Digital Twin Definition
Let us look at the simple definition first of a Digital Twin prior to going into a deep dive. A Digital Twin is a replica (representation) of physical objects (e.g. persons, vehicles, plane engines etc.) in digital format or it is a digital replica of an intangible system (sales & marketing funnel, delivery fulfillment process, etc.).
Digital Twin’s purpose,is to examine, alter or test the replicated representation without interacting with it in the real world, thus avoiding any negative consequences.
It is its own online world if you can think of it that way. You can create and alter objects that are based on reality. This has been done long before the Digital Twin concept came about, however, this definition has much more potential and scalability to monitor and replicate virtually anything you can think of.
What does it mean to business and what are the Benefits of a Digital Twin Organization?
The Digital Twin process was given a boost from the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) as it resulted in extremely affordable cost-effective implementation. Virtual twins are popular today in business and have been considered a top trend of strategic technology planning in recent years. One of the most important questions answered in recent years is how is the Digital Twin process changing the way we design, plan, manufacture, operate, simulate and forecast business today?
In the virtual platform created, a physical twin exists as a real-time digitized copy of its real-world self. This “bridge” between worlds, at its core, is used to optimize business performance. This is done through data analysis and monitoring of systems to identify any issues that come to light and ultimately prevent them from occurring and affecting downtime in a real-world setting. Simulations produced help to develop and plan for the future regarding product or service updates within the process.
The benefits are almost incalculable, as they affect all industries including, agriculture, transportation, governmental bodies, and retail for example.
So Why use a Digital Twin?
Companies must find ways to avoid risk in producing products with inherent defects in their future assets. Using Digital Twin technology, production costs can be minimized as expenses are saved early on with the product being built right the first time initially. This eliminates the steps of repetitive physical test or update failures in real-time cases. This concept can save industries an estimate of about 50% cost reduction in development overhead. There is also a marketed confidence boost in product performance as virtual twin’s development act as a valuable aid in complex decisions, preventing costly downtime, especially to robotics and machinery.

What are some practical Use Cases for Digital Twin?
The core benefit with twinning for companies regarding their processes, products or services is simply in its efficiency of running complex simulations effectively and at low cost to the organization. Businesses can race their product to market much faster than their competition today using the virtual twinning process. This technology anticipates how the product and process will perform via multiple virtual scenarios, digital simulations and analysis of the data they create. The reliability and consistency of the always updating information provides the organization with constant assurances needed to make decisions quicker, thereby speeding up production to overtake the competition.What is the future impact of Digital Twin Technology?
If we look at employers first for example, offices adopting this technology sooner rather than later will attract top tier, innovative talent. Offices can incorporate many new interactive features, improving employee satisfaction and productivity as they use the latest technology to deliver quality data-driven simulations.
Digital twin technology use by employees expands their engagement with online tools (e.g. interactive maps – geolocation etc.). Managers can supervise remotely using online tools similar to a 3D map that is created using the virtual platform based on simulations. Interactive employee meeting sessions in a ‘workroom’ would happen irrespective of global location.
Are there any challenges with the Digital Twin process?
Like any new process, there will be challenges faced by early adopters. The biggest concern to date from companies looking into this technology is the risk of the object or system they want to replicate,being misrepresented. When you consider the fact that there may be a significant amount of information regarding replicating a physical object with 100% accuracy, it stands to reason that there may be some hesitation in adoption.
This can be countered by companies whose purpose it is to design and implement Digital Twin platforms. There has been a tremendous amount of data-driven processes and techniques accumulated to date on various methods to accurately replicate physical objects using multiple inputs such as sensors, interface devices etc. They will scan the object and record data simply and accurately.
Another challenge comes from the complexity of the physical item due to be replicated. This may mean taking the extra time to open the item (for example, an aircraft engine) where the internal components may need to be individually represented using animation and code. Processes to be replicated such as CRM, prospect marketing or service delivery funnels for example are significantly easier to duplicate as they concern a flow of scenarios, ideas and software inputs more than generating moving parts that must be recorded.
Final Thoughts
Digital twin technology is a great asset to companies wanting to improve their customer experience, when looking to develop enhancements to products, operations or services and when seeking to drive innovation into new lines of business.
We are right around the corner of a new technology explosion as more companies discover the advantages of bringing their real-world objects into a virtual setting and using them in various simulations to gather valuable data on creating enhancements, new products or even future output.
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

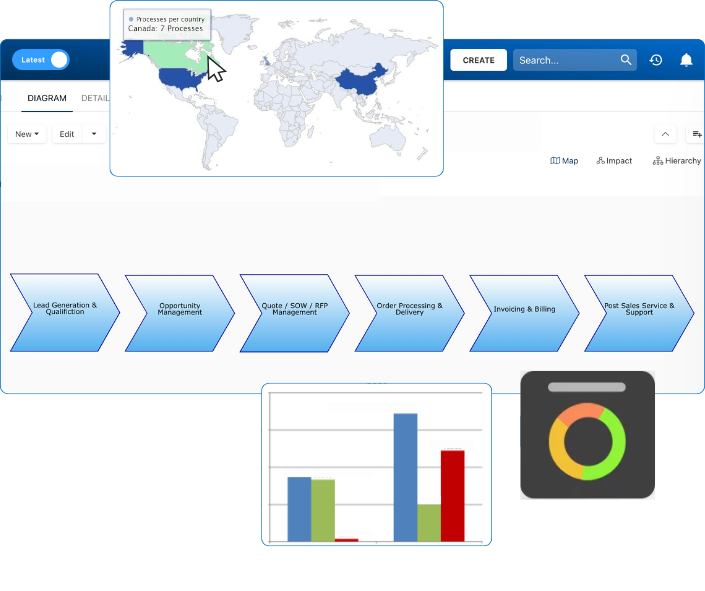
Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

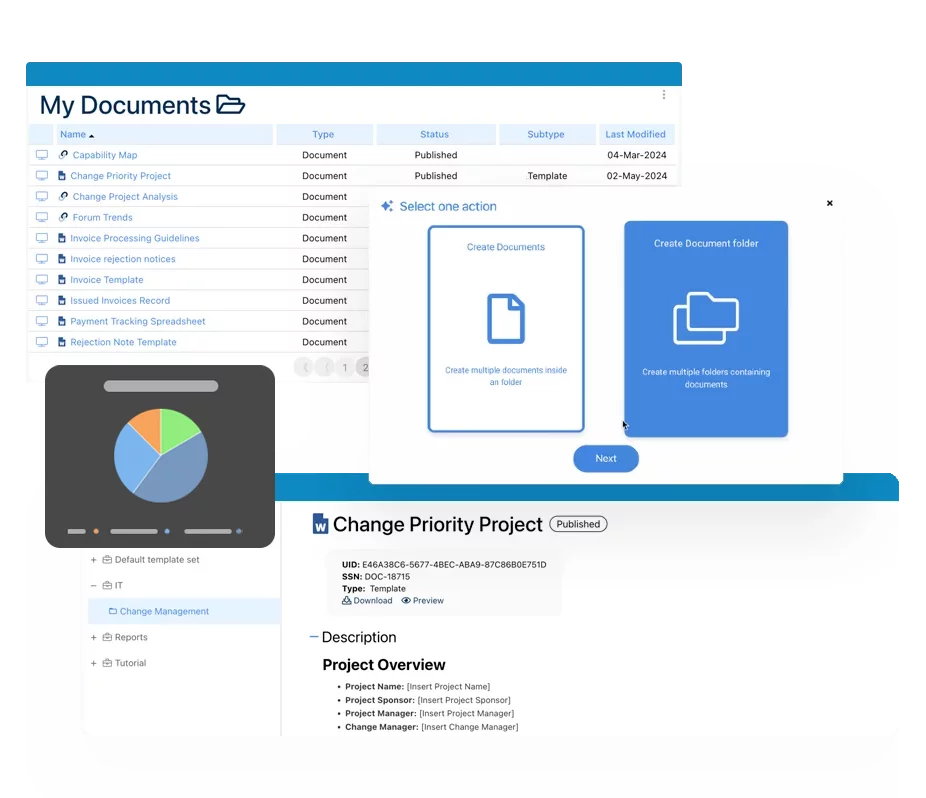
eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
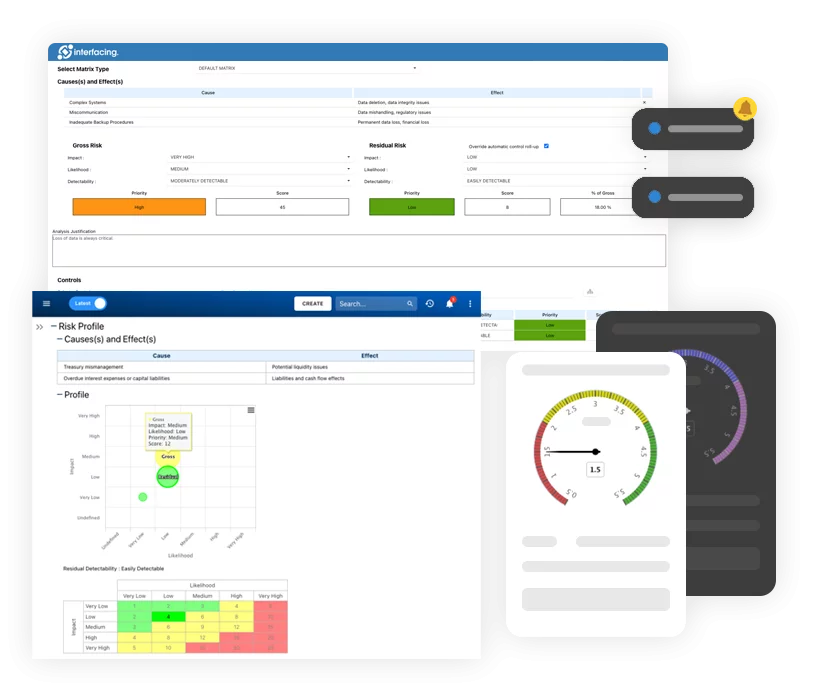
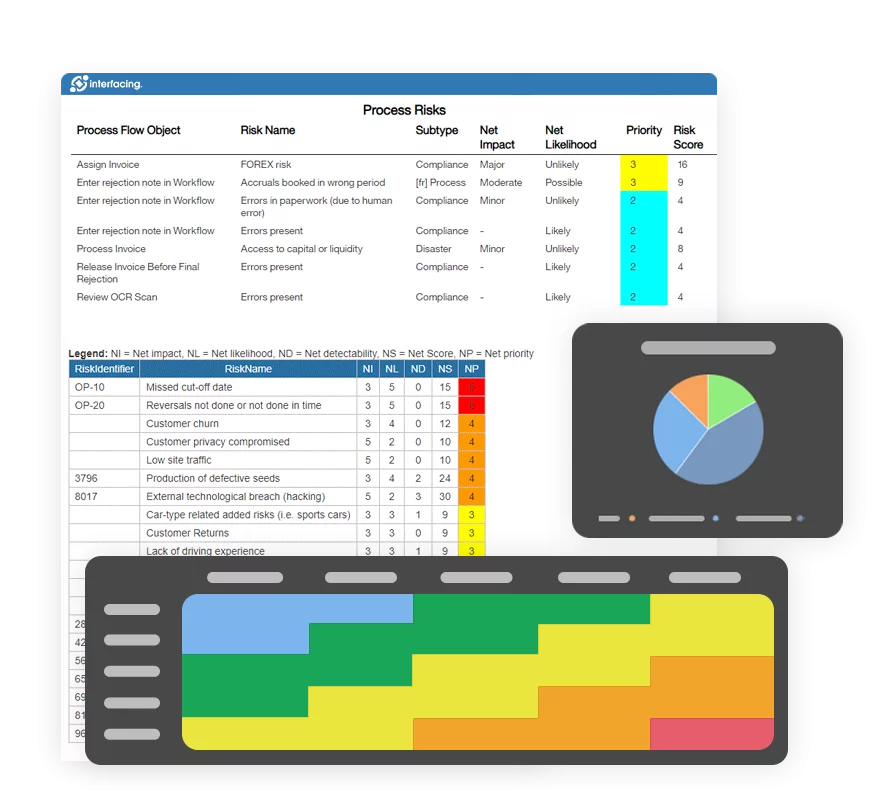
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Trusted by Customers Worldwide!
More than 400+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms