- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
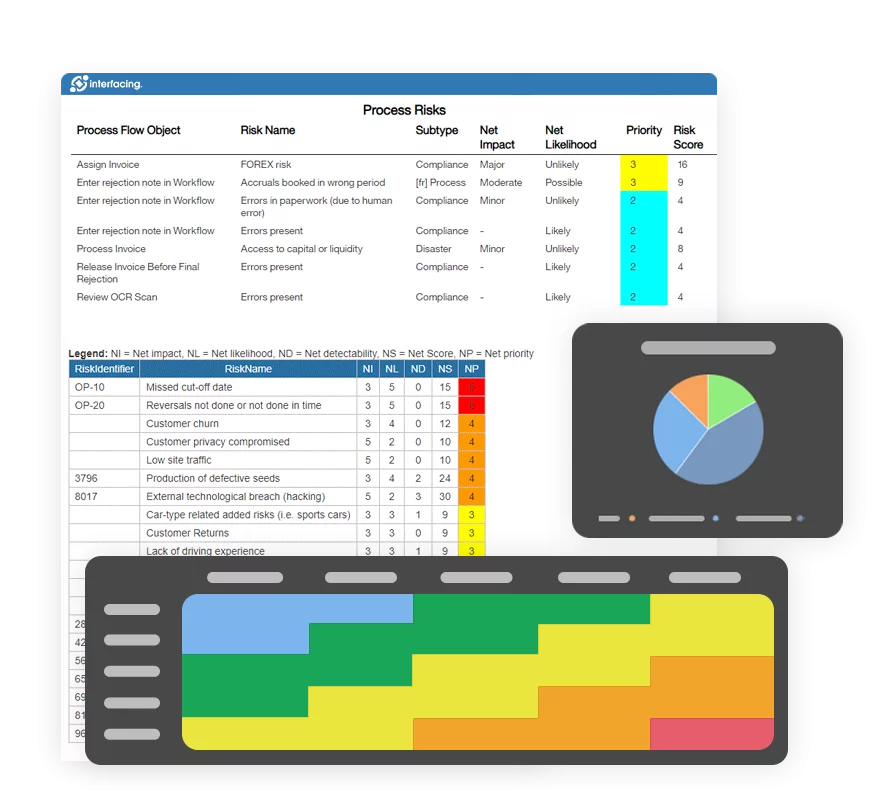
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
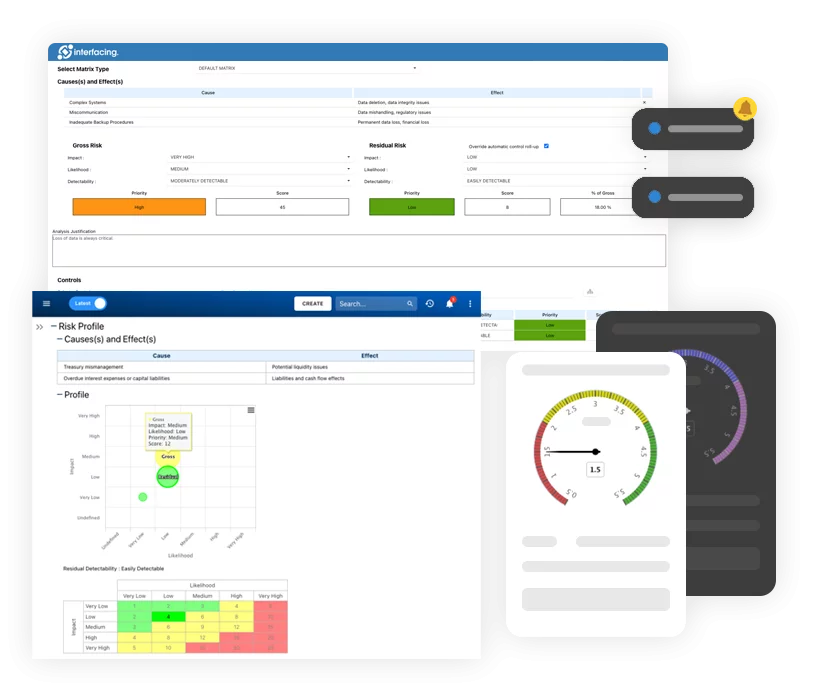
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


An Introduction to BPMN 2.0 Symbology
Please Select contact form.
Understanding the Essential Symbols and Their Roles in Business Process Modeling

An Introduction to BPMN 2.0 Symbology
A business process model and notation diagram, (BPMN diagram), is used to build easy-to-read business process model flowcharts, which can be shared across organizations and industries. BPMN diagram symbols are categorized into four main groups: flow objects, connecting objects, swimlanes, and artifacts. Let’s get started.
Basics of BPMN 2.0
The thing Business Process Modeling Notation brings is standardization and the ability to show who is doing what and when, plus the ability to make process flow paths easier to read by moving the details of a process into a more detailed level. Instead of having process taken up on a wall, you can create BPMN Process Models where you fit the primary business logic on a single page and then drill down to the next level if you want or need to see the details. There is a universal symbology to the language that bridges the gap between those in technical development, business analysts and all the way up to the C-Suites execs who can all understand the various sequence of events, activity and information that flows along an array of automated tasks.


Flow objects
Think of these symbols as the pieces to a puzzle that will form the overall workflow. Activities, Events and Gateways make up the three main flow objects.

Activities
- Task – This is the most common symbol used. It describes the precise action required in order to complete the task.
- Sub-process – Within this task, are additional sub-tasks categorized together.
- Transaction – This commonly refers to the function of payment processing but is much, much more. Transactions are best described as a set of activities that would need to be underdone if an error is detected in the process. In IT terminology it is known as a “roll-back”, i.e. you need to roll-back all the actions taken in the transaction to leave the information at the same state as when the Transaction process was started.
- Call – A Call Activity refers to Tasks and Sub-Processes that can be used in multiple or different areas of a process.

Events
This symbol serves as a trigger. It can initiate a starting point, an intermediate step, or act as the end-point of a specific process. Commonly used events can be:
- Timer – This symbol can identify the start of a timer. For example, a free trial is offered for 30 days in which a customer has the option to cancel anytime within this window. It may also be used on a certain weekday, for instance, every Tuesday, a list is compiled indicating who has cancelled the trial or who are the new free trial registrants.
- Link – Indicates a process belonging to a bigger ecosystem and links off into the direction of different tasks that comprise a new but separate set.
- Message – As it is described, messages are being passed via some technology interface, like EDI (Electronic Data or Document Interchange).
- Escalation – in order to facilitate a specific action, a higher-up authority will need to make a decision on the task. For example, an application for insurance coverage that is borderline must be escalated to the senior manager for manual review.
- Error – An interruption to the workflow has occurred, due to an issue.

Gateways
These diamond shaped symbols are used to map decision points along the workflow. They can indicate for example, forks in the road that require a decision in order to determine the next direction a process will need to take. Some examples:
- Exclusive – An example of an exclusive gateway could be when you approach a door that requires an entry code. The correct code allows entry while an incorrect code causes a different outcome.
- Inclusive – Inclusive gateways, allow processes to go down more than one path, as opposed to Exclusive gateways
- Event-based – This is the fork in the road scenario we mentioned above. A decision must be made to move ahead. Let’s say every Tuesday a list was generated of new users during the previous week. If on a particular week no new users signed up then no list would be generated on the following Tuesday.
- Parallel – These gateways can run concurrently and are not dependent on a certain condition.
Connecting objects
We know flow objects are the puzzle pieces that form the workflow. Connecting objects show us how the puzzle pieces connect with one another in the workflow. Three types of connecting objects are used here: Message flows, Sequence flows and Associations.

Message flows
These symbols indicate messages that are sent between participants in the workflow.

Sequence flows
Objects that are mapped sequentially.

Associations
Shows the relationships between various data and objects.
Swimlanes
As the name itself illustrates, think of swimlanes as comprised of individual lanes in a pool set to time a 100m swim competition. The ‘pool’ is the department (sales, marketing, customer service) and can also represent work taken outside the organization or by service providers, tc. The lane itself contains the activity that is needed relative to each role in the process. One lane may be for sales engineers, one lane may be for customer service and another for distribution for example.
Data Symbols
These symbols indicate a specific data type or information that is needed related to the current task underway. The movement of a workflow is not always impacted by data symbols. Unlike coding languages that require an in-depth understanding of a new way to program, BPMN symbols are an easy to understand visual alphabet that can be used by all lines of an organization to understand workflows and visualize Business Process Management (BPM) activity.

Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

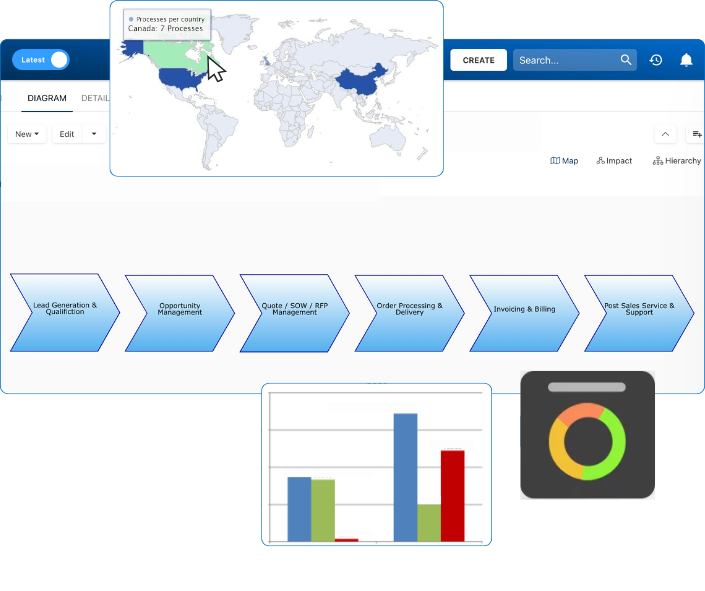
Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

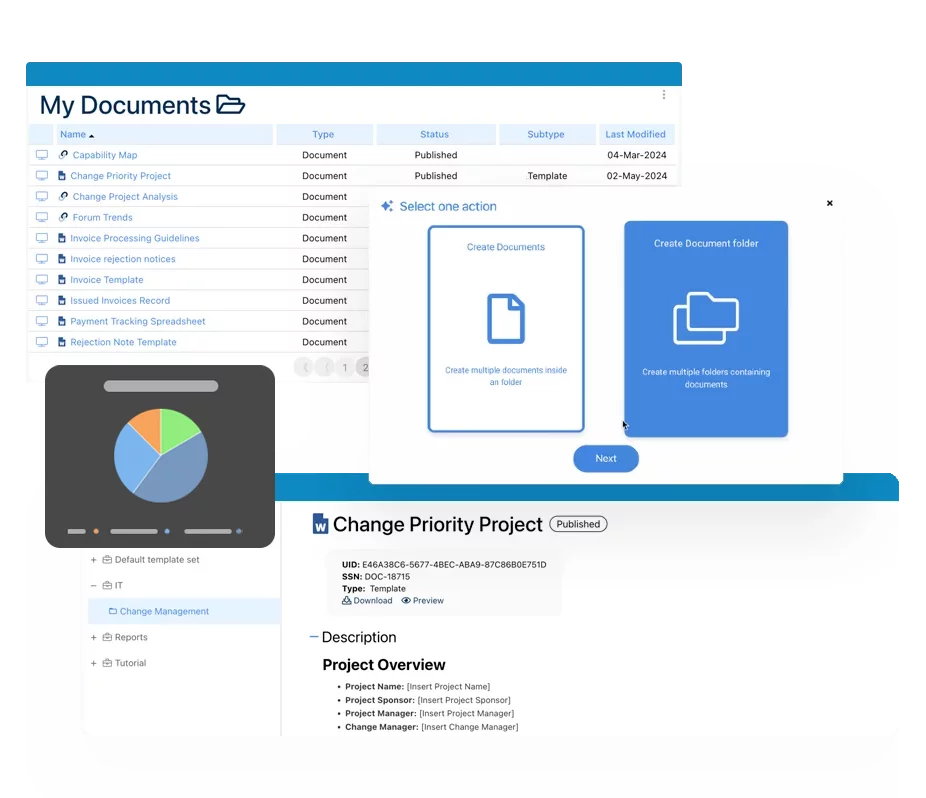
eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!