- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
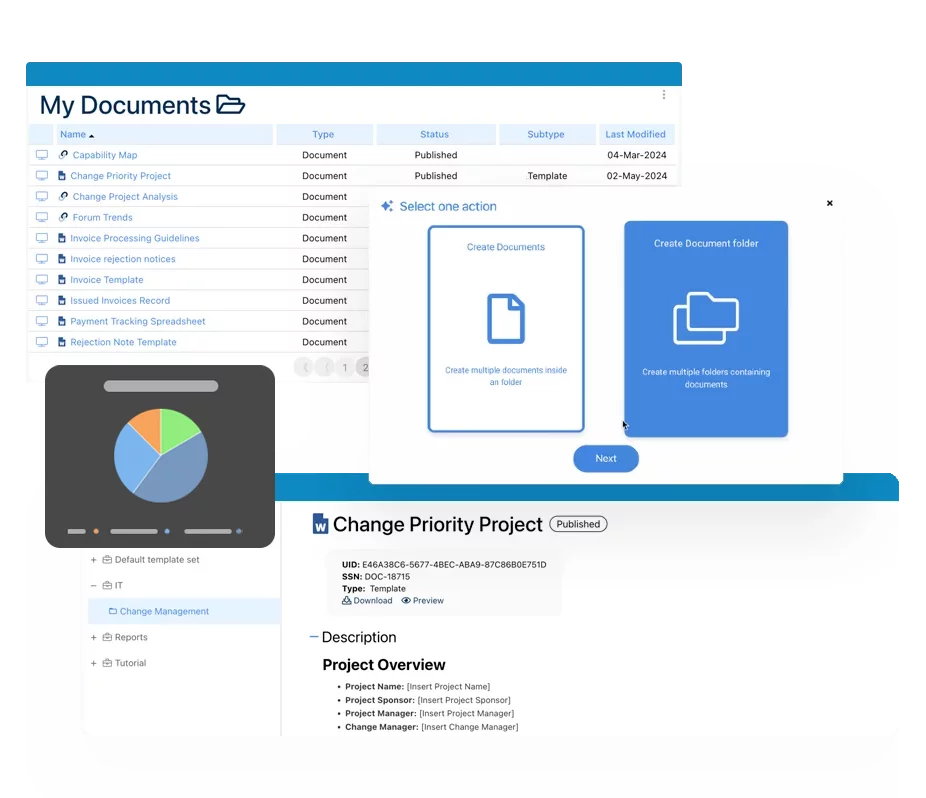
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
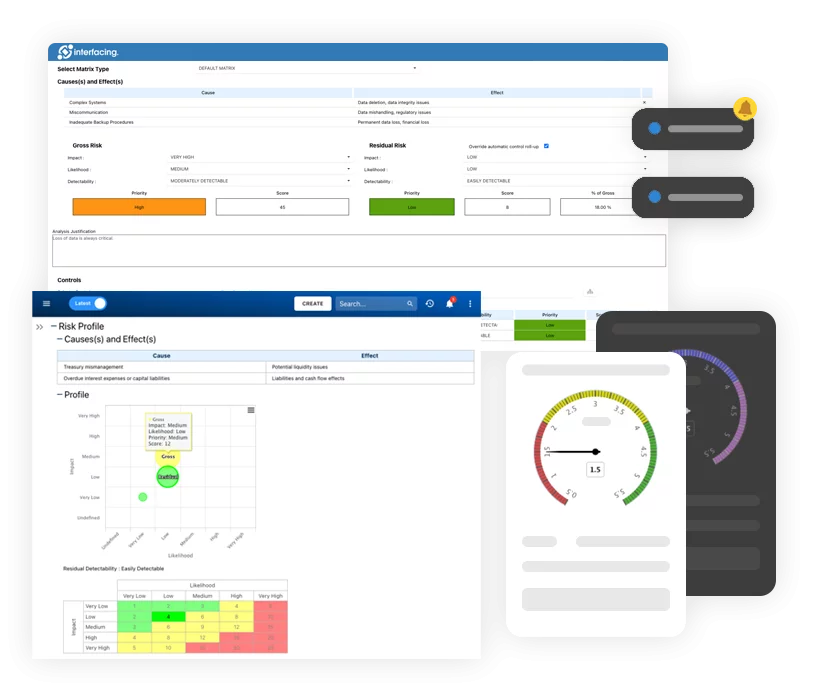
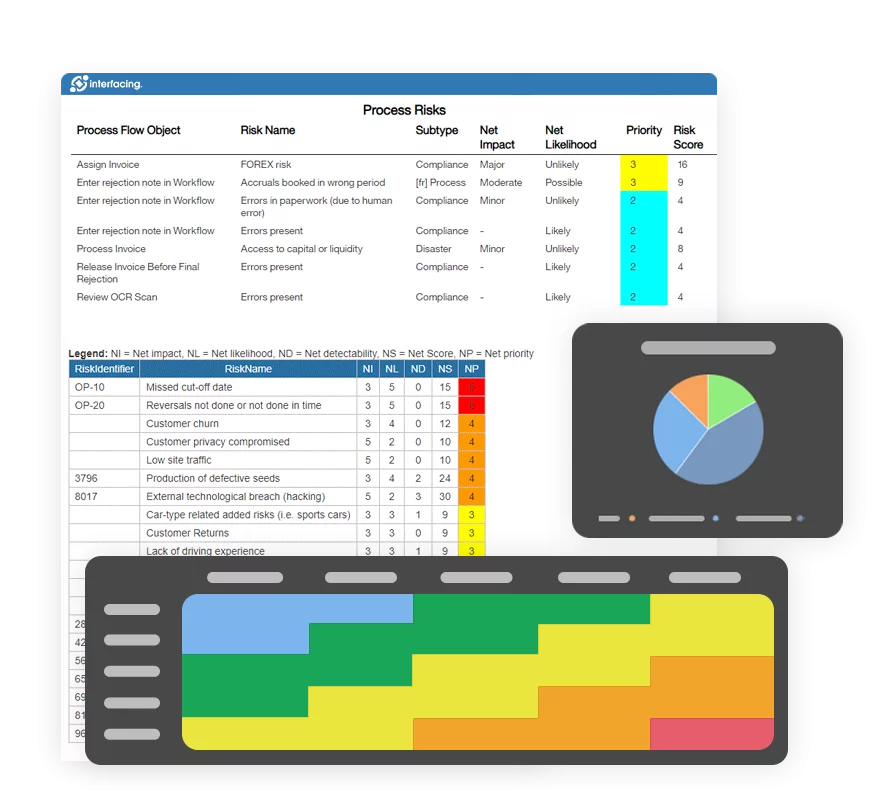
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
- MEL in Aviation
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


RACI vs. RAPID Responsibility Matrix
Please Select contact form.
A quick guide to understanding these two frameworks, their unique roles in decision-making, and when to use each for optimal clarity and efficiency.

The Challenge
Organizations often lack clarity as to who is responsible for task-execution and decision-making roles within processes and projects across the company. Due to this ambiguity, it becomes harder to run a process and project because of the overhead time of intercommunication. Organizations also often fail to create a leveled resource allocation according to their relevant skill sets resulting in overloaded and under-loaded resources.


The Solution
To resolve these problems, it is important not only to clearly define the core responsibilities but also the overall scope of each role while maintaining transparency between the resources. The best practice methodologies provide several responsibility delegation levels to overcome unnecessary time & costs during activity. Responsibility visibility ensures the highest level of quality is achieved during the required timeline, while reducing the overhead of unnecessary bureaucracy. The most popular and widely used responsibility and accountability matrix is RACI and its well-known variations RACI-VS, RACIO, RASCI. A much less widely adopted method alternative approach is RAPID. While often viewed as an opponent to RACI; RAPID’s purpose is slightly different. To understand what and when to use each one, let’s first clarify their meaning and core purposes.


Responsible
Who is/are going to implement the task.

Accountable
The authoritative and the answerable one, who will be making the decisions. This role will be questioned by the higher authorities and will face direct consequences of the failure of the tasks. Although technically the responsible roles will automatically be accountable too they may not necessarily have any high stakes. It is vital to keep just one A for each task to avoid any decisional conflicts.

Consulted
These are usually the knowledge sources whose collaboration is necessary to reach the task and project goals. They often are substantially opinionating on different subtasks.

Informed
These can and cannot belong to the core task force and can be acting as a “Responsible” in any other correlated task of the project. They are given all the latest task updates on a regular basis.
How to make a RACI chart?

Variations of RACI
RACI-VS
RACI-VS offers two extra indicators i.e. Verification (V) and Sign-Off (S). In core RACI, there is a chance of missing out any completion details against any task. To overcome any possible deficiencies in any task, RACI-VS allows marking those roles as “V” who will scrutinize the quality and correctness of a given specific task. And to supervise both “V” and “R” | “A” roles, there will be a role “S”-Sign-off who will provide the task completion verdict by approving it.
RACIO (or CAIRO)
RACIO offers an extra participation type “O” which often means “Omitted” or “Out of the Loop”. It just allows explicit mentioning of the roles excluded from the scope of a certain task. This helps in clarifying the engaged and unengaged resources in a task/project.
RASCI
“S” which stands for “Support” is a participation type which is similar to “Consult” in terms of the kind of involvement e.g. providing knowledge and resources to a task/project, but differs in the involvement duration and end goals. “Support” roles seek the completion of the task and remains actively involved throughout the task/project timeline. Whereas, the Consultancy roles do not have any such aims.
Other Variations
- DRASCI: it is just like RASCI but has a “D-Driver” who centrally delegates the responsibilities.
- DACI: it replaces “D-Driver” with “R-Responsible” in RACI. learn more
- RATSI: it’s a further derivation of RASCI which highlights the actual “T-Task” performers which can further help in detailed Resource evaluation.
What is RAPID?
RAPID is quite different from RACI. It focuses on assigning decision-making responsibilities between different roles, unlike RACI which is purely task-driven. The need for RAPID originated with the growth of continuously evolving and collaborating hierarchies of one or more companies or teams where there are multi-level managerial and leadership roles against any single decision.
RAPID has participants who:
- R: Make Recommendation
- A: Establish Agreement
- P: Perform and Execute
- I: Provide Necessary Inputs
- D: Make centralized Decisions and enforce them

RACI vs RAPID – How to choose?
Do NOT base your decision on which consulting / auditing firm you are using because they will push you towards one vs. the other based purely on their internal corporate approach standard. If you aren’t sure which methodology to adopt, best thing to do it to create a pros-cons chart based on your challenges/goals and corporate structure to evaluate which one will suit your needs best. None of the matrices can be labeled as good or bad. The effectiveness of each depends completely upon the relevance of the matrix with respect to the nature of the project, tasks and work body’s hierarchy. Then next best step is to take it on a test run with some real-world tasks, processes and projects before adopting one or the other approach enterprise wide. The test phase will quickly highlight the shortcomings of each method.
Another important heuristic to understand the applicability is to calculate the overall costs of adoption of a certain matrix and compare it to your process models to see if it is affordable in terms of time and money and can do more good than bad. RACI is usually less costly and more beneficial because usually, the task rarely is so large and complex that it would require a whole decision-making structure. Meaning if over used, RAPID can cause major decision making inefficiencies and reduce agility. Also, small to medium-sized corporations are mostly concerned with task completion and rarely make any significant amendments in the hierarchy. RAPID works better only when a certain level of experience and expertise is required to take its full advantage. Otherwise, it can become a burden and result in huge overhead costs.
Best Practice Recommendation
It is best to avoid adopting two or more completely different matrices at once. Practitioners usually go for simpler options so that all the team members can easily understand the bigger picture.
RACI is the most feasible of all the options and it makes it easier for the leaders to start from scratch and improvise to find the best-fitted variation, however, it has shortcomings within real-world situations. Hence, our recommendation is to adopt the RASCI & RACI VS extensions as part of your responsibility assignment program.
Enhancing Role Clarity with RASCI-VS in EPC
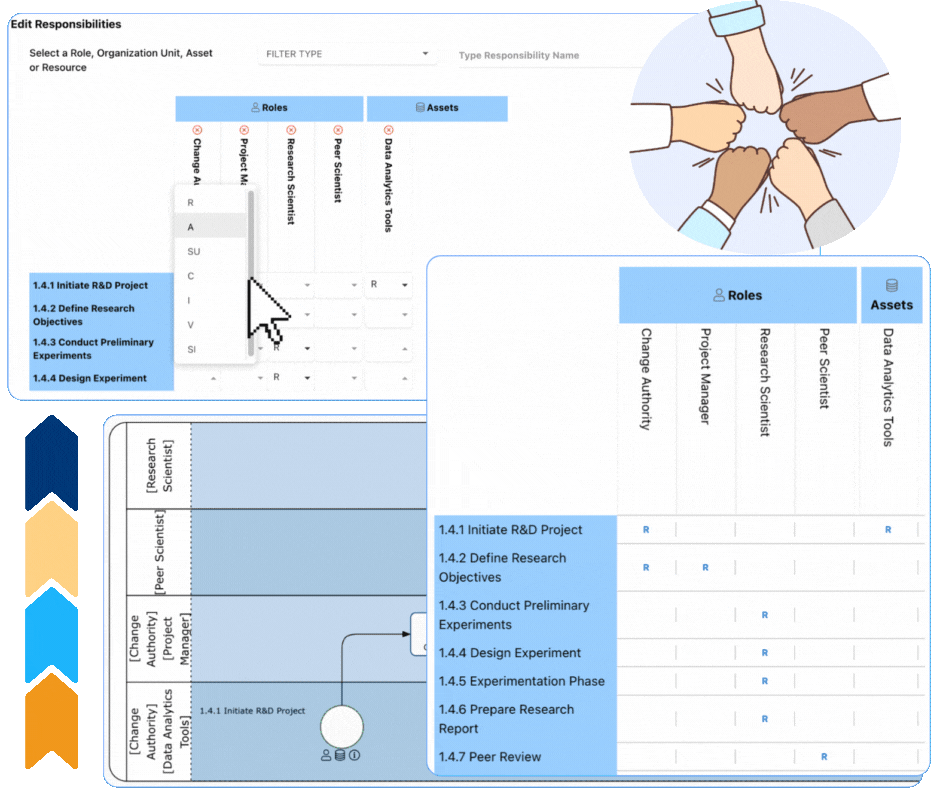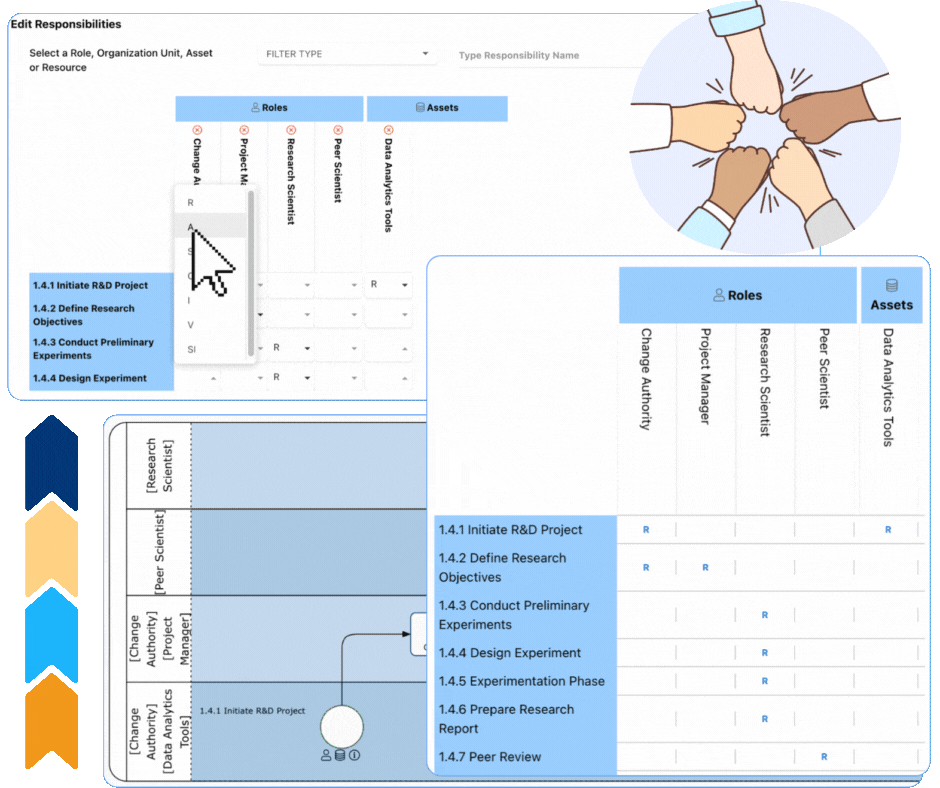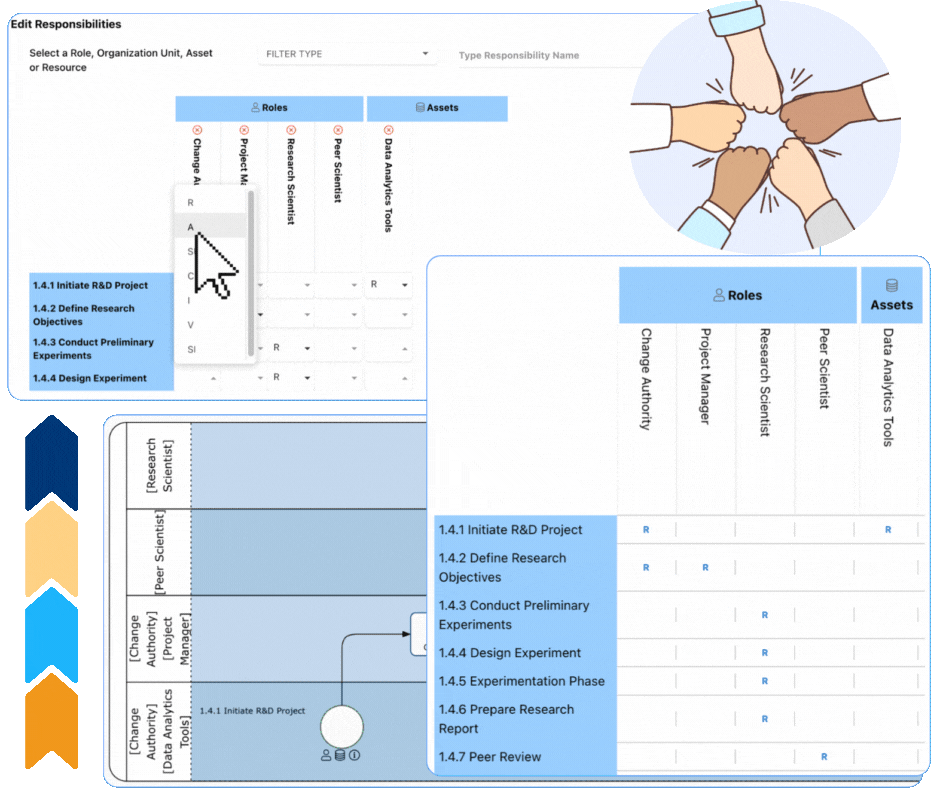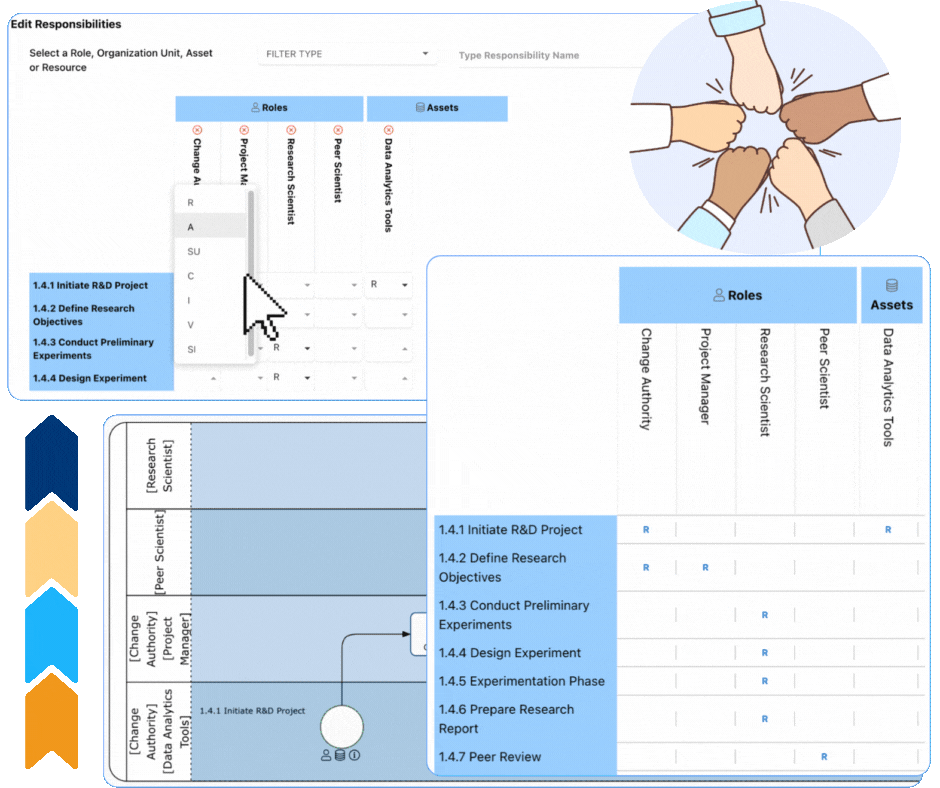

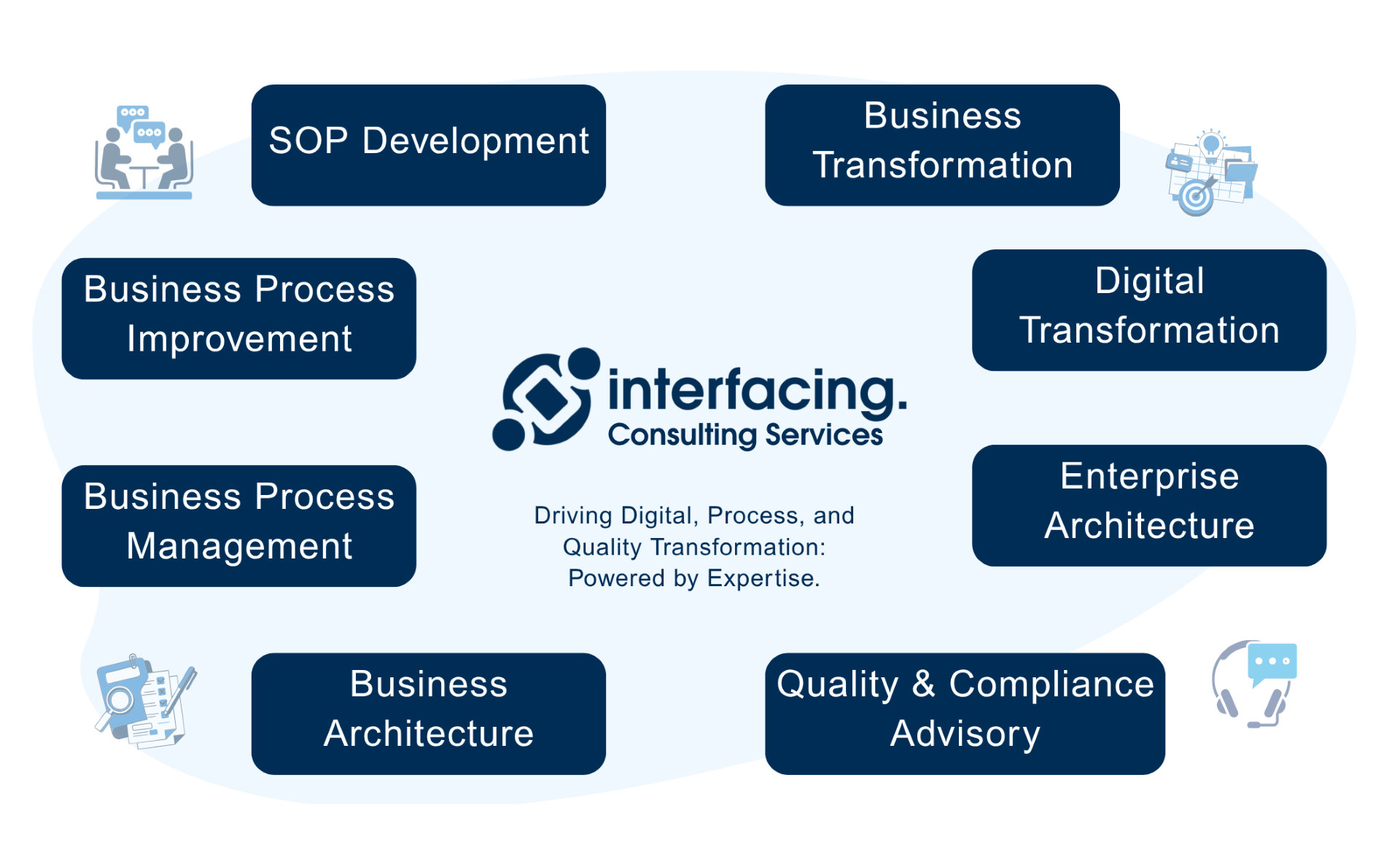
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
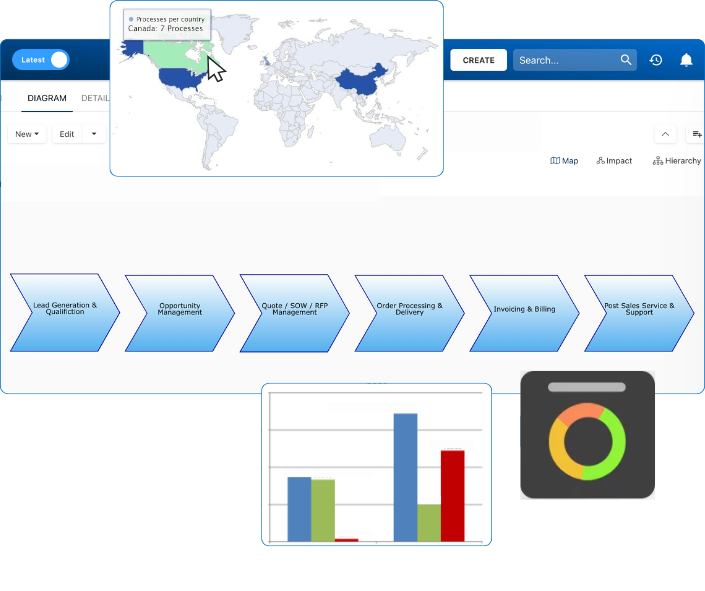
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Trusted by Customers Worldwide!
More than 400+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms