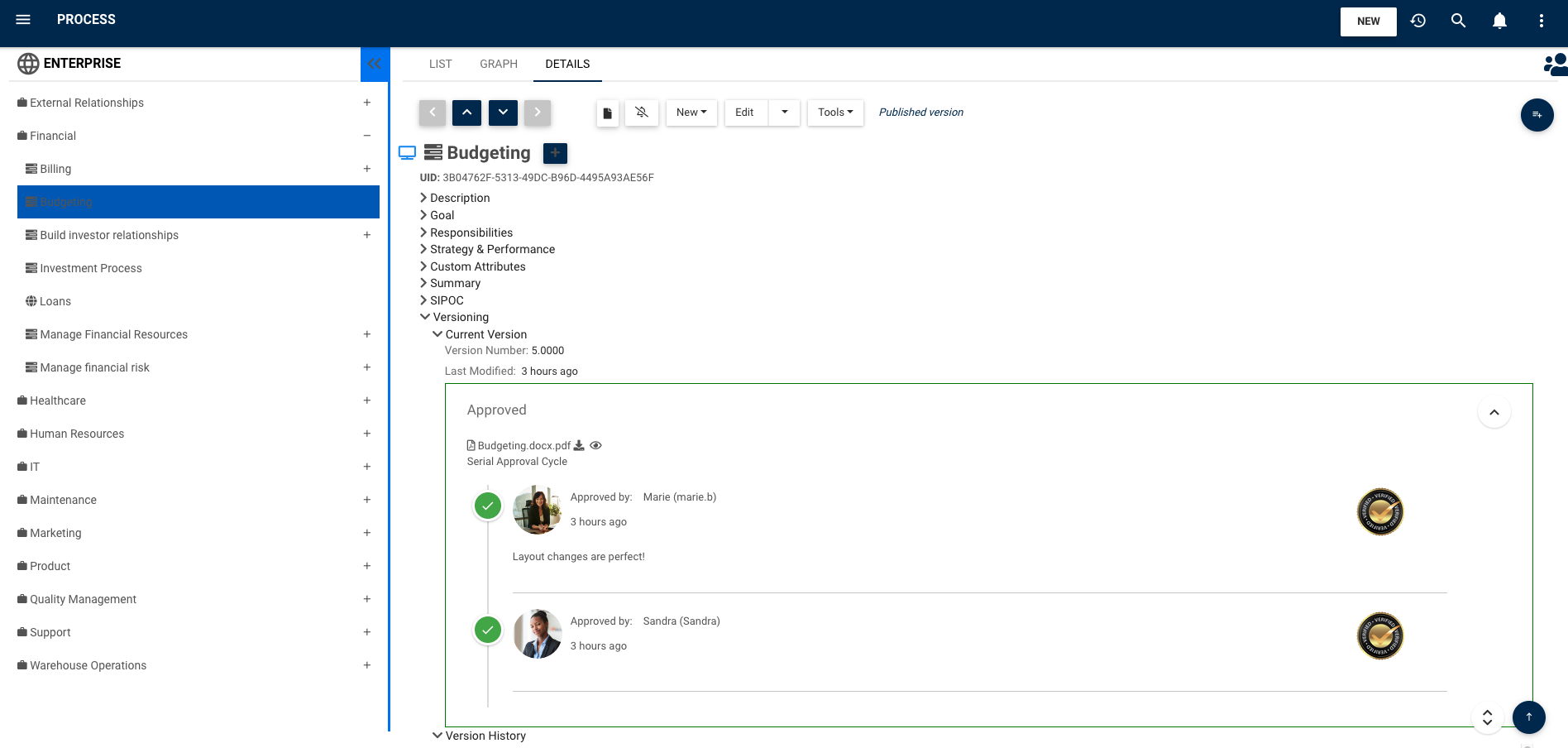
EPC simplifies this need with automated control measures such as review and approval cycles and draft vs. published version read/ write and delete security access rights on all content. Additionally the EPC platform tracks and stores all historical details of a modification, from request through to implementation, including all specifics of a change for detailed audit reporting.
Gartner® Certified
Enterprise Process Center® recognized by Gartner® as a global leader in Business Operation System, Operational Intelligence & Enterprise Business Process Analysis (EBPA) including Enterprise Architecture, Business Process Analysis, Strategy-to-Execution & Workflow Automation.
The EPC Toolkit provides organization with:
Communication & Notifications
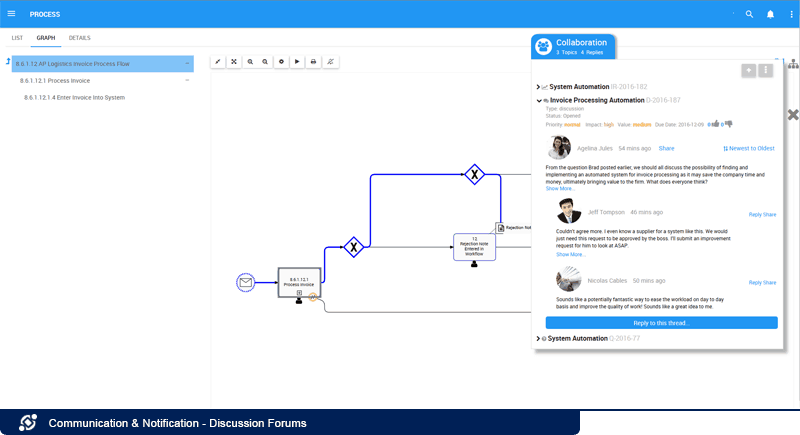
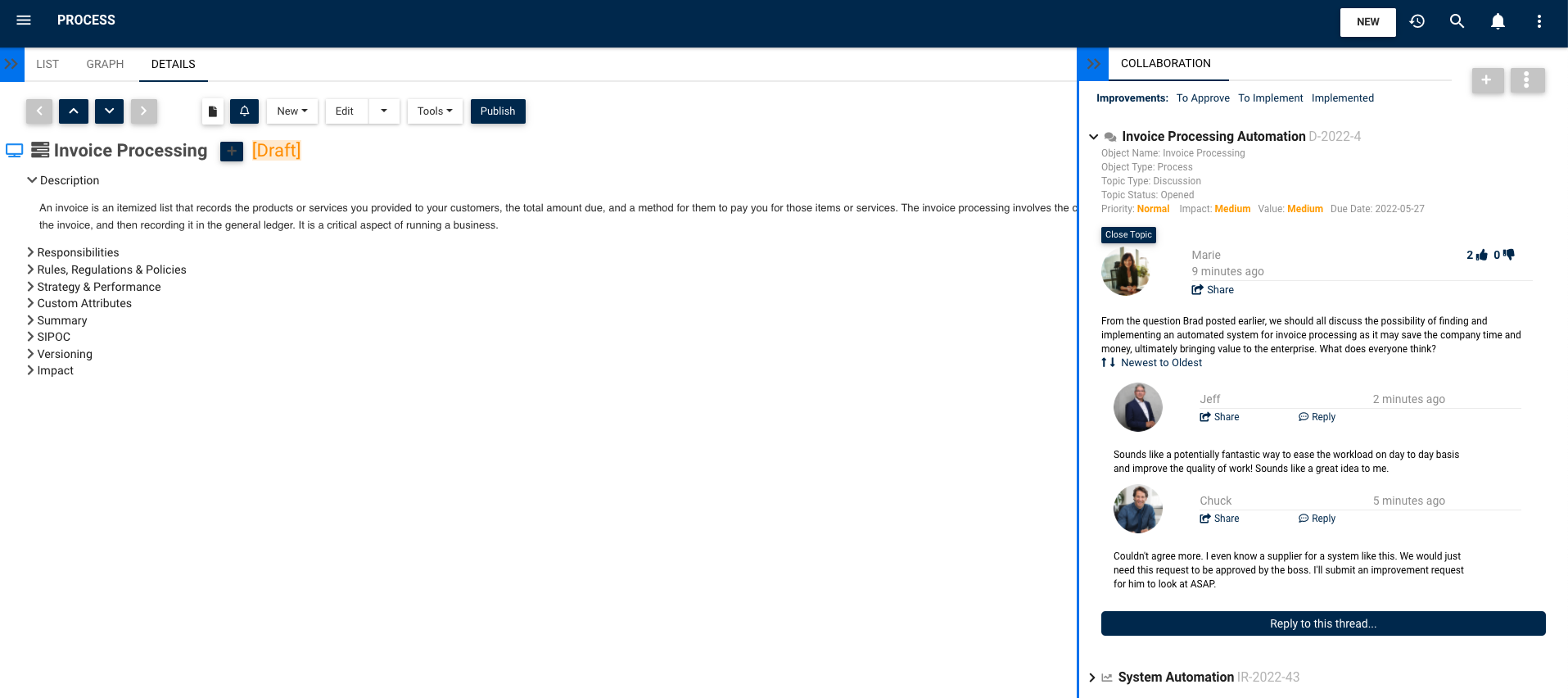
Discussion Forums:
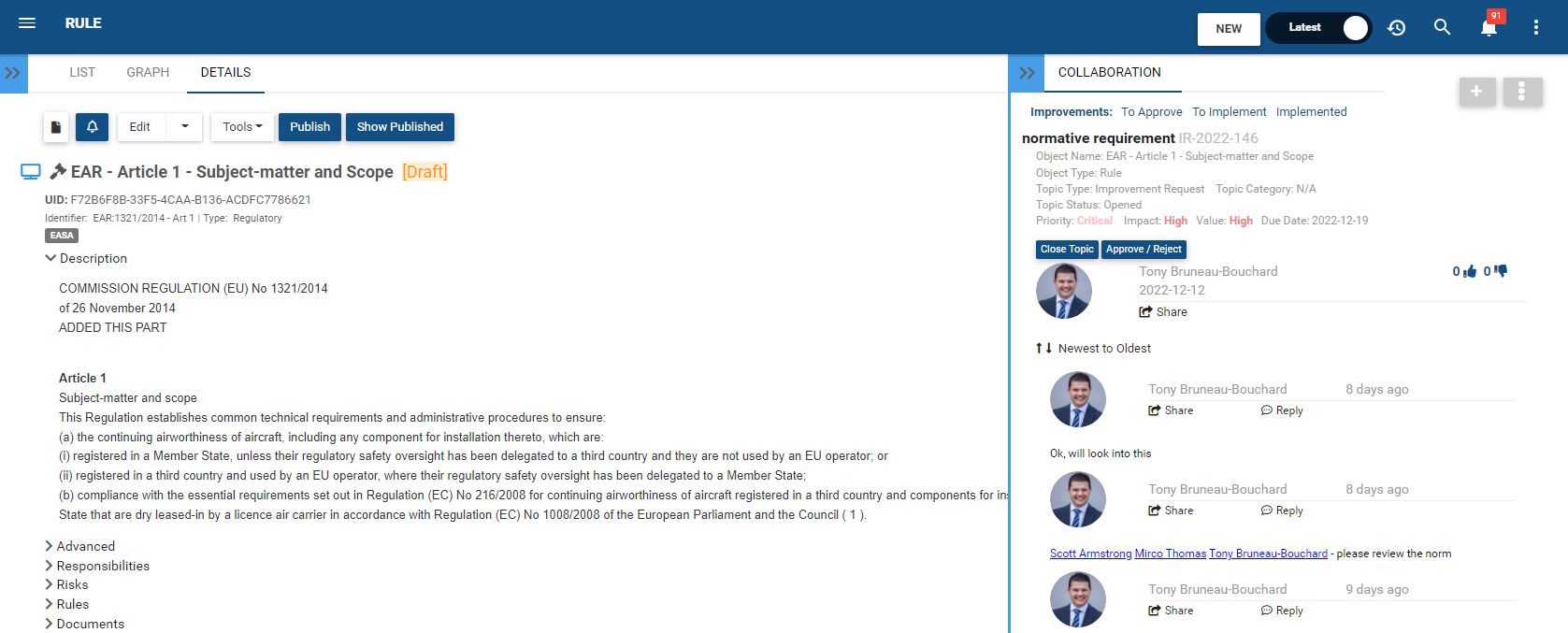
Employees can ask questions, suggest improvements or raise incidents on all content managed within the system (processes, application, documents, business rules, etc.) with colleagues across different sites, locations or regions. Posts will notify all those subscribed to contribute to the conversation and assign tasks to those that are accountable to take action. Sharing challenges, solutions and best practices with experts across locations bolsters collaboration and continuous improvement.
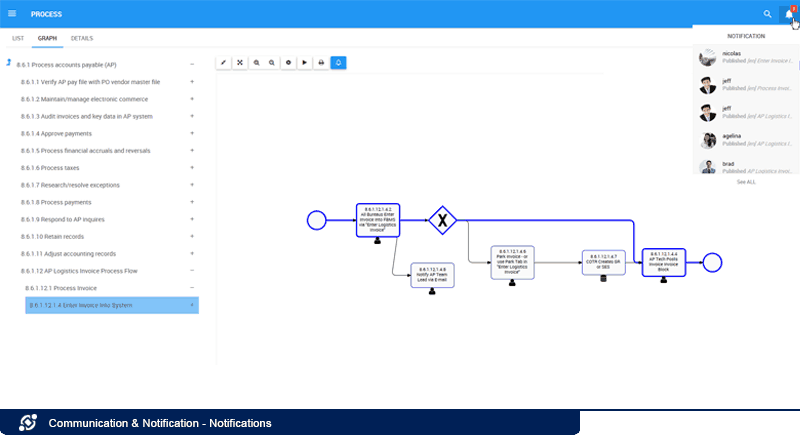
Notifications:
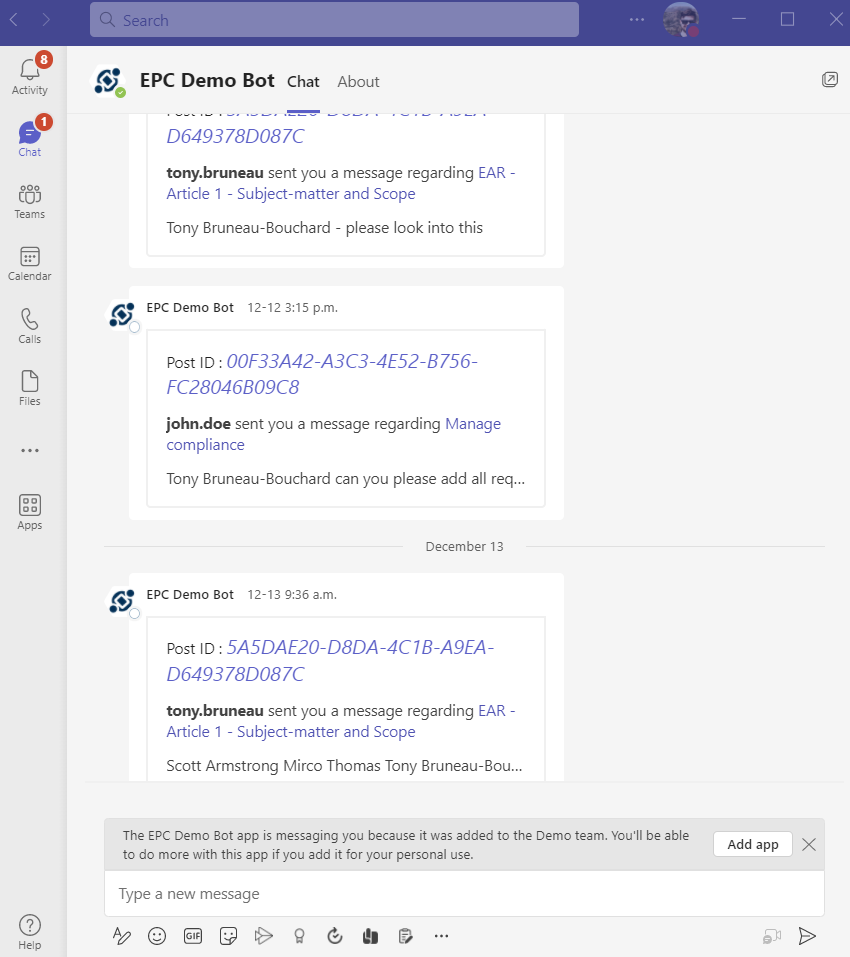
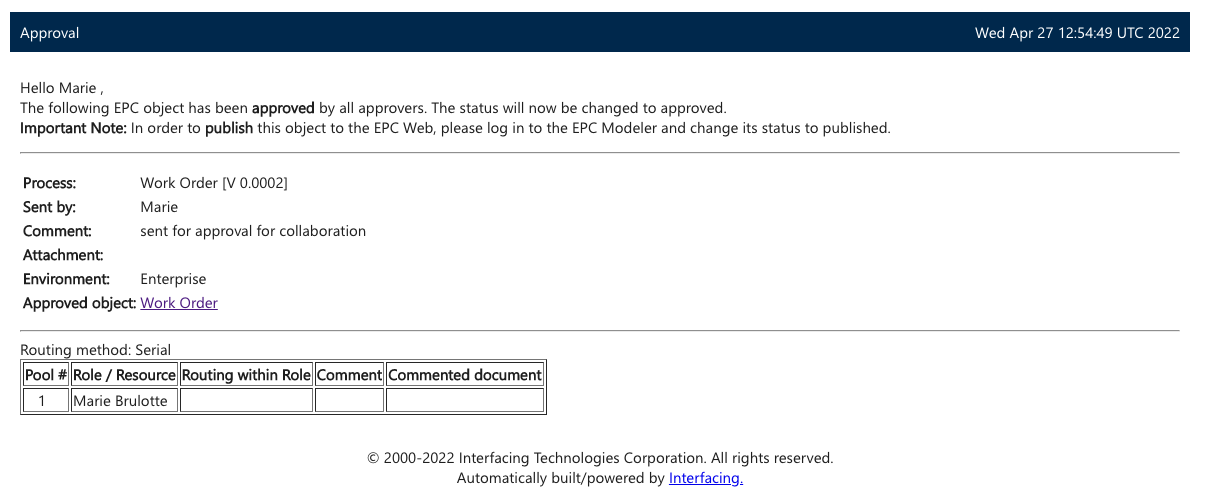
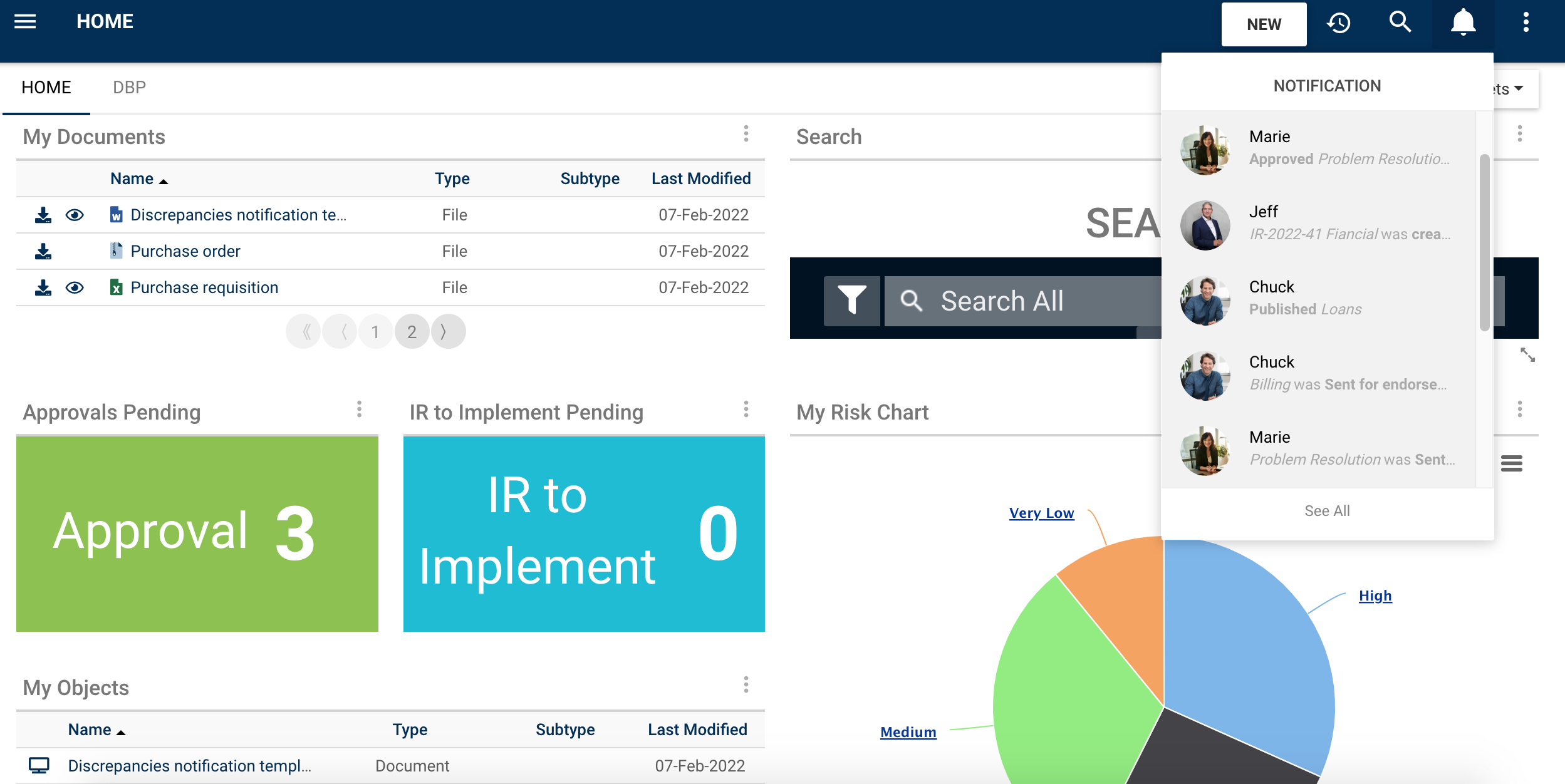
EPC highlights the number of new notifications since last logged in directly within the header and at all times so employees know new versions are available or actions need to be taken. Additionally, the best way to reach many employees is by pushing information to their inboxes so that there is no excuse as to why they may be using an outdated version. The EPC integrates with all email servers to automatically notify users of discussion postings and tasks to be completed such as upcoming or overdue reviews, required approvals, or newly published versions to confirm. Emails contain direct URLs to the posting or action so users can quickly navigate to content or actions with a single click.
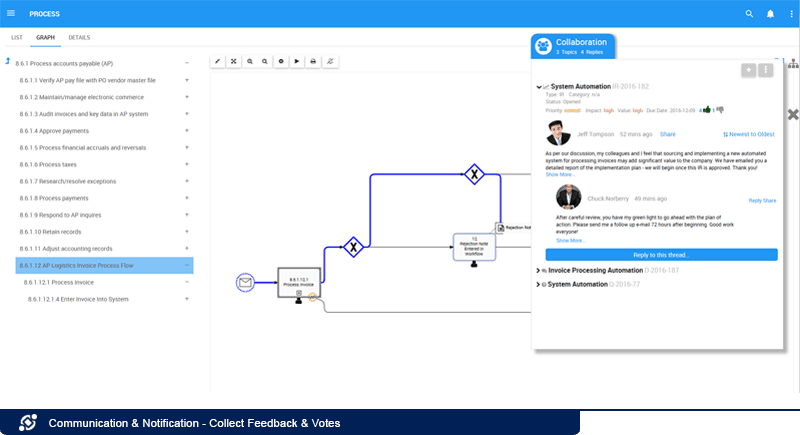
Collect Feedback & Votes:
Stakeholders can provide feedback and vote for a change request so the accountable can make a well-informed decision whether to approve or reject an adjustment. Voting gives everyone a voice and ensures that “single source” recommendations are not applied before collecting input from other stakeholder because a change that may be an improvement to some but detriment to others (eg. improve efficiency but risk non-compliance, or reduces manual activities but causes downstream information gaps or customer satisfaction).
Post Tracking:
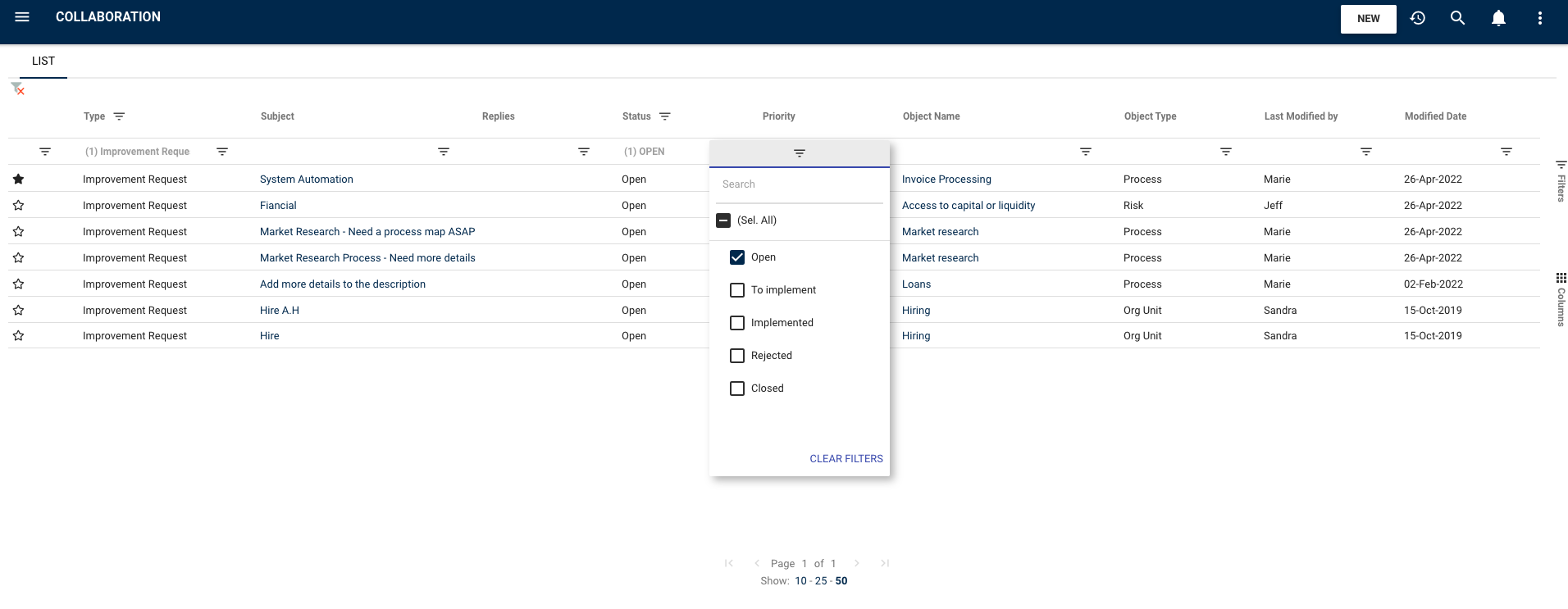
Employees can track their own requests and management monitor the progress of all questions, incidents and change requests by applying filters according to their status (e.g. Open, Approved, Work in Progress, Waiting for Publish, Closed), deadline or priority.
Increased User Adoption:
The EPC inspires individuals to speak their mind: it encourages critical thinking through well thought out responses, makes key employees more accessible and motivates individuals to communicate transparently with one another. In turn, a community will be formed and a process culture will grow homogeneously across the organization.
Microsoft Teams Collaboration
Apps for collaboration are crucial in connecting people, systems, and processes. However, as Microsoft Teams has seen more engagement, the threats to IT governance have increased. EPC offers a straightforward and efficient Teams governance solution that prevents unstructured information and makes it possible for a genuinely contemporary collaborative experience.
Multi-User Collaboration
Collaborative Development:
Many users can be granted access to create maps and perform changes on objects. This allows them to collaborate together. Observing each others’ activities at a bird’s eye view helps them think critically and spot the areas where they can potentially improve their work.
Redundancy elimination:
Roles, risks, processes and other objects can be reused as many times as needed. This eliminates the redundancies and inconsistencies that lead to a loss in efficiency and unnecessary monitoring.
Automated communications:
Subscriptions:
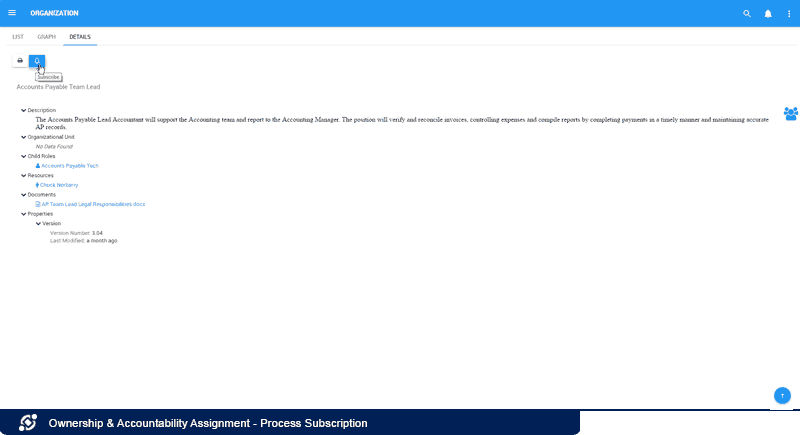
Users can also stay informed on objects that may impact them indirectly by subscribing to them. They would thus receive notifications if changes would take place.
Ownership & Accountability Assignment
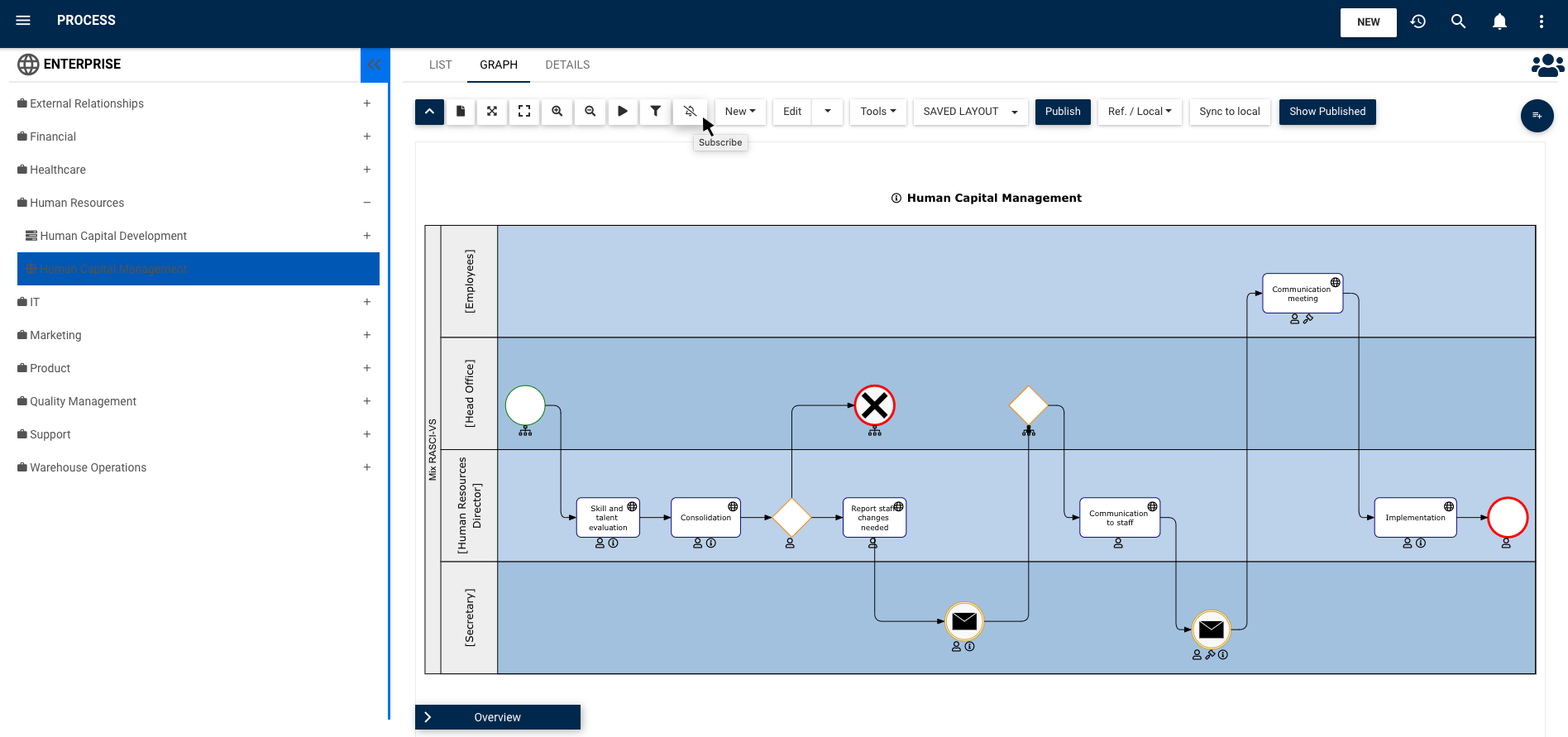
RASCI-VS Matrix:
By using the RASCI-VS matrix to assign responsibilities, they can better understand what is expected from them and see which assets have been made available to them. This increases employee accountability.
Recurrent Notifications:
Process Subscriptions:
Even if employees aren’t directly associated to objects, they may still want to monitor them. For instance, a marketing employee may want to know if the employee assigned to a role she interacts with changes from one day to the other. She can thus subscribe to the existing role to be updated once the adjustment takes place.
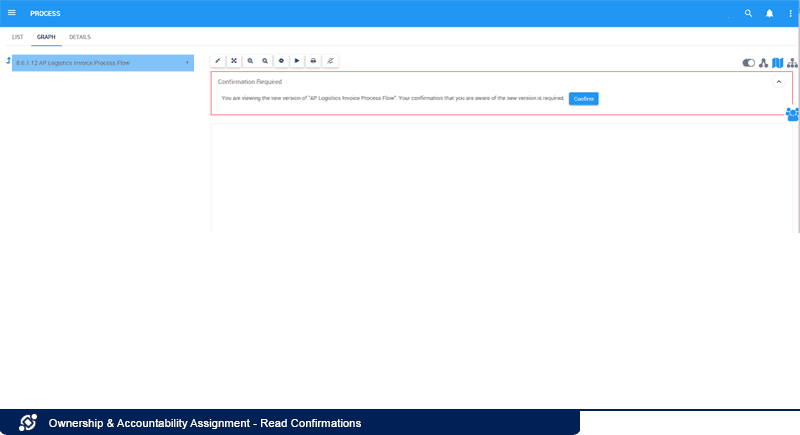
Read Confirmations:
Management can detect when their staff have seen information that was directed to them. They can therefore ensure that information was adequately transmitted, and make sure that changes are adopted and actions are performed.
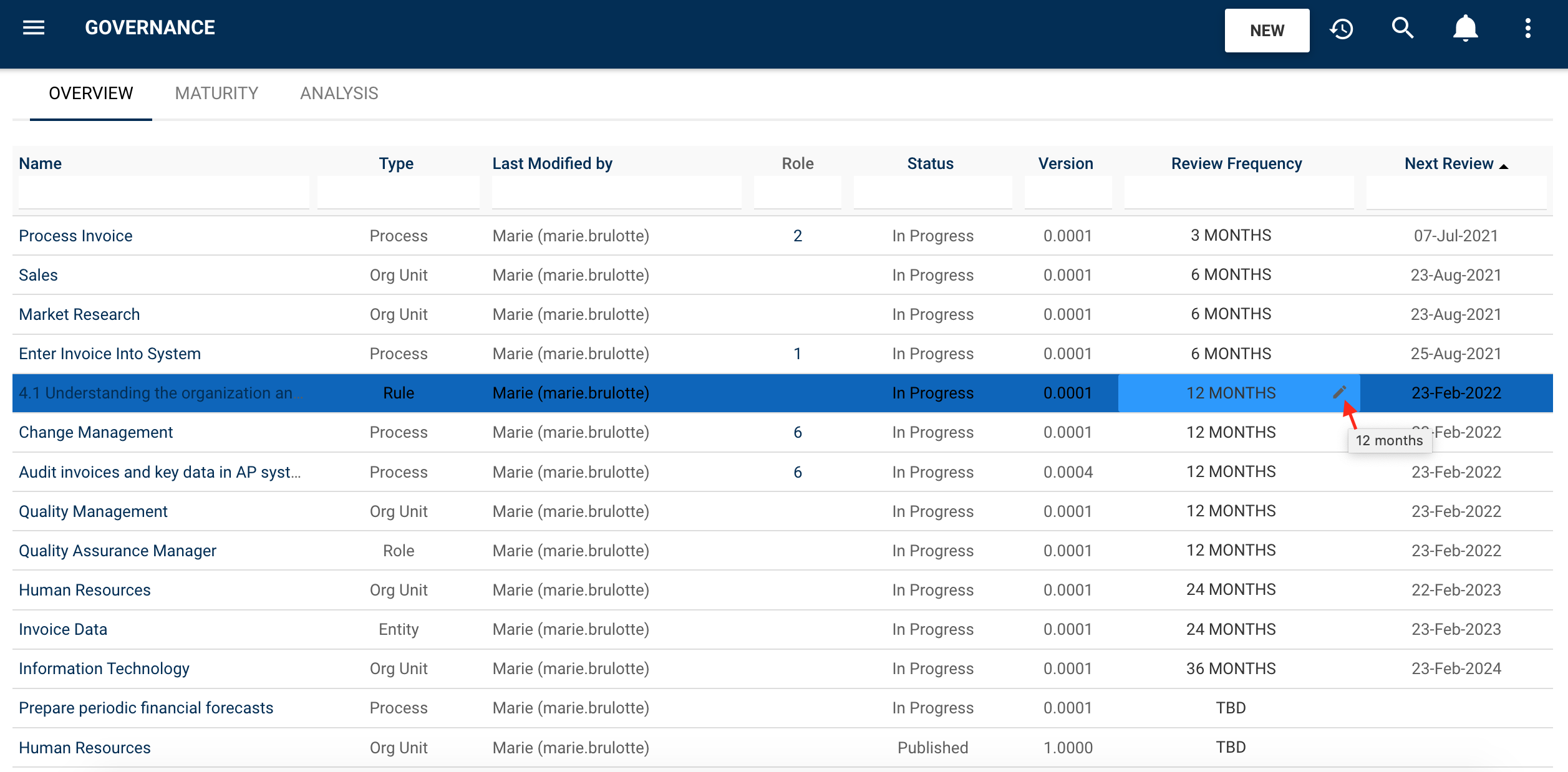
Automated revision cycles:
Organizations can be ensured that information is kept up to date at all times through prompts requiring responsible employees to validate information’s currency. This mitigates the risk of having to reassess processes for new project launches such as ERP implementations.
Change Lifecycle Management
Automated review scheduling:
Analysts can schedule recurrent review cycles to confirm that their processes are up to date. Process owners are automatically informed of these well ahead of process expiration dates, and must either confirm or reject requests.
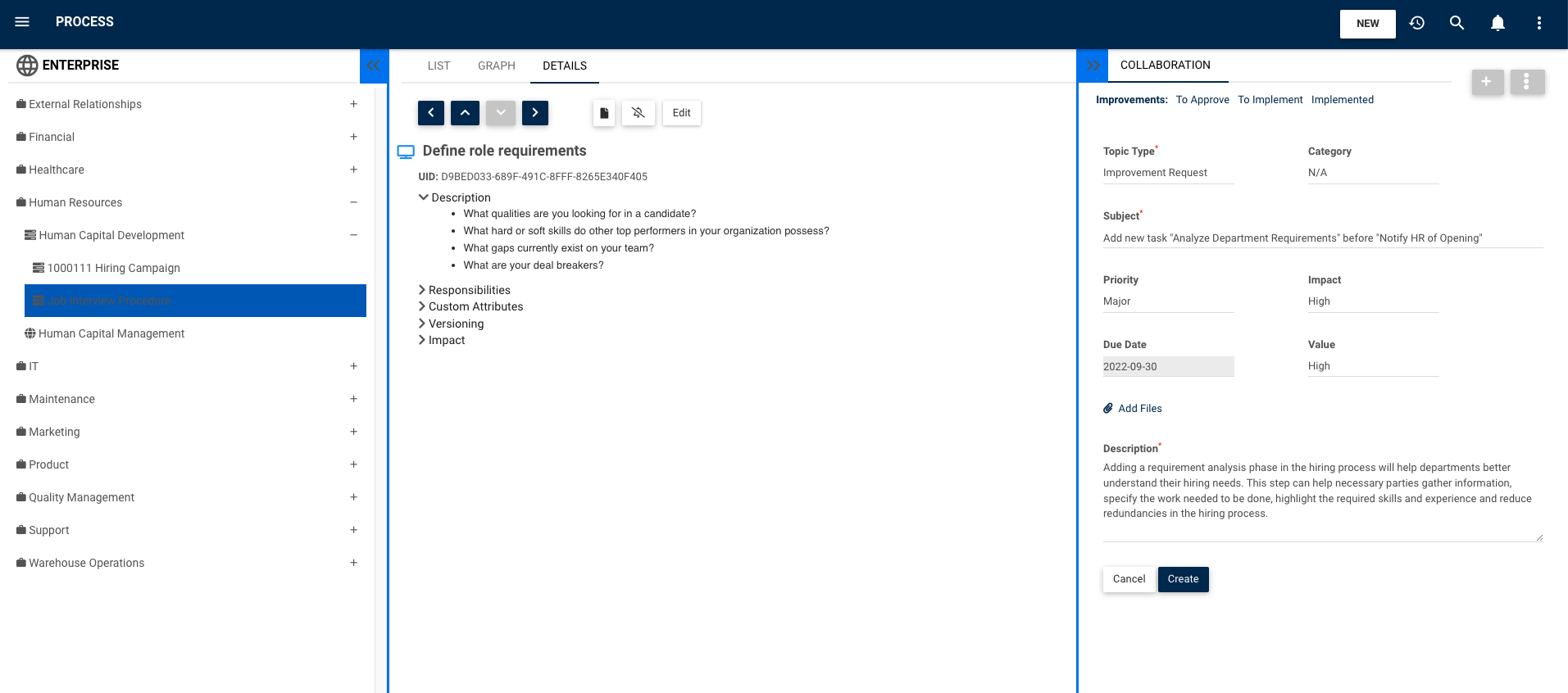
Improvement requests:
Task assignment & notifications:
If processes are marked as outdated or if a improvement request is filed and approved, a notification can be sent to a dedicated employee with a instruction to perform the changes.
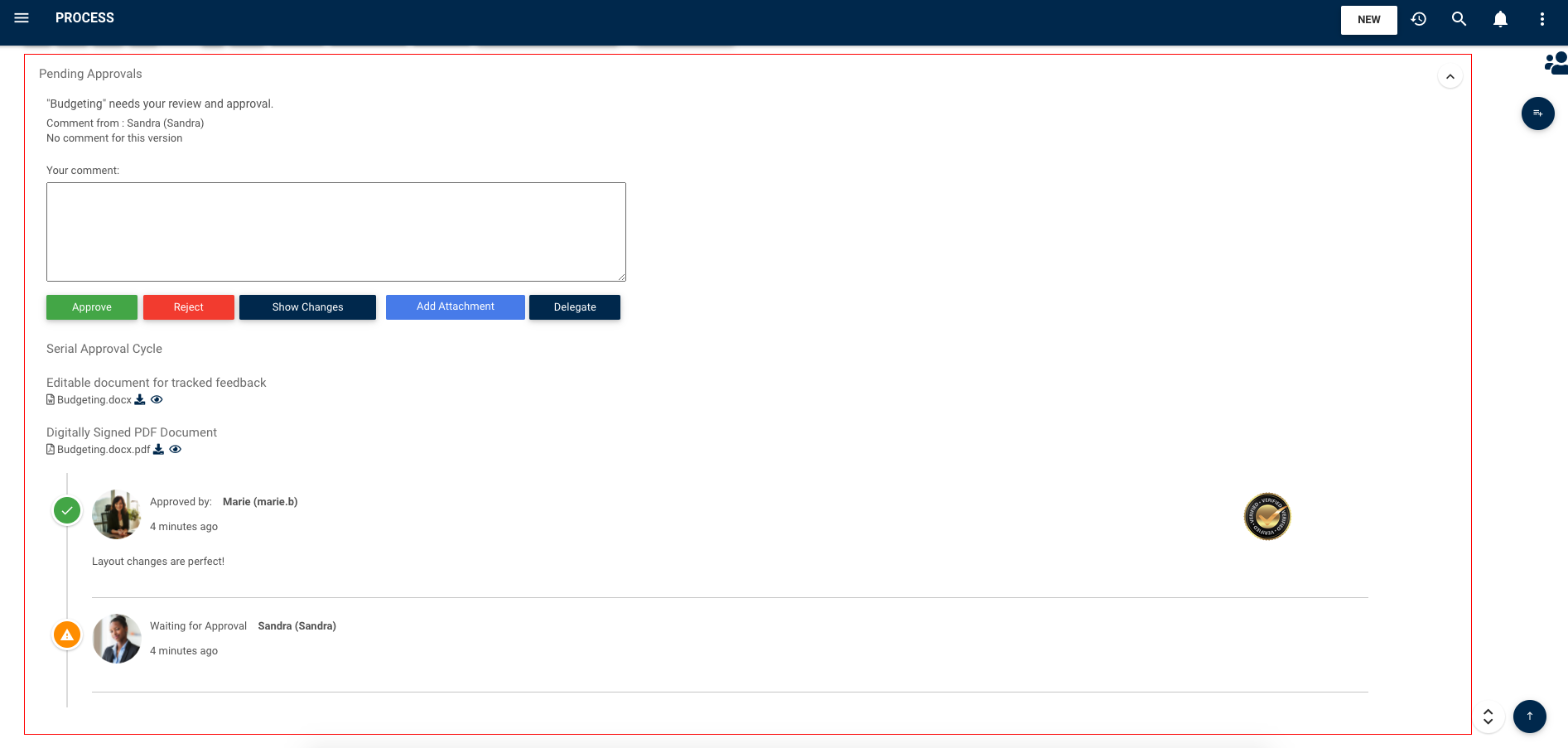
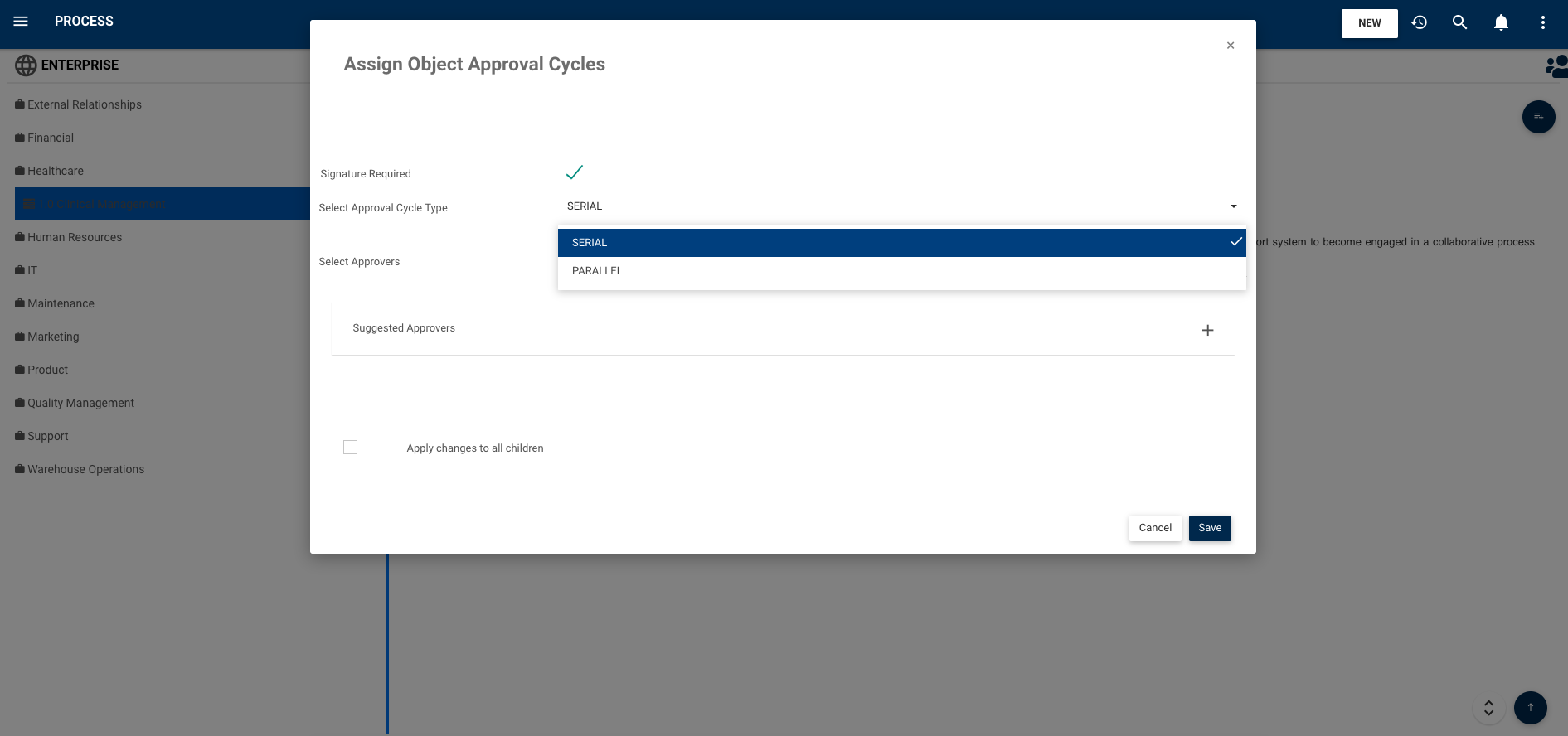
Serial vs. parallel approvals:
Once the changes have been made, they must be approved. The approval path can be set to either escalate from bottom-up or to notify all approvers simultaneously. If the parallel path is selected and one of the required approvers rejects the changes, the request is sent back to the dedicated employee along with feedback.
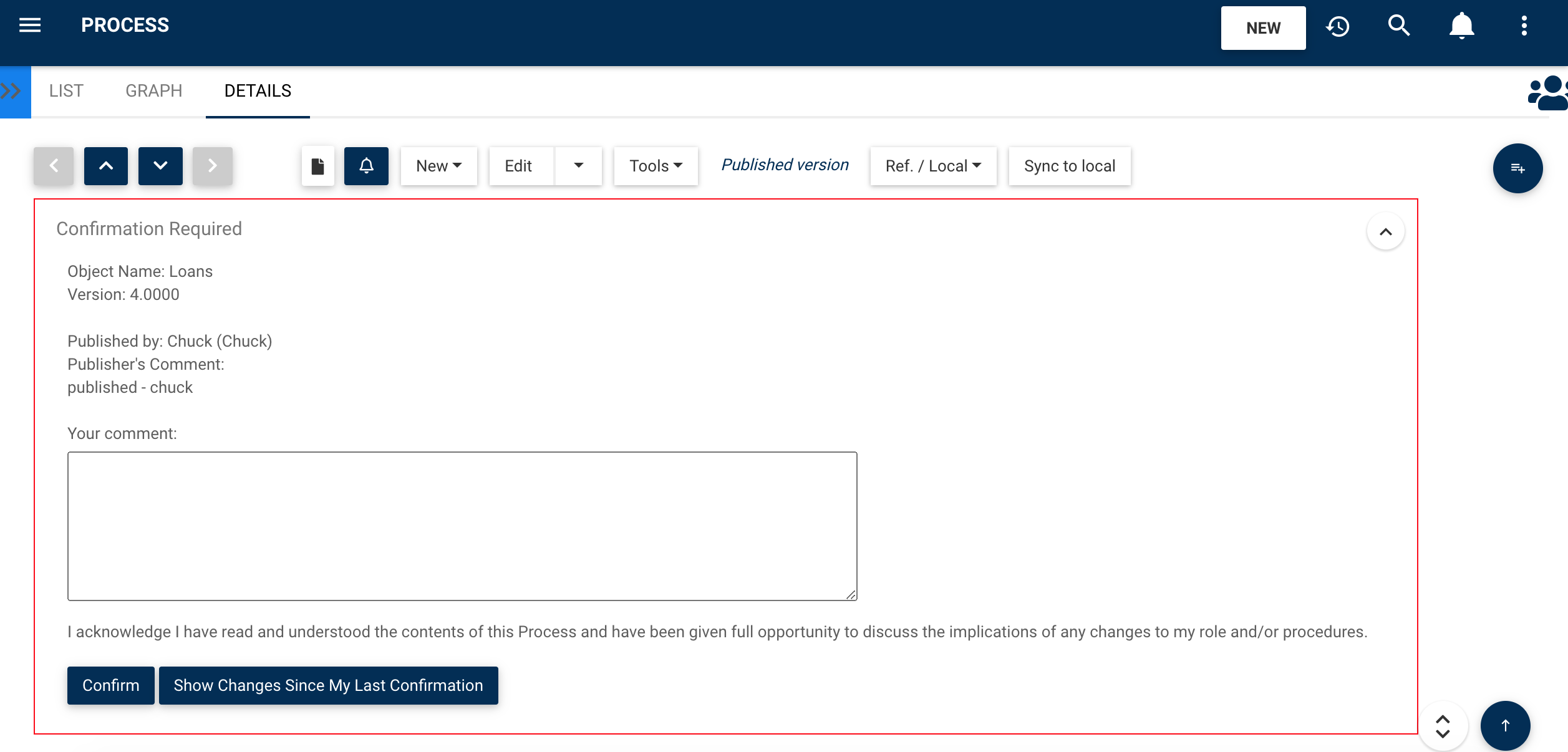
Read Confirmations:
Once the changes have been approved, all affected employees receive a new version notification. They must then examine it and confirm that they are aware of the changes. This ensures that operations are consistently aligned.
Improvement Lifecycle Historic:
Users benefit from a detailed historic of the changes, rejections and approvals that were involved in the improvement of any given object throughout its life cycle.
Versioning & Audit Trail
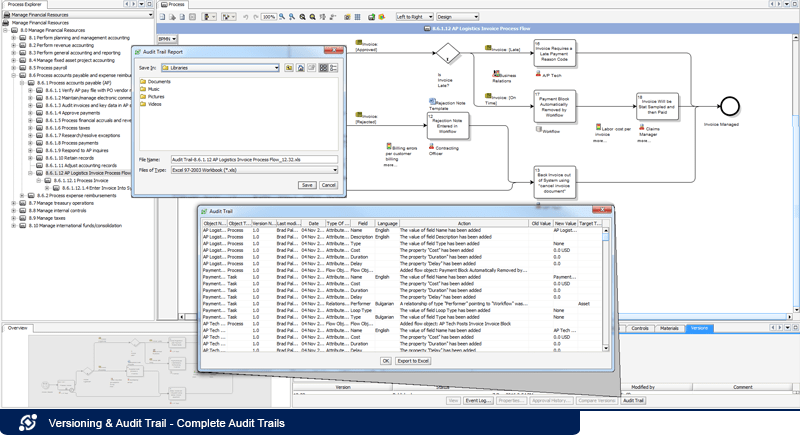
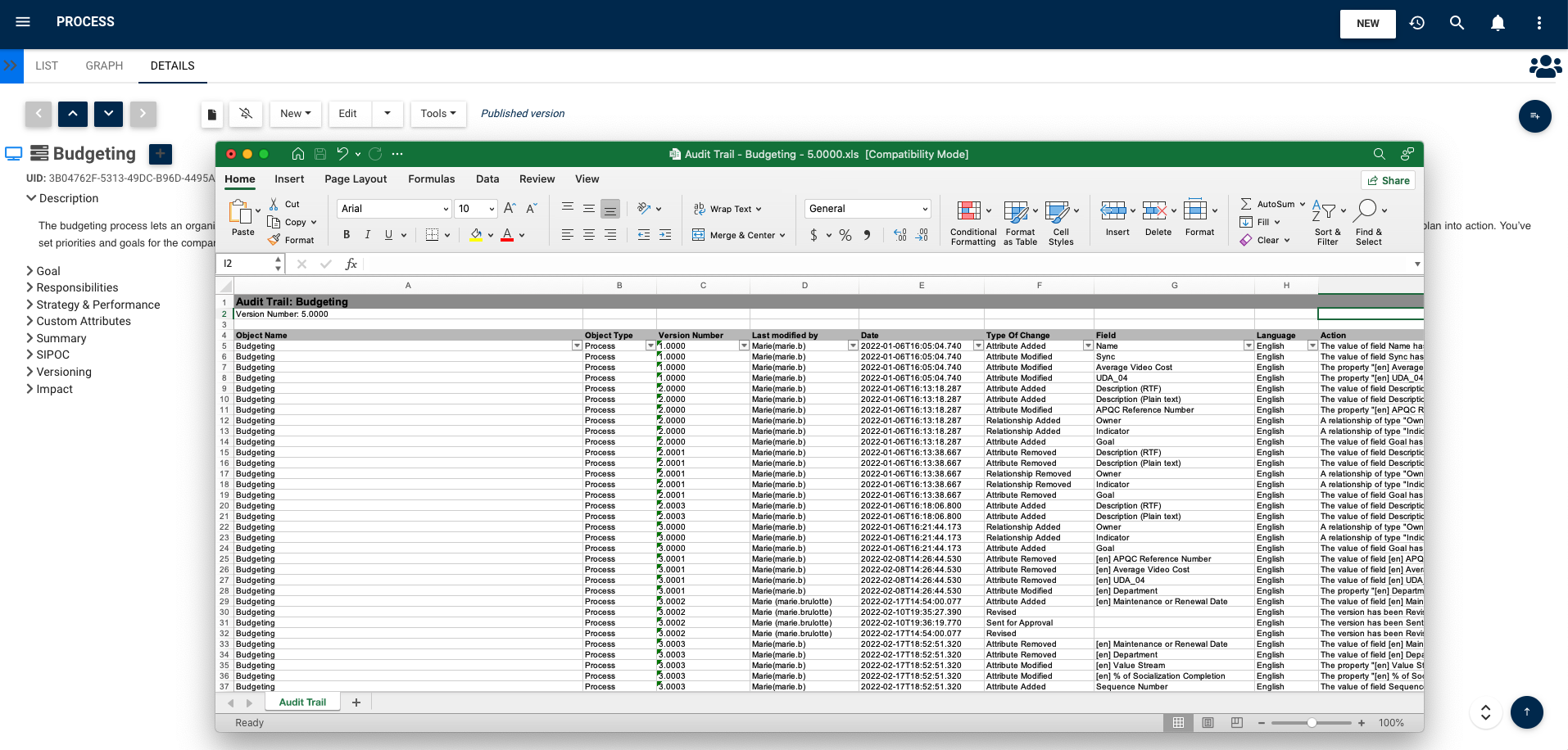
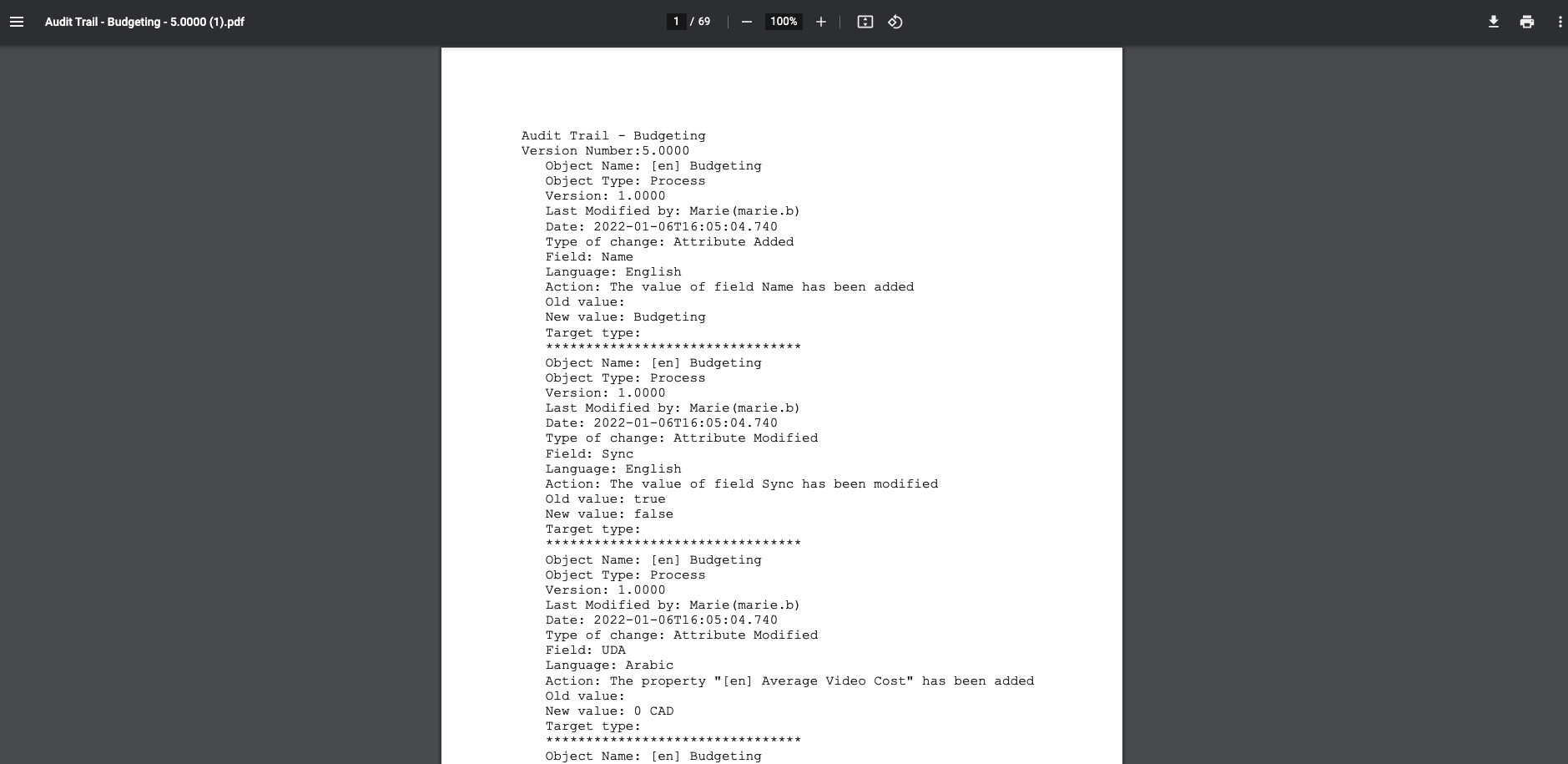
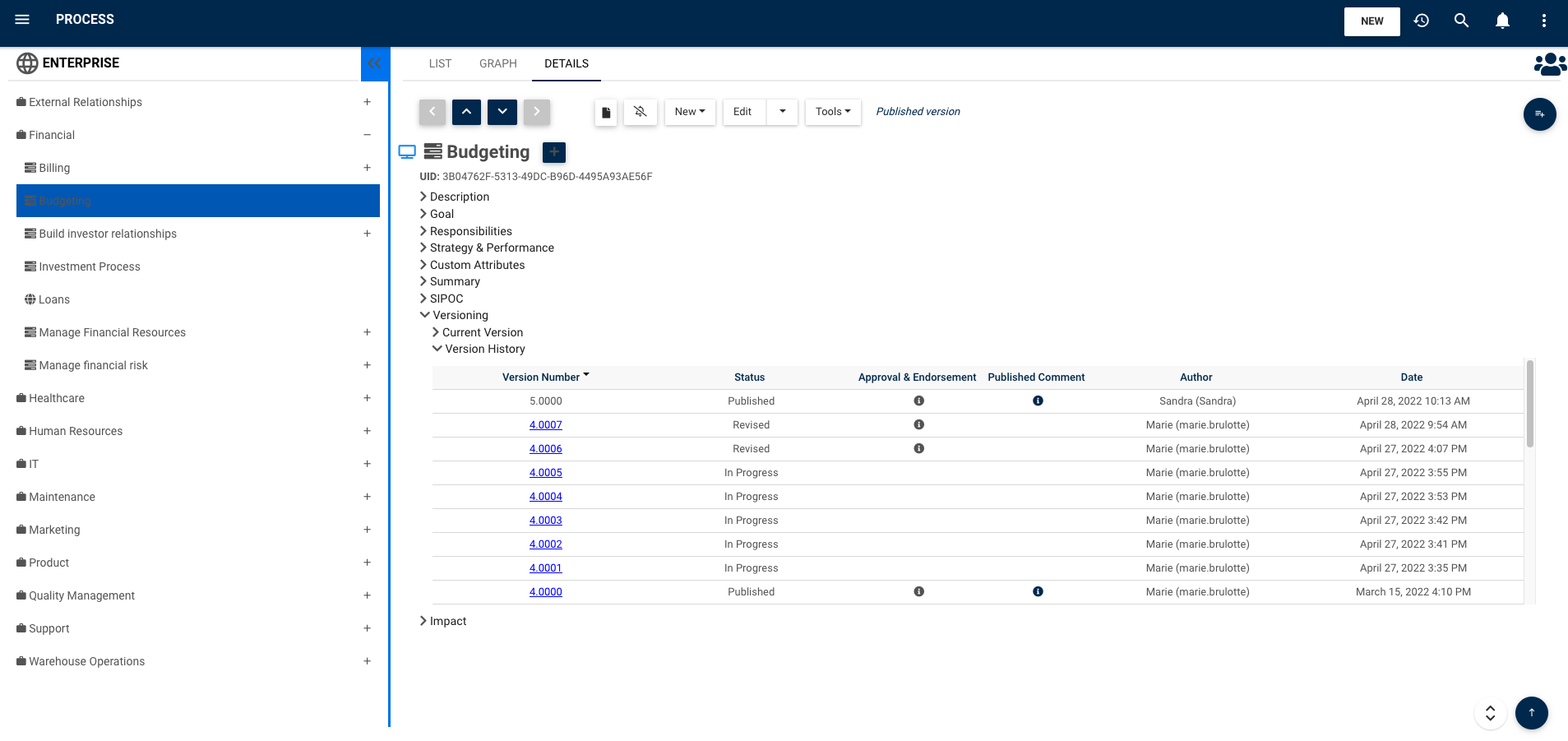
Complete audit trails:
The EPC preserves a historic of every change (when, who, what) that has taken place throughout an object’s existence. These can be either viewed within the suite or can be exported into Excel or PDF format for reporting purposes.
Version comparisons:
While audit trails detail every change within a single form, analysts can also compare a version of a given object against a previous one. Besides, in the process map, users have the right to compare current version of a process against any previous one. This enables management to visualize the object’s and the process’s changes through time and helps replicate some of the older version’s characteristics. Additionally, previous versions are visible and restorable, whether they have been published or only saved.
Major and Minor version stamping:
Analysts can indicate the degree of a change through its version’s stamp. Major changes can be demonstrated by rounding up to the closest integer (e.g. 1.03 to 2), while minor changes can be depicted by rounding up decimals.
Approval History:
The full history, including comments, revised documents, digital signatures, etc can be tracked and viewed for any given modification on any object requiring an approval cycle.
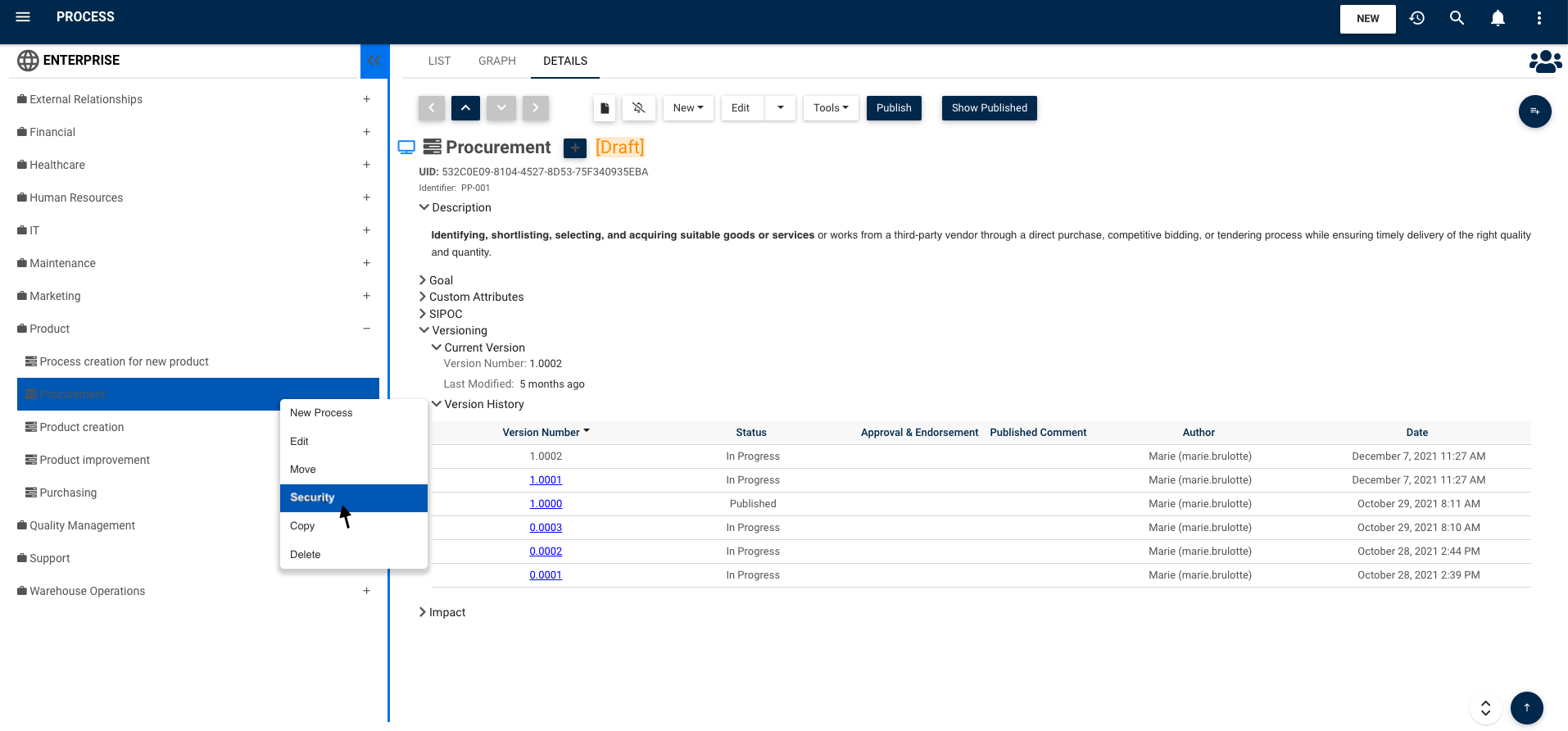
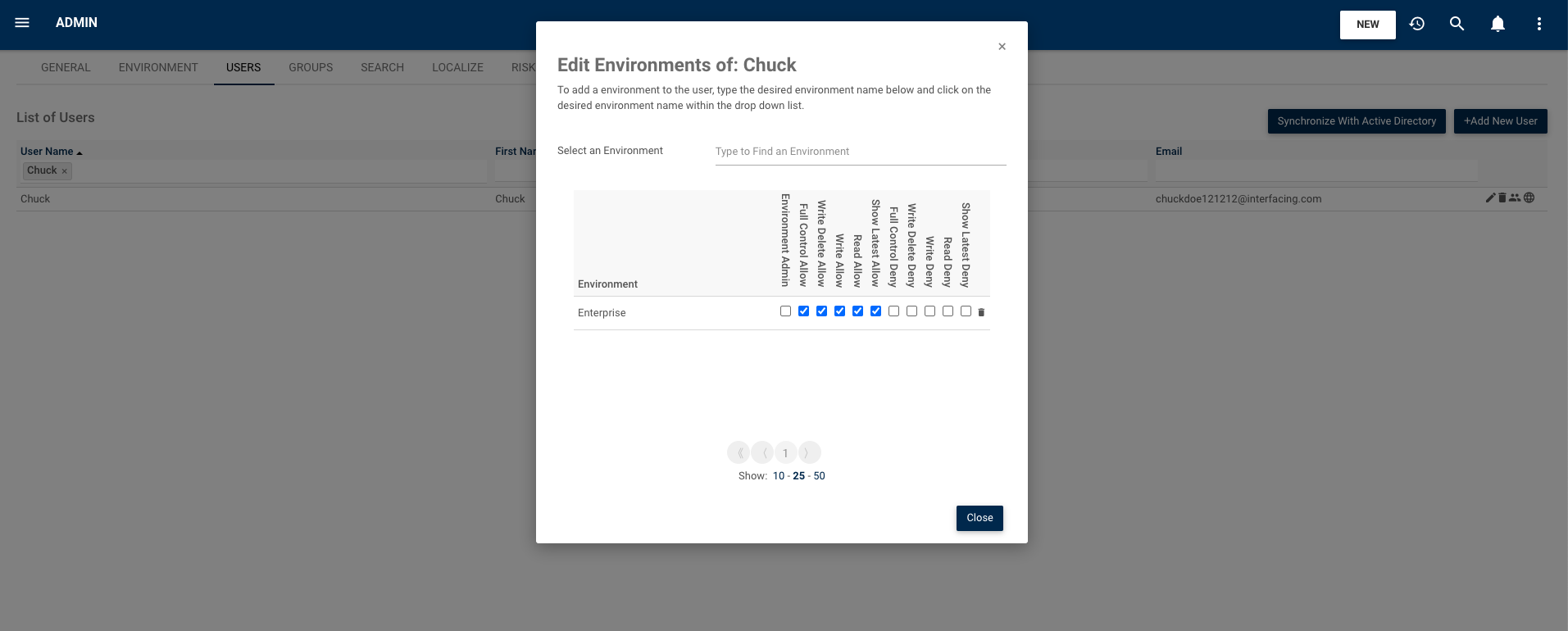
Security Access Management
Draft and official versioning:
When analysts apply changes, they have the option to either publish the changes or mark them in progress. End-users can only see published content to avoid confusion. If analysts need to consult, engage and inform certain end-users of the changes, they can also set “show latest allow” security for those end-users who don’t have edit right to see changes made within the draft of the process.
Role-based Access Control:
Users are given unique credentials that are based on their roles. This ensures that each role has the same permissions and access rights, which facilitates system maintenance.
User Authentication:
EPC Administrators can manage user authentication with Active Directory. The EPC supports Single Sign-on (SSO), NTLM2 and SAML 2.0; this flexibility ensures that login credentials are held and managed centrally within a single system.
Encrypted communications:
Delete, Write, Read and Approval Permissions:
User grouping:
Users access rights can be pooled by creating groups. This simplifies maintenance as quick changes can be made to a set of users rather than having to modify them individually. In exceptional circumstances, specific users within these groups can be given special access rights to some information.
Security inheritance:
New objects inherit the permissions granted to their parents, which significantly facilitates system maintenance efforts. If users cannot access certain folders or objects within the EPC, they cannot access anything (including other objects) held within them either.
Internationalization Management
Default map widget type on home page:
The number and concentration of localized processes per country is now available in this new widget and can be visualized directly on a world map.
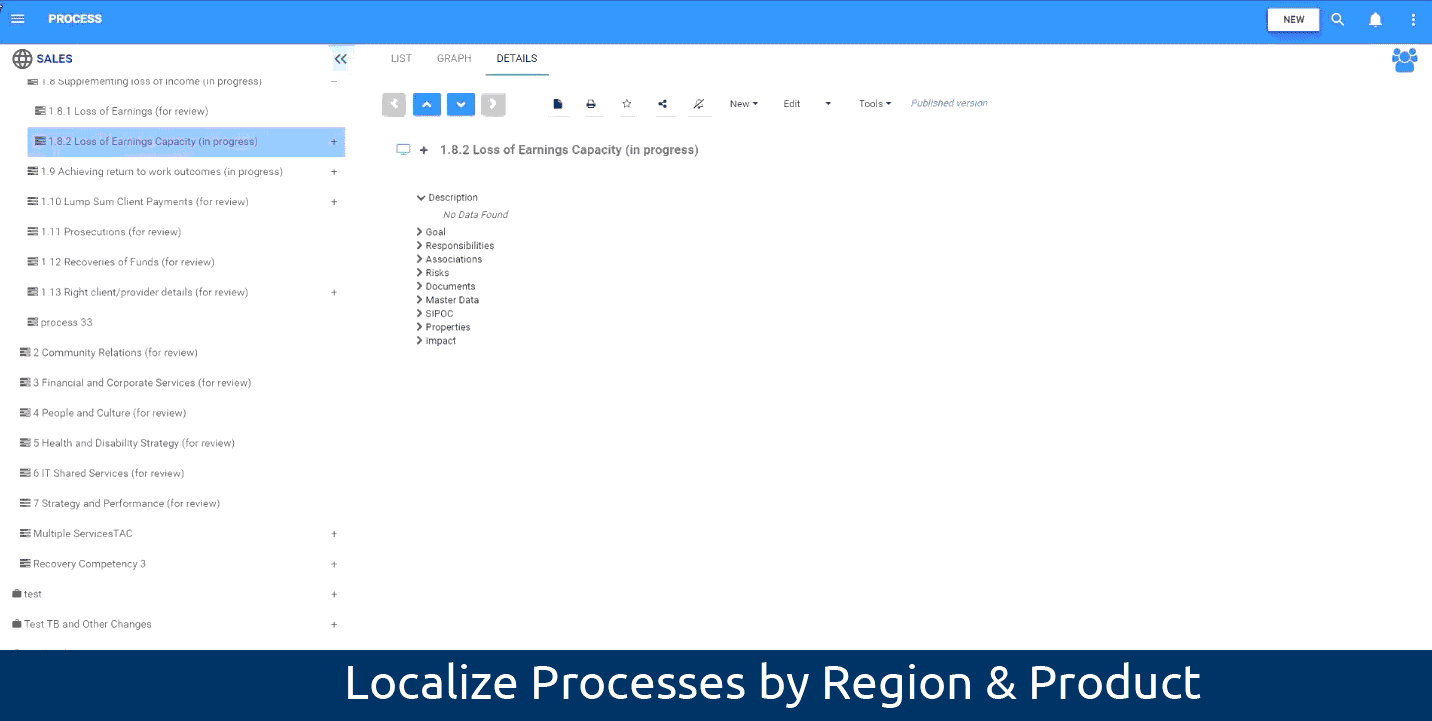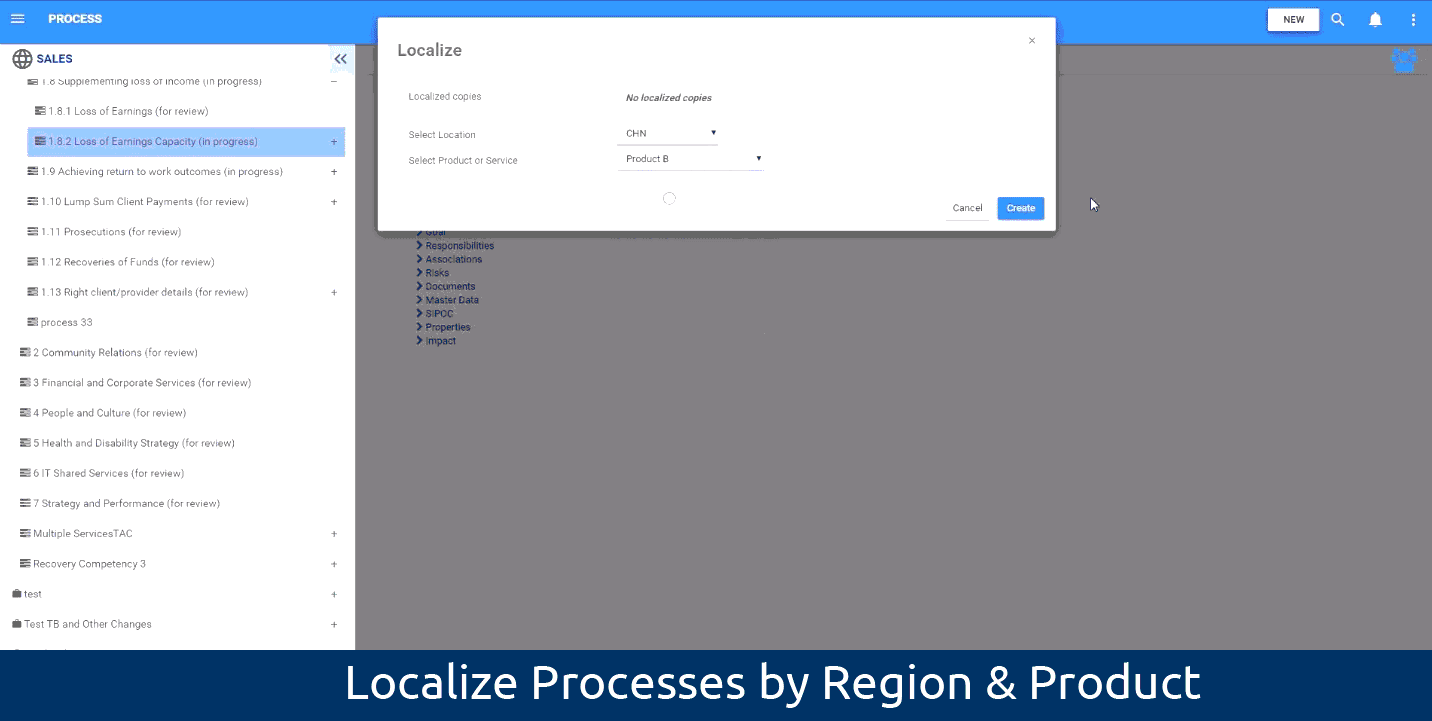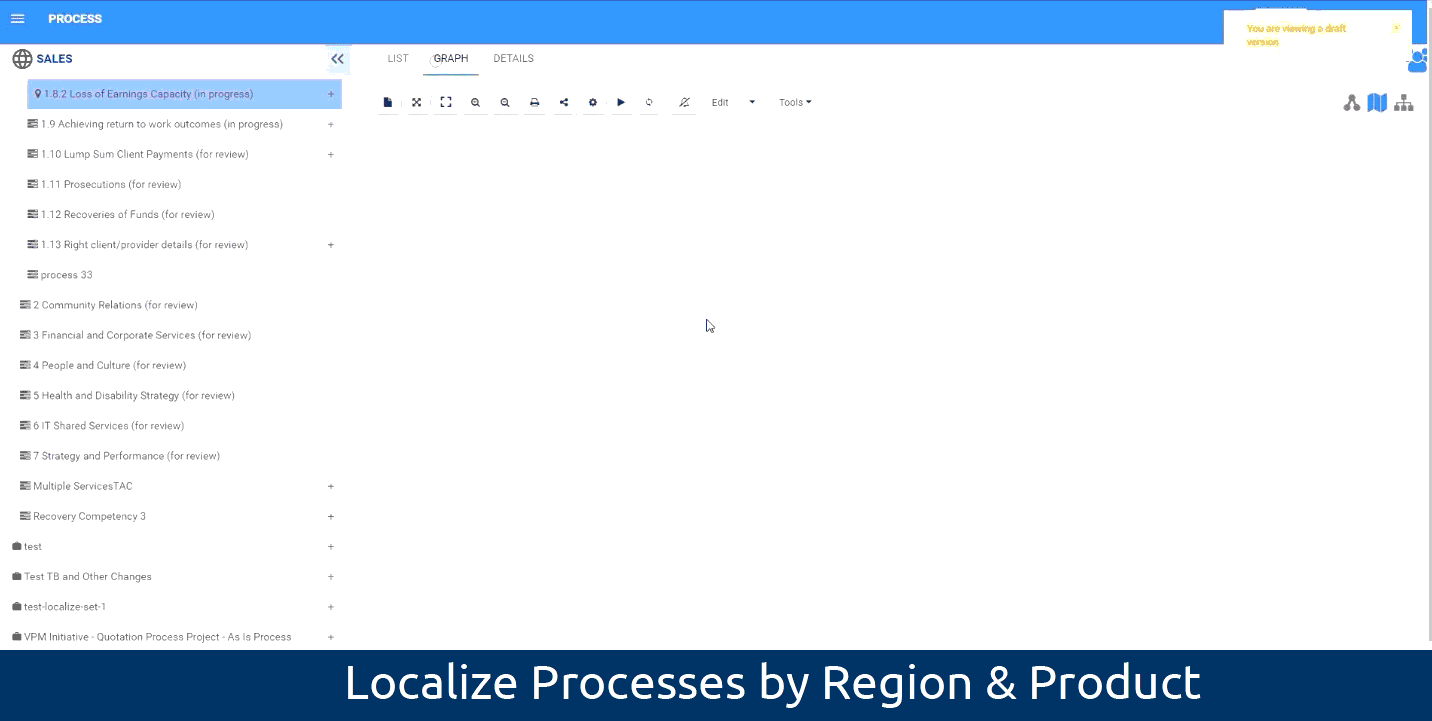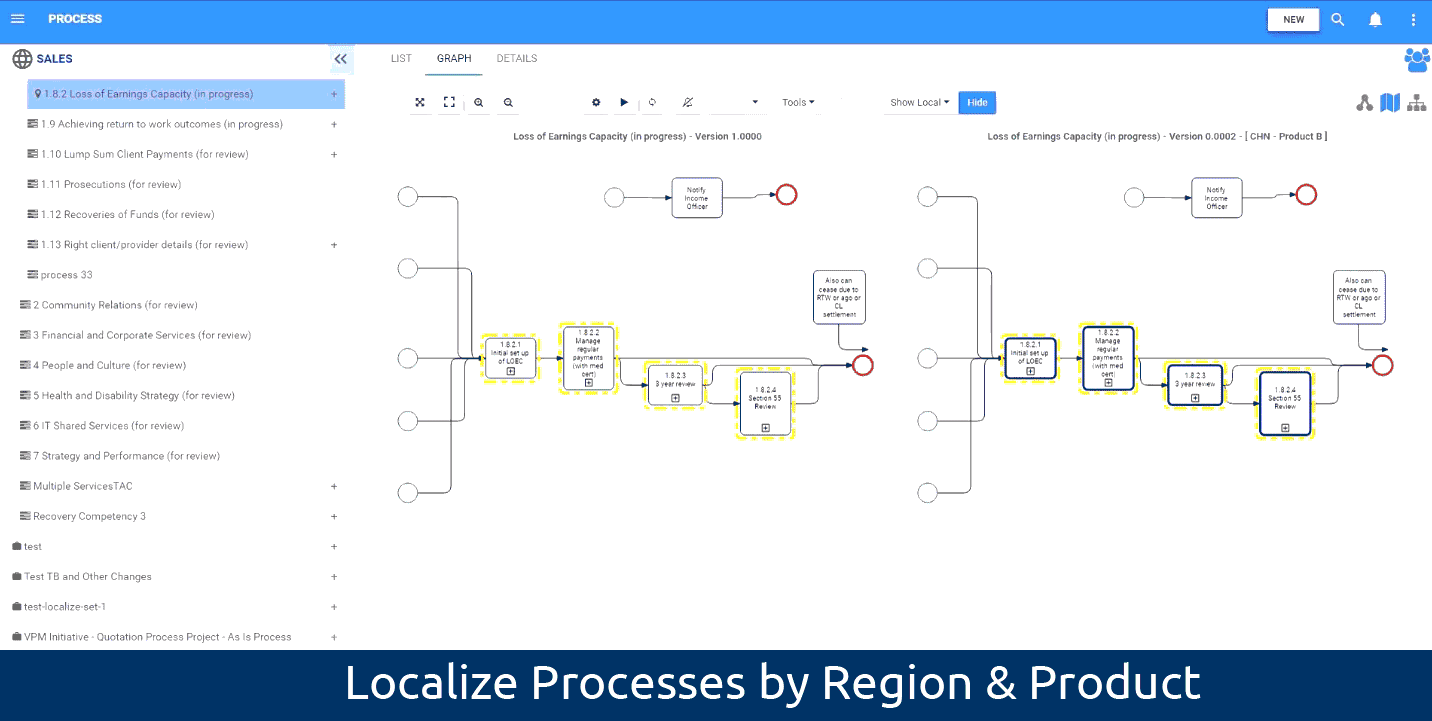
Localization of processes to manage associated processes:
The EPC enables users to tweak a process’s certain properties and characteristics, create localized copies of the process, then designate those copies by location or product and service in order to accommodate regional differences of a process. Users don’t need to re-map localized processes for each country since localization inherits the source process. This advanced new feature will help you better monitor and improve your processes around the globe, or across product and service.
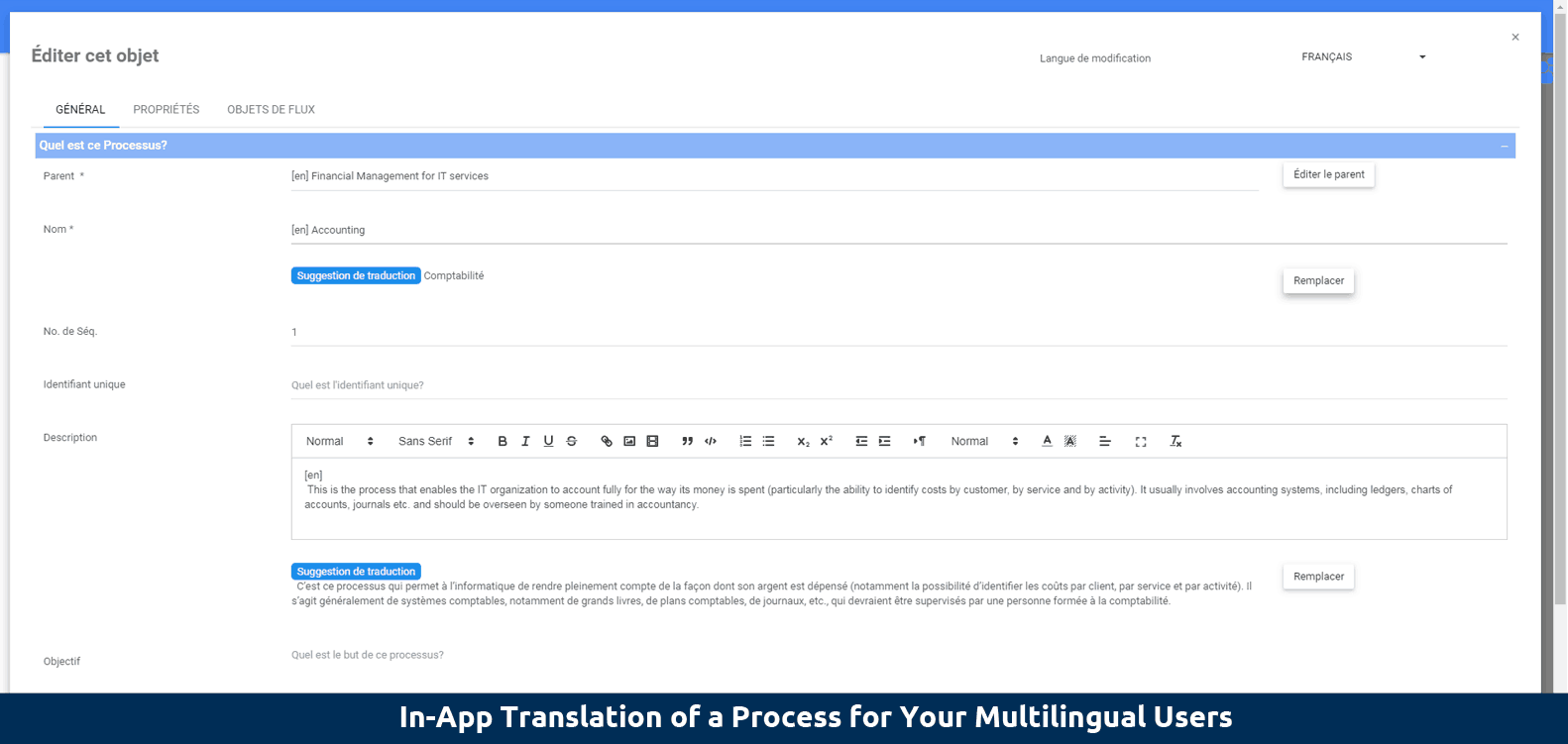
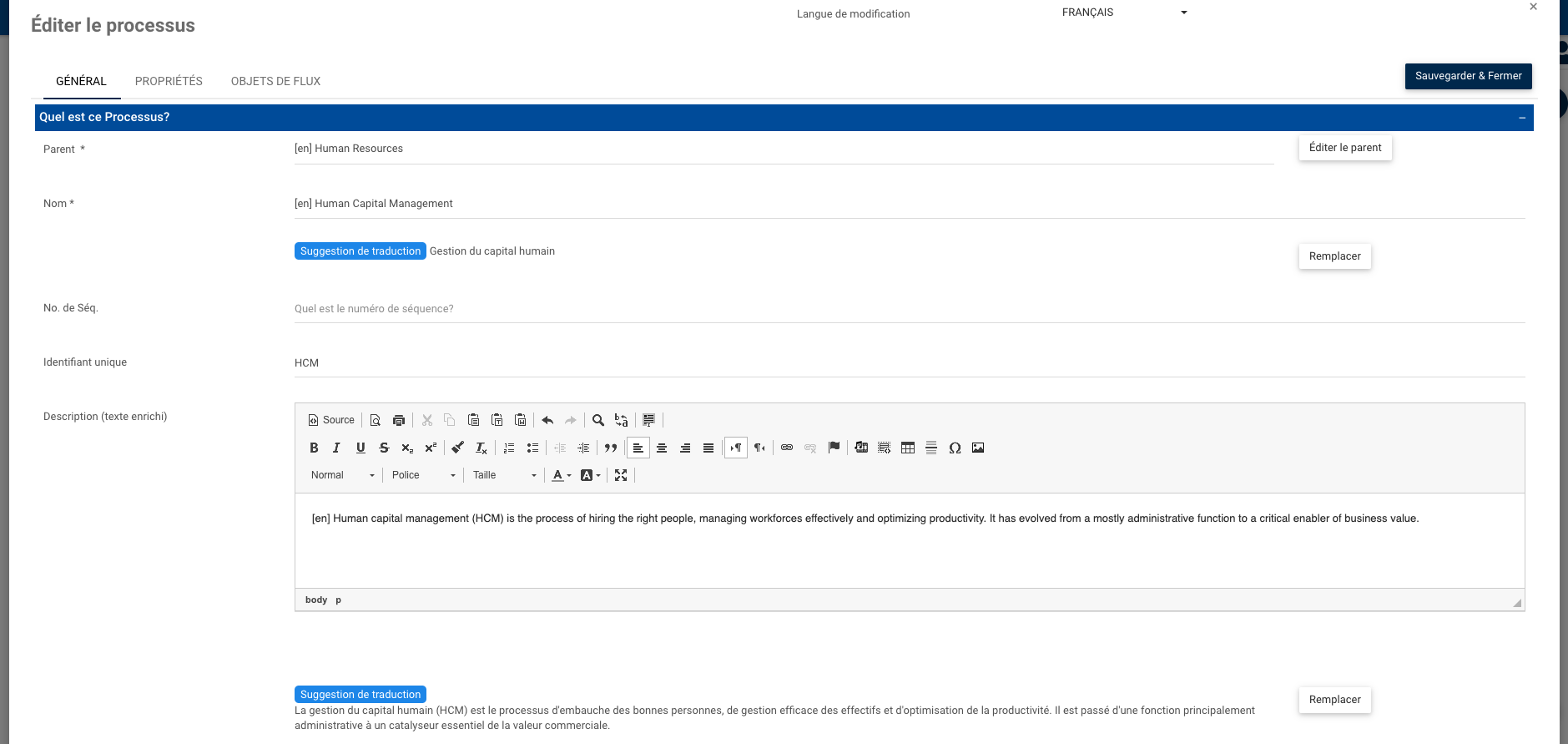
In-App content translation suggestions:
Localized content will benefit global users to better understand a process in their mother tongues. The EPC has augmented multilingual capabilities to give dynamic translation suggestions, allowing users to create multilingual copies of a process without translating from scratch or leaving the EPC. Users are capable of reviewing the proposed translation before confirming it, or adjusting the proposed translation based on users’ language expertise.
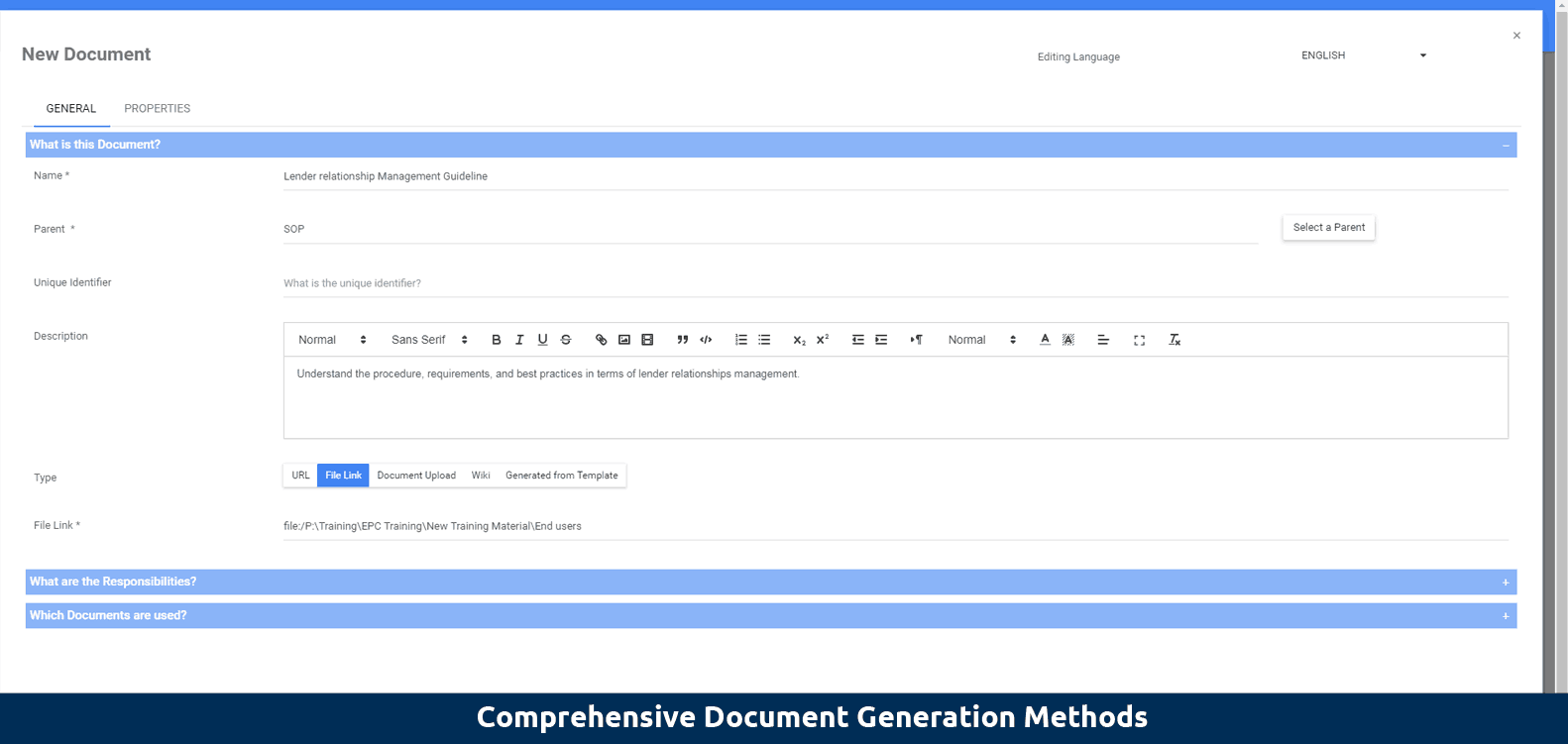
Different documents for different standards:
Faced with different regulations, rules and requirements in different regions, users might need to implement different templates to generate local documents. Using the EPC, users have the ability to leverage their existing content and generate various documents, including SOP (standard operating procedure), process workbook, policy & analysis workbook, and any type of documentation from an existing template, making standardizing documents quick and effortless.
Process synchronization for multi-user collaboration:
The “Sync” button within the process map allows multiple users (global users) to view changes of a map as they are made in real time by another user (process mapper). By using this new feature, users can visualize, understand, and collaborate on a process in real time, which will further prevent unnecessary process modifications due to misunderstanding or lack of communication.
Detailed Analytics for EPC Usage
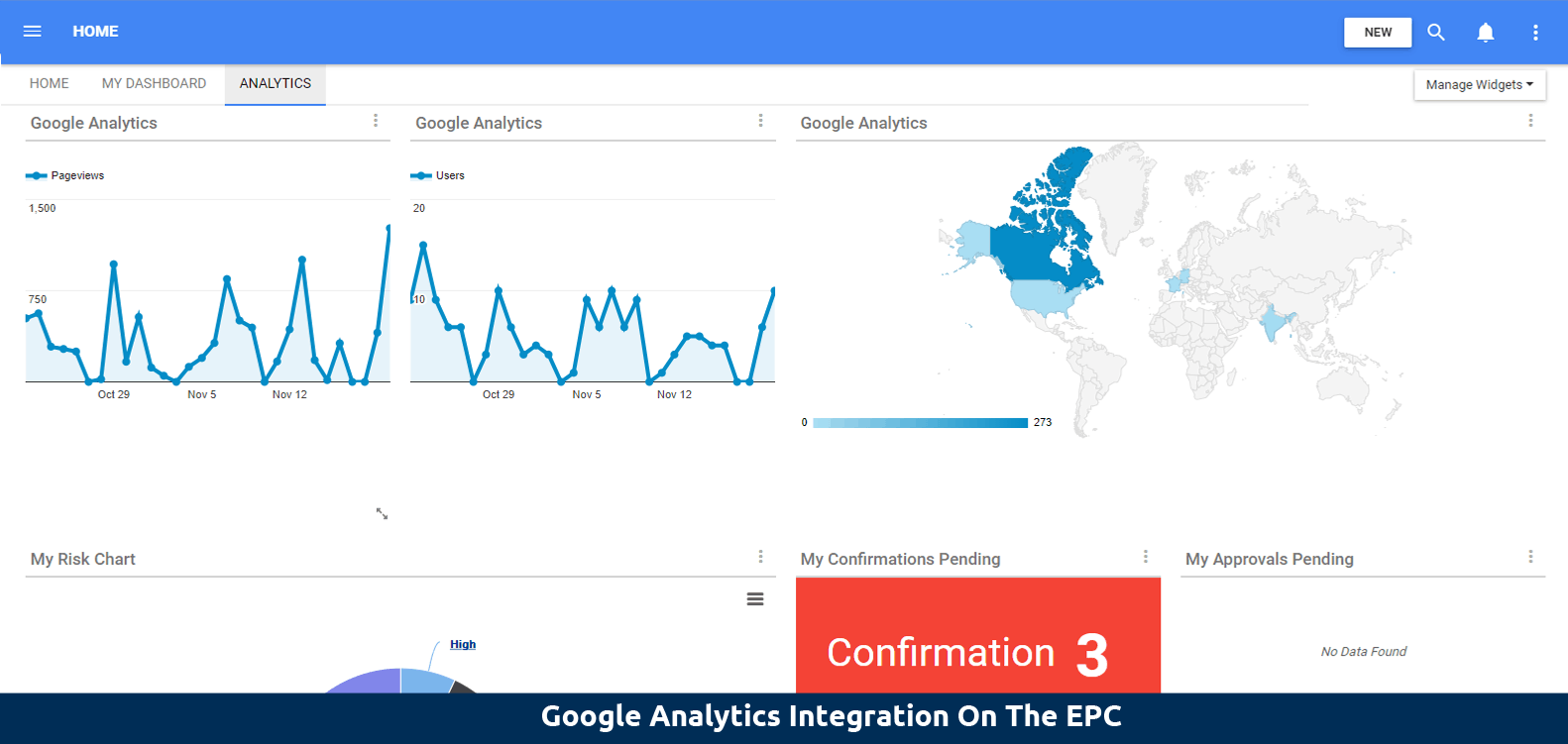
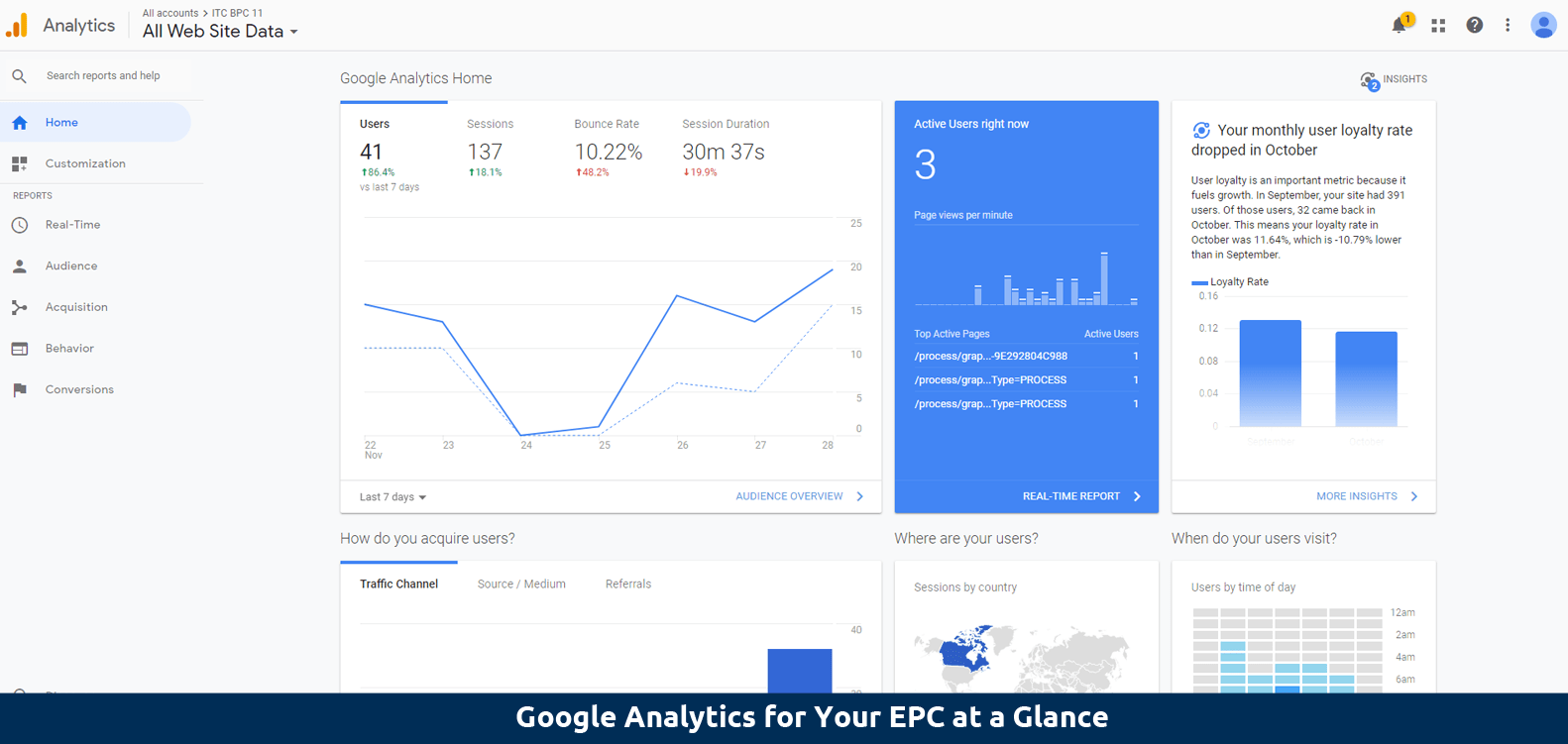
Real-time tracking to monitor activities on the EPC:
With real-time data, you can dynamically view and get reports to monitor usage of the EPC, including number of active users, most viewed pages, number of users on each page, geographic locations of users, and which objects users are interacting with. It is worth mentioning that you have full control over your users’ data privacy by keeping your users anonymous in the Google Analytics for your information security.
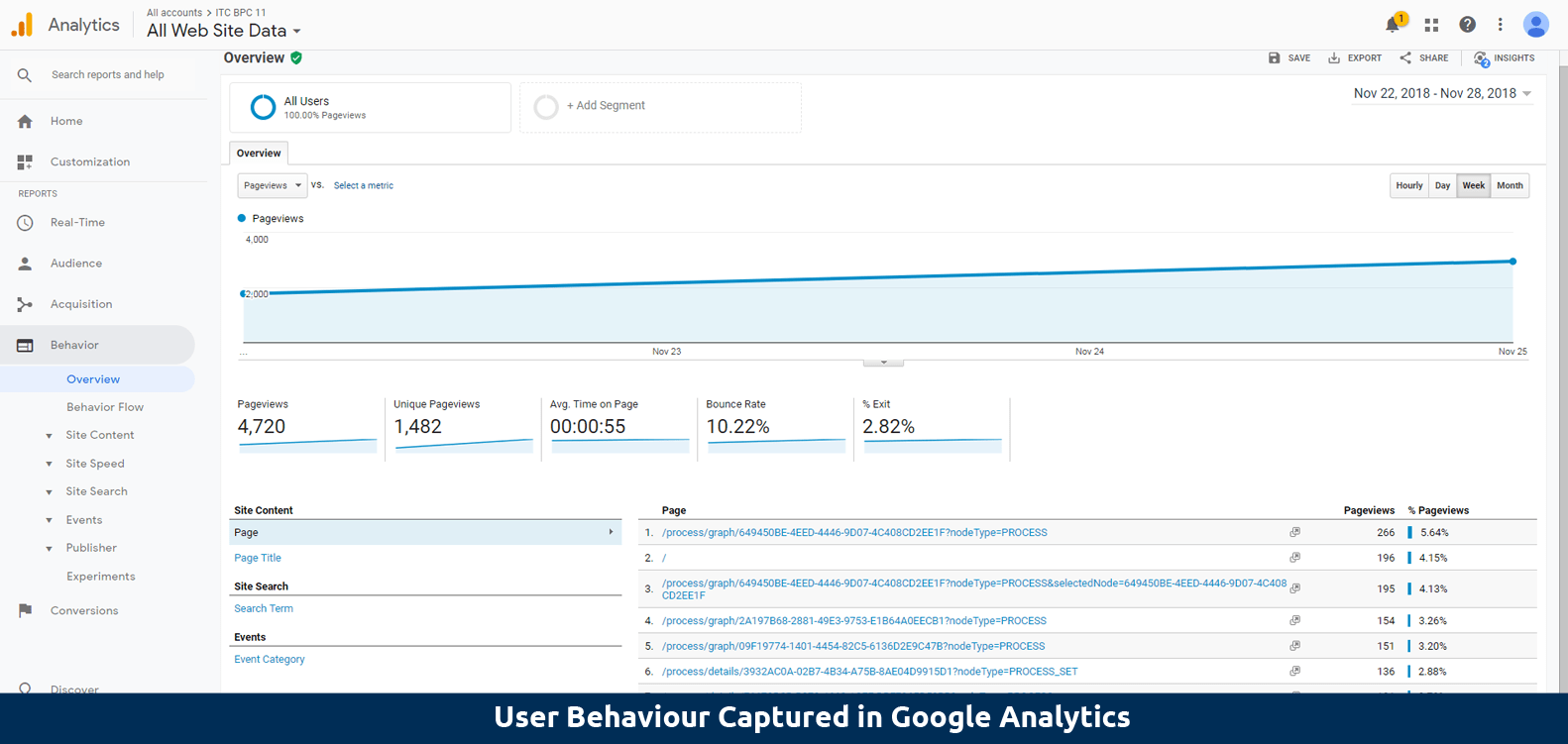
User behavior tracking to measure what matters the most on the EPC:
The more you know about your users, the better you know how to invest, personalize, and deploy the EPC. Through user behavior tracking, you can monitor the EPC’s performance under comprehensive metrics including number of total visits, unique page views, number of sessions per country, average session duration, number of downloads per object, average time spent per object… Understanding user behavior will help you improve configuration to boost user adoption rates, daily usage and loyalty of the EPC.
Event Tracking to assess user engagement on the EPC:
The event tracking records user interactions with elements of the EPC, such as downloads of PDF and other media, time spent watching a video, numbers of approval cycles and confirmations, frequency of collaboration posts on the forum, etc., to help you estimate user engagement throughout your organization.
Try It Now For Free!
Discover how Enterprise Process Center® can help prepare your business processes, risks and performance respond quickly and efficiently with your Business Process Governance & Business Process Collaboration.