- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
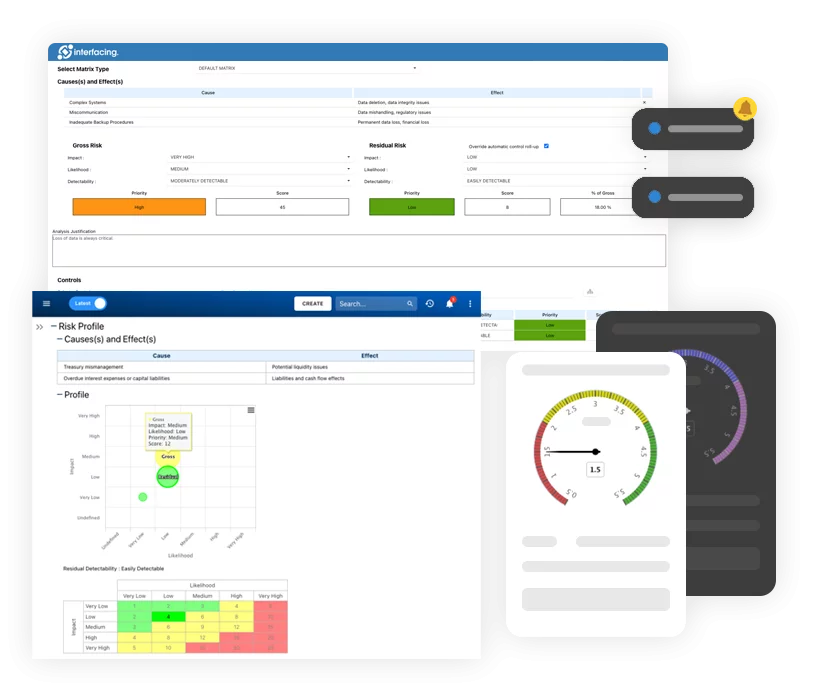
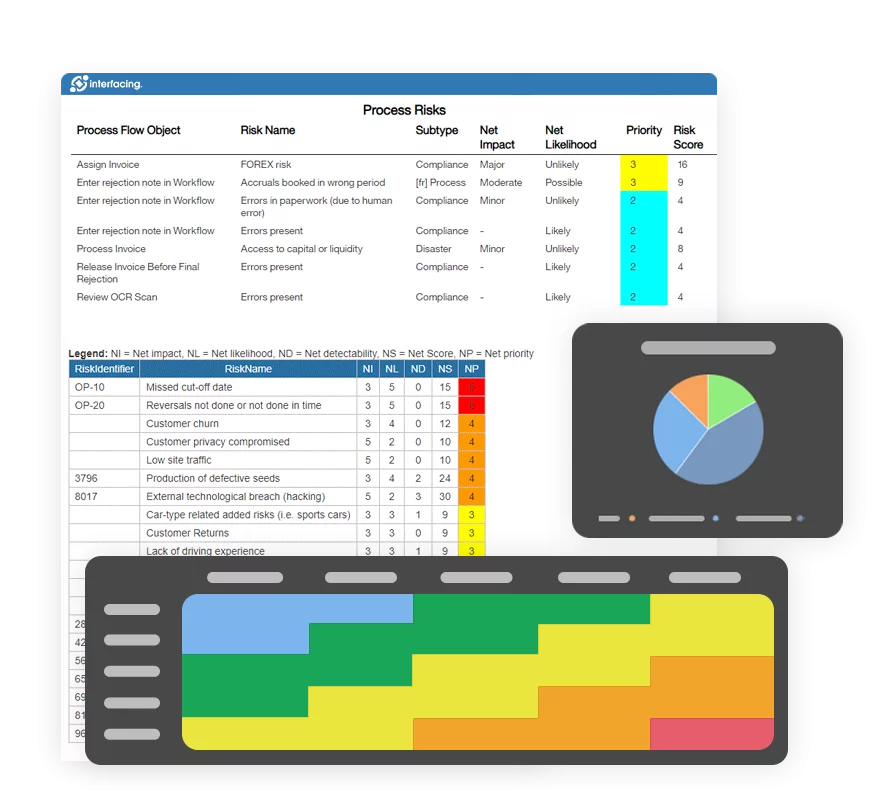
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


What is a Digital Signature?
Please Select contact form.
Unlocking the Potential of Digital Signatures: Secure, Fast & Reliable

What is a Digital Signature?
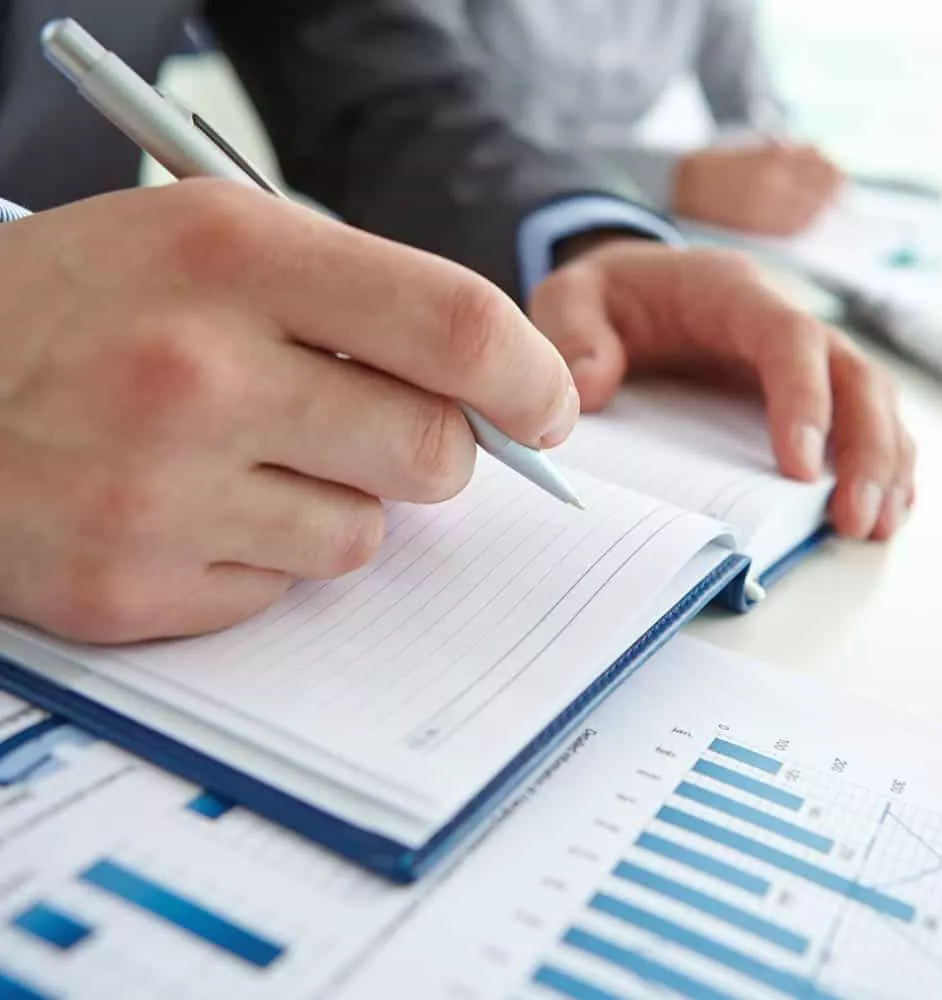
Think about a digital signature like an “electronic fingerprint”. Using a securely coded message, the digital signature associates the signer with a document in a recorded and secure transaction. The standard accepted format for digital signatures is called a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). This provides the highest level of security and is universally accepted as a specific type of electronic signature (eSignature).
Digital Signature vs. Electronic Signature
eSignatures covers a fairly broad category encompassing many types of electronic signatures. This category includes digital signatures which is one specific type of eSignature. Both digital signatures and other solutions in the eSignature category allows you to authenticate and sign documents. What the difference is though is in the acceptance of a digital signature versus all other types of eSignatures due to technical implementation, legal, cultural, and even geographical use.
This means that specifically, eSignatures varies greatly between countries that may use more open technology-neutral laws – Canada, United States, United Kingdom and Australia – to those countries using technology based on local standards – European Union, South America, Asia. Additionally, certain industries will support standards that a specific digital signature technology will be based on.


So How does a Digital Signature Work?
Imagine digital signatures as similar to a handwritten signature. They are each unique to the signer.
As an example, here at Interfacing, we follow a specific protocol called PKI. This allows for us to use FDA 21 CFR part 11, which uses the highest global standards in place (more about that later on). PKI requires the document provider to generate two keys. These keys are mathematical algorithms (long numbers) in which one will be a private key and the other is a public key.


Now when a document is electronically signed, the signature is created by using the signer’s private key, which of course is kept securely in place by the signer. This is now where the mathematical algorithm comes in. It will act as a cypher and create data to match the signed document. This process is known as a “hash” and will encrypt the data. The result is that the encrypted data is now the digital signature. This signature will also show the time the document was electronically signed. At this point, if for whatever reason the document is changed, the digital signature will become automatically invalidated.
Let’s look at an example. Amanda has just signed an electronic agreement to sell her home using her private key. The buyer, Nicholas, now receives the document. Nicholas also received the public key that came with the document. If this public key cannot validate the signature (using the cypher created by the keys), it means that this signature is either not Amanda’s or that the document was changed since it was signed. Her signature is now considered invalid.
When we talk about the integrity of a digital eSignature, we need to discuss how PKI’s requirement is that the keys need to be created, used, and saved all in a secure form. This manner of security normally requires the use of a reliable Certificate Authority (CA). RSA is one company, for example, that provides secure certification.
How You Benefit with Digital Signatures:
Enterprise Process Center Suite

All details included to prevent tampering or forgery
Once the document has been certified, it will include the users signature image, timestamp, user info, and document encryption. Each detail supporting the digital signature will be listed in the PDF Audit tab and verified accordingly.

The value is in time savings
With Enterprise Process Center Suite, you will no longer need to manually generate documents in one tool then load them to another tool, sign them, and then manually bring them back again. This is done automatically for you.

Auto re-certification. An industry leading innovation
As an industry leading innovation, Enterprise Process Center Suite will auto re-certify that both the public key and private key. information matches at the point of audit verification. You will see this with a confirmation seal. Normally this verification is done manually but our Enterprise Process Center Suite will accomplish this task automatically, allowing the user to easily identify if the seal confirms successful verification. Without the seal, the document will be recognized as having been tampered with.

Built out a customized Docker based robust, re-usable digital-signature micro-service.
As a result, we support many different aspects of digital signature technology. For example, we support the PDF e-signature standard, allowing you to digitally sign any PDF. Additionally we can also digitally sign any unit of data content using this method.
So when a user approves a document, we can digitally sign the PDF (human-centric) while at the same time, digitally sign the database content (data-centric) related to the document. This will ensure that we have a complete snapshot of the information: document and data used to generate the document together.
Digital Signature Process in EPC Explained

The process of approval is quick and easy with the selection of authorized individuals assigned with Approver designation.

You may now check your document for authorized verification of the digital signature. The seal to the right indicates it is currenlty certified.

When an auditor intends to review both history and control, they can open the file from the process version history icon to display the following information.
Did you know?
- Enterprise Process Center
Suite digital signatures can contain multiple approvals. - The Enterprise Process Center Suite supports role based workflows – meaning the resource doesn’t need to be assigned directly, a role can be assigned in its place.
- The Enterprise Process Center Suite supports both serial and parallel workflows.
- Approval Suggestion in the Enterprise Process Center Suite recommends the approval workflow based on similarity analysis of related content to help the user decide who is the most applicable approver.
Digital Signature General Workflow in EPC
1. An editor assigns approvers and sends the object for approval.
2. The approvers receive an in-app and email notification.
3. The approvers navigate to the object and see the option to preview the document.
4. The users click on the approved button (assuming they are approving).
5. An authentication window is prompted including the approvers’ signature.
6. Each time a user approves the object, their signature is added into the document.
7. Once the object is published, an auditor can go to the version history of the object and download/preview the document with all the signatures.
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Trusted by Customers Worldwide!
More than 400+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms