Comparing – ISO 27001 vs. ISO 27002
Summary
- You can only achieve certification on ISO 27001
- ISO 27002 supports ISO 27001 as a reference/guidance tool.
- ISO 27002 provides granular detail on description and implementation for controls mentioned in ISO 27001
If your world involves information security in any context, you have most likely encountered ISO 27001:2013. This is the international standard describing best practices for an ISMS (information security management system).
You may not be as familiar though with a supplementary standard in the ISO 27000 family known as ISO 27002:2022. This updated standard provides advice on implementing the security controls listed in Annex A of ISO 27001.
It’s important to note that while ISO 27001 remains the more popular standard, and of course the one organizations certify to, neither should be considered in isolation of each other.
What is ISO 27001
The central framework of the ISO 27000 series is ISO 27001. This is a series of documentation detailing various parts of information security management. This standard is the resource for the required implementation of ISMS. Essentially, this documentation is an overview of everything you must do to meet compliance standards.
ISO 27001 is particularly useful when beginning a project. It also serves as an excellent resource if an organization is seeking general advice without having a full-scale implementation defined yet.
Meeting the requirements include:
- Assembling a project team and beginning the project
- Having a GAP analysis completed
- Scoping out the ISMS
- Starting a high-level policy development process
- Completion of a risk assessment
- Selecting and Applying controls
- Initiate risk documentation
- Complete staff awareness training
- Complete the assessment, and review of an internal audit and also
- Opt for a certification audit
A look at ISO 27002
As noted above, ISO 27002 is a supplementary standard to ISO27001. It focuses the controls for information security and how organizations may choose to implement them.
These controls can be found in Annex A of ISO 27001. This is the reference most information security experts will refer to when the topic of security controls is discussed. It’s important to note that while the outline of each control in Annex A is only a few sentences, ISO 27002 refers to each control with an average of one page per each.
This is simply because the ISO 27002 standard must explain how each control works, what is the objective of said control, and how that particular control can be implemented.
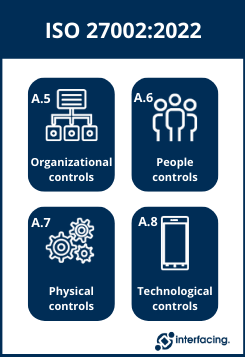
These controls are grouped in ISO 27002 under four domains:
- Organizational controls (clause 5)
- People controls (clause 6)
- Physical controls (clause 7)
- Technological controls (clause 8)
Additionally, there are 2 annexes referenced:
- Annex A – Using attributes
- Annex B – Correspondence with ISO/IEC 27002:2013
The ultimate impact of ISO 27002 is in its contribution to the stability of and organizations ISMS. A key difference is that ISO 27002 is not intended to distinguish between applicable controls used or not within an organization. ISO 27002 is to be used as a reference for the selection of security controls rather than a certification process.
Comparing ISO 27001 and ISO 27002
There are three notable differences between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002:
Detail
ISO 27001 provides only an outline of each aspect of ISMS. Specific advice can be found in additional standards. ISO 27002 is one of the additional standards. An example can be found below.
From ISO 27001
A.6.2.1 Mobile Device Policy in ISO 27001:2013
Control
A policy and supporting security measures should be adopted to manage the risks introduced by using mobile devices.
From ISO 27002
A.6.2.1 Mobile Device Policy in ISO 27001:2013
Control
A policy and supporting security measures should be adopted to manage the risks introduced by using mobile devices.
Implementation Guidance
When using mobile devices, special care should be taken to ensure that business information is not compromised. The mobile device policy should take into account the risks of working with mobile devices in unprotected environments.
The mobile device policy should consider:
- a) registration of mobile devices;
- b) requirements for physical protection;
- c) restriction for software installation;
- d) requirements for mobile device software versions and for applying patches;
- e) restriction of connection to information services;
- f) access controls;
- g) cryptographic techniques;
- h) malware protection;
- i) remote disabling, erasure or lockout;
- j) backups;
- k) usage of web services and web apps.
Care should be taken when using mobile devices in public places, meeting rooms and other unprotected areas. Protection should be in place to avoid the unauthorized access to or disclosure of the information stored and processed by these devices, e.g. using cryptographic techniques and enforcing the use of secret authentication information.
Mobile devices should also be physically protected against theft especially when left, for example, in cars and other forms of transport, hotel rooms, conference centres and meeting places. A specific procedure taking into account legal, insurance and other security requirements of the organization should be established for cases of theft or loss of mobile devices. Devices carrying important, sensitive or critical business information should not be left unattended and, where possible, should be physically locked away, or special locks should be used to secure the devices.
Training should be arranged for personnel using mobile devices to raise their awareness of the additional risks resulting from this way of working and the controls that should be implemented.
Where the mobile device policy allows the use of privately owned mobile devices, the policy and related security measures should also consider:
- a) separation of private and business use of the devices, including using software to support such separation and protect business data on a private device;
- b) providing access to business information only after users have signed an end user agreement acknowledging their duties (physical protection, software updating etc.), waiving ownership of business data, allowing remote wiping of data by the organization in case of theft or loss of the device or when no longer authorized to use the service. This policy needs to take account of privacy legislation.
Certification
You can only certify to ISO 27001 and not to ISO 27002. This is because ISO 27001 is the management standard providing a complete list of compliance requirements. ISO 27002, as a supplementary standard, addresses only one specific aspect of an ISMS.
Applicability
When implementing an ISMS, it is important to understand that not all security controls will be applied to your organization.
That is clearly mentioned in ISO 27001 where it specifies that organizations must conduct a risk assessment in order to identify and then prioritize information security threats.
ISO 27002 does not mention this part so if you were to only use this standard, it would be extremely difficult to figure out what controls an organization would need to adopt.
When can each standard be used?
While ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 are in the same ISO series, they have different functions that are very helpful though under different circumstances.
ISO 27001 is ideal for an organization to begin with when planning and ISMS framework. Its primary objective is to provide security to the information security infrastructure. It’s secondary objective is to attain certification.
Organizations should use ISO 27001 when they:
- Intend to certify to international standards
- Do not have an ISMS in place
- Are looking to assess and mitigate risks to security in the organization
- Must comply with legal, business, or regulatory requirements
Once an organization identifies what controls will be implemented, ISO 27002 can be referenced as guidance on how each control operates.
How Interfacing can Help Ease the Burden of ISO/IEC 27001 Documentation
With the growing complexity of managing ISO 27000 series requirements, organizing information in a central location becomes increasingly important. When an auditor comes to site, they will assess management’s oversight of their third-party service providers as well as the company’s own controls. The majority of this oversight revolves mainly around documentation and the ability to review it. Proving this to an auditor means providing them with a record management system that can draw on the accuracy & speed of access to the who, when and how’s of the organizations operations objectives.
Interfacing’s Enterprise Process Center® digital platform solution maintains a complete library of:
- Processes
- Procedures
- Roles & responsibilities
- Risks
- All requirements
- Internal policies
- Aligned indicators (KPIs)
- Controlled indicators (Monitoring)
All of the above within a centralized Integrated Management System (IMS), allowing your organization to fast-track certification and simplify creation, communication (new & changes) and update of information security controls, processes and associated/related documentation.
Additionally Interfacing’s IMS also offers a Quality Management System for automating the training of your different controls and audits (action item management/CAPA) as well as managing all your documentation, files, processes, procedures, roles, risks & controls.
We offer an entire library of content to jump start your program or use as a reference library for the operating controls used to validate the maturity of your current ISO 27001 documentation.
Why Interfacing?
Interfacing’s Enterprise Process Center® (EPC) provides you with a tool to control your compliance processes by helping you manage the audit, assessment and execution of your underlying business process management. This will make compliance easier and more transparent throughout your organization.
Enterprise Process Center® will give your company the ability to automatically and continuously monitor and manage your compliance initiatives. Implementing controls associated with processes and tasks ensures that compliance requirements are followed, while automatic tracking and documentation of all process changes gives management complete oversight.
If you would like to see more or discuss how Interfacing can help your organization, be sure to click below.
Contact us more for information.
Gain Transparency with the Enterprise Process Center®
Interfacing’s Digital Twin Organization software provides the transparency and Governance to improve Quality, Efficiency and ensure Regulatory Compliance.
Read Our Blogs
Take a moment to read blogs about GXP, Regulatory Compliance, today’s trends, and much much more!
Discover how your organization benefits from an Interfacing solution.
A key differentiator of Interfacing to other digital and business transformation consulting firms is that Interfacing offers its own innovative technology solution in support of transformation programs. Interfacing’s software solutions deliver the transparency required to reduce complexity, improve execution and facilitates agility and change.
Interfacing’s integrated management system is a one-stop-shop for managing transformation programs. We know it’s a very competitive environment out there. It is for that reason our strength is in our commitment to maintain flexibility throughout the project lifecycle whether it is in our innovative products or in our team of experts.
Try It Now For Free!
Document, improve, standardize, and monitor your business processes, risks and performance with Interfacing’s Business Process Management Software (BPM Software) the Enterprise Process Center®!