- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


eQMS for Quality Automation and Compliance
Please Select contact form.
Quality System Automation, Data Integration, Reporting & Analytics

What is a Quality Management System (QMS)
According to the American Society for Quality (ASQ), a Quality Management System (QMS) is a formalized framework that defines the processes, procedures, and responsibilities required to achieve quality objectives across an organization.
In regulated environments, quality management must operate within a governed operating model that connects quality processes, risks, controls, and compliance requirements to ensure audit readiness and accountability.
A QMS enables organizations to consistently meet customer, regulatory, and industry requirements by establishing how work is performed, monitored, reviewed, and improved. By linking quality activities directly to execution, oversight, and governance, a QMS supports repeatable, measurable outcomes and provides a foundation for continuous improvement aligned with organizational goals.


Enterprise Quality Management System (EQMS)
An Enterprise Quality Management System (eQMS) extends the principles of a traditional QMS by digitizing and integrating quality processes across the entire organization.
Organizations adopt eQMS solutions to manage quality, compliance, and regulatory requirements at scale. An eQMS provides structured workflows, defined ownership, and traceability across production, service delivery, and supporting business processes, helping enterprises maintain consistency and accountability.
Modern eQMS platforms evolved from manual tools and spreadsheets into centralized, enterprise-grade systems that support collaboration, controlled documentation, approvals, and performance monitoring. By integrating with IT infrastructure and data models, an eQMS enables cross-functional teams to work from a single source of truth while maintaining audit readiness.
While capabilities may vary by industry and organization size, most eQMS platforms commonly include:
- Web-based platform
- Taking a BPM approach to functionality involves applications that are built on a platform with integration to other applications.
- Interoperability with other Enterprise Resources Planning (ERP) applications.
- The GUI is role-based and focuses on execution of the workflow process.
Key Benefits of an eQMS Solution
An eQMS provides organizations with a structured, scalable approach to managing quality and compliance across the enterprise.
By centralizing quality processes and automating approvals, tracking, and reporting, an eQMS reduces operational risk, improves visibility, and enables faster, more consistent decision-making. Organizations gain the ability to proactively identify issues, enforce standards, and demonstrate compliance during audits and inspections.
Overview of Our
Interfacing eQMS Capabilities
Quality Management System Capabilities Overview
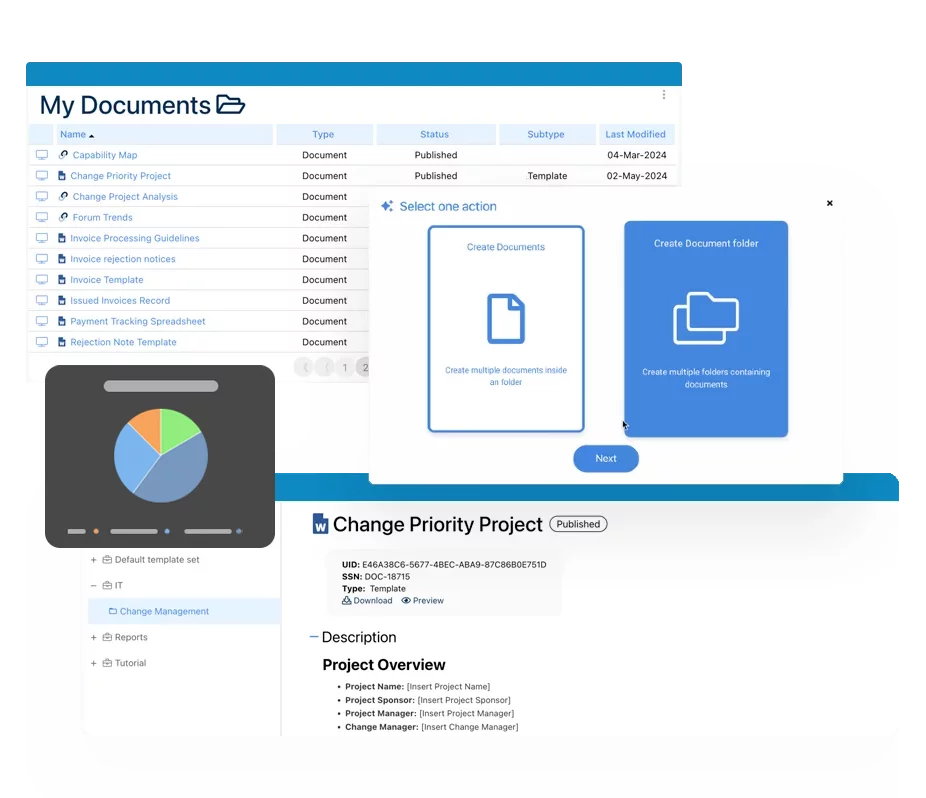
Documents & Records Management
Documents and records management within a Quality Management System (QMS) ensures that controlled documents, records, and evidence are created, reviewed, approved, distributed, and retained in a compliant and auditable manner.
Interfacing’s eQMS centralizes document control across policies, procedures, work instructions, and records, providing full visibility into document status, ownership, version history, and approval workflows. Automated lifecycle management reduces manual effort while maintaining alignment with quality and regulatory requirements.
Teams can collaborate securely across locations to co-author, review, comment, approve, and electronically sign documents. Built-in notifications, read confirmations, and retention controls ensure documents are distributed, acknowledged, and archived according to defined governance rules.
By enforcing role-based access, version control, audit trails, and secure records retention, organizations maintain audit readiness while improving efficiency, traceability, and confidence in their quality documentation.
- Adding new Documents
- Unique IDs and tags by document
- Version control by document
- Archive, move and delete existing documents
- Structure document in a hierarchy, folders
- Creates templates for Records and ability to reuse the workflow template
- Audit log / trail on changes to metadata
- Workflow for approvals, reviews
- Electronic signature on approvals
- Delegation on reviews, approvals
- Notifications, emails for workflows
- System check for publications and approvals
- Collaborate and raise change requests
- Multi-lingual support – UI, Metadata translation suggestions & Documents
- Document Name
- Document ID
- Organizational Unit
- Full Text
- Meta data (Type, Categories, Attributes)
- Filterable columns
- Last modified data
- Last modified by
- Any user-defined attributes (UDAs)


Audit Management
Interfacing’s audit management support for your organization includes compliance with the standards of a wide variety of internal and external audits. Standards from the FDA, ISO, quality and clinical audits are a few of the governing agencies establishing compliance specifications that must be met. Our DBP will automate tasks normally done manually in excel, offering the reusability of audit definitions and further testing, evidence and sampling requirements; meaning that you will only need to define audit and test requirements once, and use them across multiple audits. This includes the ability to perform both internal and external audits (supplier, customer, regulatory requirements etc.).
When using our Digital Business Platform, not only will you be able to follow the audit step by step, you can also escalate the audit with major / minor findings all the way to CAPA in Action Items Management. One of our tools is used in Gantt chats regarding audit planning, capacity management, ISO requirements management and more.
- Capture all audit & test instances within one repository
- Search & sort audit fields by ID, name, frequency, sample size, etc.
- Triggered-to-start ad hoc audit & pre-scheduled audit
- Set key audit attributes such as auditor and auditee, deadline, trigger to start, prerequisite, etc.
- View, edit and add sample results for different audit purposes
- Determine sample effectiveness and accuracy through automation
- Complete audit trails & reports
- Trigger CAPA via failed audits, incidents, or ad hoc requests
- Add multiple action items (AI) that define specific criteria (e.g. AI name, owner, action type, priority, etc.)
- Assign AIs to specific resources with clear deadlines & level of priority
- Automatic escalation CAPA request to its AI owner or a different role of equal responsibility in case of absence of its AI owner
- Allow AI owner to request extension on his assigned AI
- Collect & store AI evidence to validate completion



Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
We think of CAPA much like the immune system of an organization. If a deviation or systemic breakdown occurs in an organizations processes or manufacturing steps, CAPA is the rigorous process in place that will identify why the defect or failure occurred. Corrective Action Preventive Action (CAPA) is the process used to investigate and solve organizations problems, and will identify and take corrective action to prevent the reoccurrence of root causes. Interfacing’s DBP assists CAPA to prevent recurrence of any root cause of a failure or defect.
Our DBP will raise either on an ad-hoc basis or as an output of an Incident or Audit investigation findings. It will raise actions that can be traced to a source and implemented as part of a Action Items Management plan.
- Date raised
- Type
- Deadline date
- Issue description
- Root cause
- CAPA action items
- Test Info tab – displays all completed tests inherited from previous form
- Failed audit or incident information inherited on form
- View/edit/add multiple CAPA action items
- Responsible roles and status of action items available in real-time


Quality Events including Non-Conformity, Complaint etc.
Non-conformance management is a requirement to meet ISO 9001 standards. Interfacing’s Digital Business Platform (DBP) eQMS software solution combines document and process management to significantly improve the management of any non-conformances and their associated action plans. With our DBP, you can identify and raise non-conformity issues discovered in an audit to create an Action Items Management plan. The benefits are impactful. In another example, in a production process, anomalies can be identified in the design stage, saving significant expense than those resolved further along the process in manufacturing or even out to distribution or making its way into consumer sales.
Implementing and monitoring non-conformances and the effectiveness of each to avoid adverse business operations are made possible through eQMS. With an eQMS, each incident will be recorded with all associated action items tracked.
- Identification of root cause, main reason for the NC or what went wrong
- Why the work doesn’t meet specs
- What can be done to prevent the problem from happening again
- Explanation of corrective action taken or to be taken
- Key people involved in the NC and specs affected under the NC


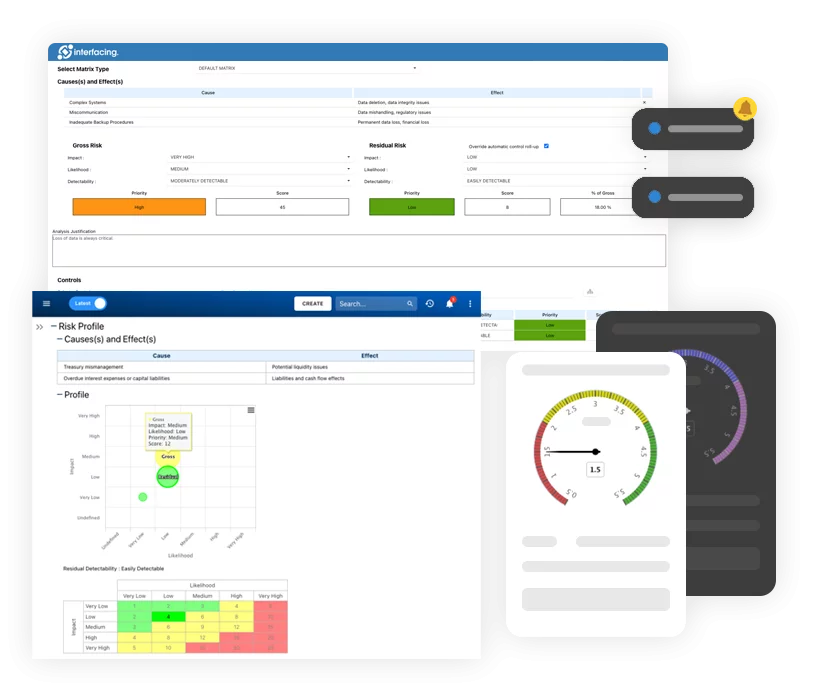
Risk Management
Enterprise Process Center® (EPC) facilitates organizations to be proactive vs. reactive when it comes to risk control and process risk management strategies. Not only is risk management important to protect against disaster striking, but by integrating controls into daily operations you can ensure that quality standards are met and customer satisfaction is maintained. Additionally, there is nothing greater than the cost of “non-compliance”, hence, comprehensive risk and process transparency is a necessity to comply with laws and regulatory requirements such as Sarbanes Oxley, Basel III, IMF, HIPAA, FDA, ISO 15000, among others.
- Detailed risk library including identifier, description, type, category, responsible resources (via RASCI-VS)
- Customizable risk matrices including risk likelihood, impact, score, percentage, color and priority
- Import/export risk details via Excel
- End-to end process visibility associated with risks
- Filter, search, & report risks by attributes
- Reusable risks & controls
- Trigger CAPA based on process & task risk analysis
View the cause & effect of risks to track critical risk information; risk managers analyze and prioritize risk mitigation
Extended risk editing (gross risk per process, net risk per control on process, specific controls per process, override roll-up calculation per process)
Detect a risk’s occurrence; automated risk roll-up algorithm for risk scoring
Residual risk provides realistic view of potential impact
Risk matrix visualizes 5 different levels of risks residing in processes


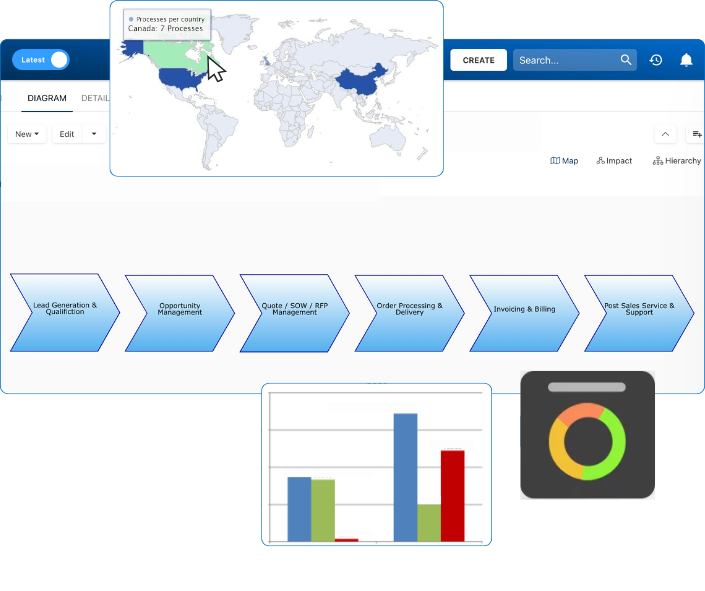
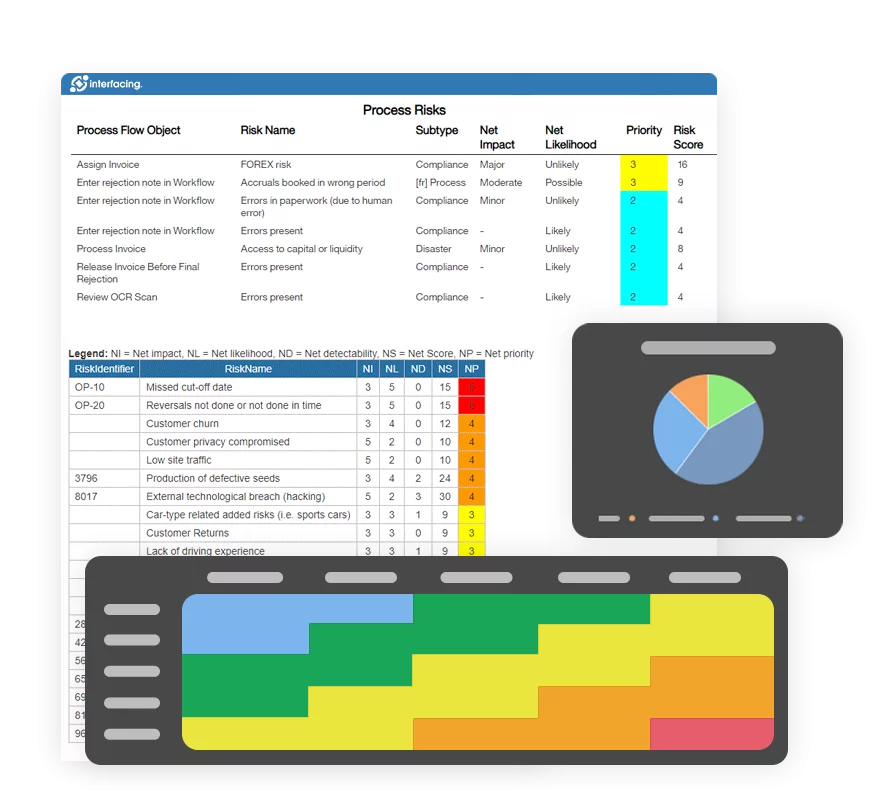
Incident Management Reports & Dashboards
Review QMS incident reports through customized dashboards, which offer interactive charts and visual representations of incident data. Users can filter, analyze, and drill down into incident metrics, supporting effective decision-making and swift response actions.
The dashboard simplifies tracking due dates, action items, and other critical incident details, thereby improving oversight, compliance, and overall audit readiness. By identifying key risk and control indicators and quantifying threshold limits, management can monitor measures to ensure policies are enforced and standards are maintained, while ensuring that documentation and evidence are always prepared for internal or external audits.
- Incident Analysis reporting
- Incident graphs and reports generated from data can be exported to Word, PDF, or print
- Incident reports with detailed drilldowns to view subsets of metrics and relative information
- Incorporate dashboards and charts into forms
- Monitor test progressions, percentage of resolved incidents in real-time
- View number of incidents logged per location, within a specific time frame
- General controls and risks report & custom report


Environmental, Health & Safety
The procedures and actions taken to respond and resolve Environmental, Health and Safety incidents that occur is known as Incident Management. Interfacing’s DBP will support these actions by tracking and escalating remediation from start to finish. DBP will perform root cause analysis (RCA) and Incident analysis related to Environmental, Health and Safety events.
A Digital Business Platform solution ensures that all incidents are quickly addressed and high quality standards are maintained. Teams also benefit from improvements in operations, preventing recurrence of future incidents.
- Reuse information from previous stages of an incident process
- Perform root cause analysis & risk analysis
- Set multiple review cycles & approval cycles
- Trigger an escalation to CAPA if needed
- Track incident with tracking code at any stage of the process
- Incident reports with detailed drilldowns to view subsets of relative information
- Incident investigation with E-signature confirmation of completion


Supplier & Product Management / SCAR
Interfacing’s EPC and Digital Business Platform automation extends CAPA compliance to suppliers. All tasks are streamlined in the Supplier Corrective Action Request (SCAR) process in relation to any life science organization. For these organizations, it is critical that accountability is a major component of quality management and compliance with FDA regulations. Interfacing’s eQMS solution considerably reduces audit time while increasing product quality and safety in conformance to regulatory compliance.
- Conduct Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Leverage best practice Root Cause Methodologies (5 Ws, Comparative Analysis, 3×5 Why)
- Root cause is embedded in the workflow
- Directly send tasks to users as part of SCAR workflow
- Raise action items on suppliers (SCAR)
- Reuse centrally managed Supplier information
- Notify the supplier directly
- View/edit/add multiple SCAR action items
- Responsible roles and status of action items available in real-time


Training Management
Today’s challenge in training is actually managing the amount and frequency of training that occurs across the organization’s enterprise operations. This challenge impacts the singular tracking of a specific employee most. Interfacing’s Digital Business Platform supports your business’s training management with its ability to effortlessly link to all Learning Management Systems (LMSs) within the organization.
Measure training efficacy through controlled questionnaires or quiz’s after a completed training session to ensure your training management program meets regulatory requirements and successfully achieves the high threshold of your organization’s institutional knowledge.
This gives training administrators visibility across all training platforms related to regulatory requirements, processes, documents and training itself. Think of it as a central repository to monitor and track all training.
- Define customized questionnaires for pre / post training to measure efficacy
- Leverage standard questionnaires to quickly build new training templates
- Provide direct link to training materials
- Reuse documented compliance requirements from the IMS repository (Regulatory, Documents, Processes)
- Assign training dynamically
- Provide users with a calendar / Gantt view of their trainings
- Provide instructors with a view for their courses
- De-activate training after use
- Request extension for training
- Managers to sign-off on training post-completion


Control Management: Risk Indicator Audit , Analysis & Reporting,
EPC offers within a single collaborative platform an area where analysts can identify, assess and prioritize risk mitigation plans, and auditors can schedule then execute control audits and implement corrective action plans based on test results. Furthermore, by identifying key risk and control indicators and quantifying threshold limits; management can monitor measures to ensure policies are enforced and standards are maintained.
- Monitor controls through audits
- Recurrent audit scheduling
- Implement CAPAs based on test results
- COSO Cube ERM framework
- General analysis, critical path analysis & high-risk path analysis generated in a dynamic manner
- General controls and risks report & custom report
- Reusable key risk & control indicators (KRIs, KCIs) for more than one source
- Target threshold setting for continuous improvement


Pharmacovigilance
Pharmacovigilance (PV) plays a pivotal role in healthcare by systematically gathering, monitoring, researching, and evaluating information from healthcare providers and patients about adverse medication effects. This vital process ensures public health safety and enhances patient care by effectively managing the risks associated with drug therapies. PV not only facilitates regulatory compliance but also fosters drug development, bolsters market confidence, and, most importantly, elevates patient safety. Seamlessly integrate with other modules such as BPM, QMS, and other enterprise systems to optimize operational efficiency.
- Standardized Data Management: Effortlessly capture, process, and analyze adverse events according to a standard workflow and form to ensure precise and prompt data handling.
- Automated Workflow Optimization: Enhance pharmacovigilance processes with automated workflows, reducing manual tasks and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintain compliance with global regulatory standards by following a standard workflow and leveraging electronic signatures.
- Proactive Risk Management: Identify data trends and address potential risks in a timely manner.
- Enhanced Reporting: The system supports the ability to generate records for any adverse event.
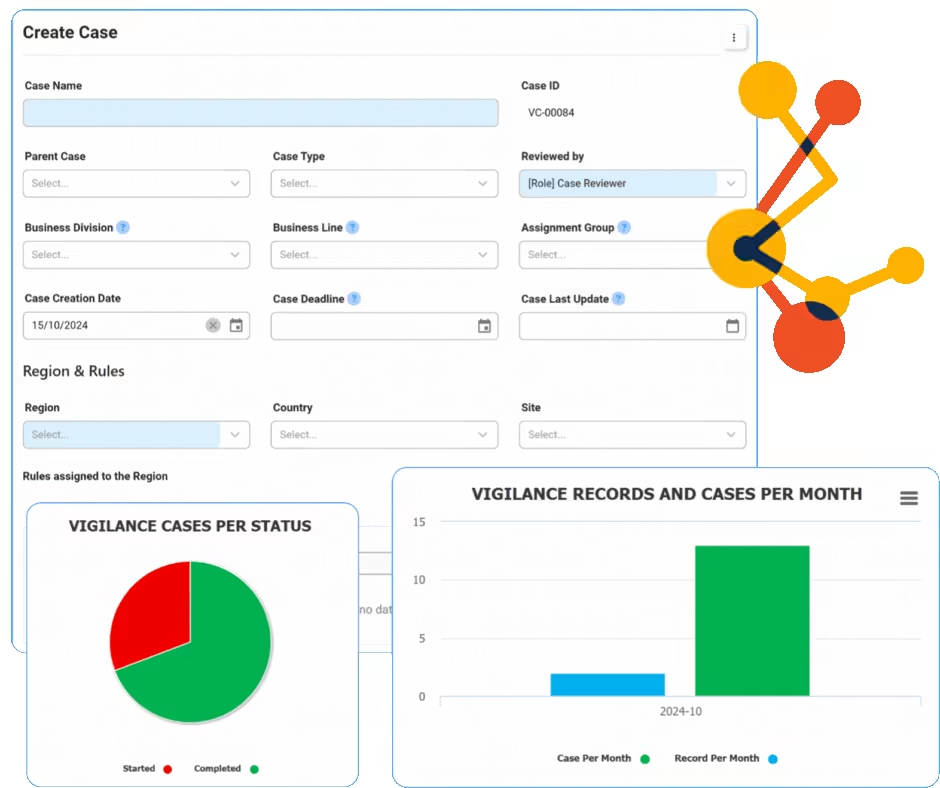

Action Items Management
Action Item Management within a Quality Management System (QMS) involves the systematic tracking and handling of tasks generated from quality processes, ensuring compliance and continuous improvement. Interfacing’s eQMS provides tools for assigning, monitoring, and documenting actions, enhancing accountability and efficiency. The platform integrates various functionalities to streamline communication and ensure that all quality-related tasks are completed promptly and effectively. Utilizing Interfacing’s solution can help organizations improve their quality processes, reduce non-compliance risks, and promote a culture of continuous improvement.
- Monitor controls through audits
- Recurrent audit scheduling
- Streamlined Extension Request Handling
- Implement CAPAs based on test results
- COSO Cube ERM framework
- General analysis, critical path analysis & high-risk path analysis generated in a dynamic manner
- General controls and risks report & custom report
- Reusable key risk & control indicators (KRIs, KCIs) for more than one source
- Target threshold setting for continuous improvement


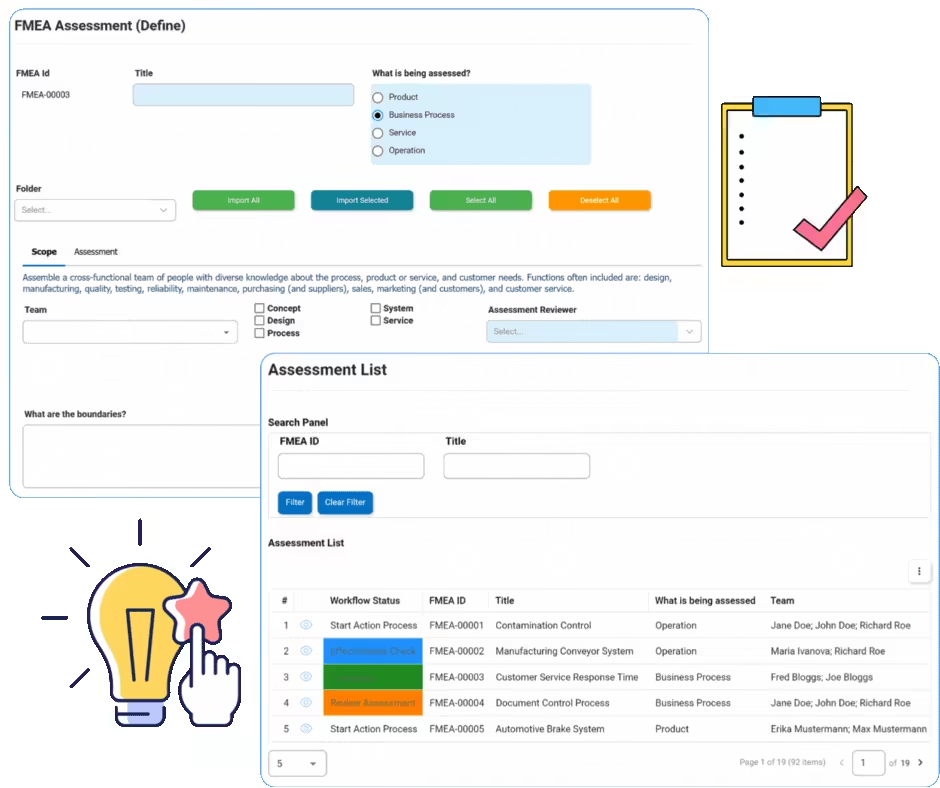
FMEA
FMEA identifies failure modes and their effects in processes. It will identify design inputs or special characteristics down to the end user. Interfacing’s eQMS software automation platform allows rapid notification of the severity ranking or danger of the effects of the failure. The next steps immediately following the notification include identification of the causes and the mechanisms involved in the failure mode.
EPC offers within a single collaborative digital platform the ability for users to implement corrective action plans based on Inspection / FMEA.
- Date raised
- Inspection Type
- Deadline date
- Reason for Inspection
- Effort
- Inspector
- Supplier targeted
- Plan inspections and capacity
- Time-based inspection planning
- Assign inspectors ahead of time
- Inspection by type (such as Supplier, Internal, External, etc.)
- Triggered start of the inspection
- Search & sort inspection fields by ID, name, frequency, location, etc.

Management Review
EPC offers within a single collaborative platform an area where analysts can identify, assess and prioritize risk mitigation plans, and auditors can schedule then execute control audits and implement corrective action plans based on test results. Furthermore, by identifying key risk and control indicators and quantifying threshold limits; management can monitor measures to ensure policies are enforced and standards are maintained.
- Monitor controls through audits
- Recurrent audit scheduling
- Implement CAPAs based on test results
- COSO Cube ERM framework
- General analysis, critical path analysis & high-risk path analysis generated in a dynamic manner
- General controls and risks report & custom report
- Reusable key risk & control indicators (KRIs, KCIs) for more than one source
- Target threshold setting for continuous improvement



Electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) & ISO
Interfacing is here to assist you with the always evolving changes to compliance requirements that need to be addressed immediately. We lead the way to corporate transparency with our easy to deploy and comprehensive digital Integrated Management System (IMS) solutions for all your compliance, risk and process management needs.

Customer Focus
IMS allows business users to define and share your organization’s governing policies, so as to ensure compliance. By automatically applying these policies to the related processes, IMS takes care of compliance for you.

Leadership
IMS standardizes processes to meet compliance with corporate and regulatory policies, eliminating many of the errors created by manual compliance solutions. By automating the processes and providing appropriate reporting and tracking, errors can be avoided, resulting in significant cost savings.

Engagement of People
Complete audit trails that allow you to track all processes and changes can be extracted and reported – a vital component for managing change and ensuring process compliance to standards and regulations. This improved visibility allows you to identify and correct weaknesses with ease.

Process Approach
IMS streamlines processes and their development and allows for their fully integrated end-to-end management. Our solution helps you cut through the clutter and maximize the effectiveness of your processes every time.

Improvement
IMS lets you streamline and automate your compliance initiatives, including reporting and executing change, which lowers the soft and hard costs of compliance and risk management.

Evidence Based Decision Making
One example is better control awareness on how gaps and faulty assumptions suddenly come to light through implementation of SOX compliance procedures. Inadequate controls are quickly identified as complex manual processes are automated through implementation of newer, more accurate workflows.

Relationship Management
IMS lets you streamline and automate your compliance initiatives, including reporting and executing change, which lowers the soft and hard costs of compliance and risk management.
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Trusted by Customers Worldwide!
More than 400+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms