- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


Business Continuity Management
Please Select contact form.
Continuity Planning System Automation, Data Integration, Reporting & Analytics

What is Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Definition:
A holistic management process that identifies potential threats and their impacts to the business operations of an organization.
It examines what the impacts of those threats are if they are realized, on the organization and provides a framework to ensure organizational resilience with built-in capabilities, prepared to effectively safeguard the interests of stakeholders, brand reputation, and other value-defined activities.
- Emergency Response,
- Crisis Management
- Disaster Recovery (technology continuity)
- Business Continuity (organizational/operational relocation)
Discover:
BCM / BIA

Proactive compliance
Our process methodology and support for business rules and risk/control management allows for effective process design that has all the appropriate checks and balances.

Create portable process manuals / BCPs
Ability to generate a complete output of your processes and all related information that is ready for print. This makes for an excellent collaborative tool and allows your agents to share information more widely.

Ensure transparency
Know where resources are being used and maintain efficient work habits by planning well in advance.

Implement standard methodologies
Avoid the need for continual trial and error in improving your agency’s operational efficiency; get a head start by taking advantage of industry standards.

Encourage collaboration
By uniting goals and creating a common framework for your agents, they will be able to cooperate at a previously unattained level.

Manage workflow
Integrate your people, processes, and technology by taking advantage of our workflow engine to deliver work to where it is needed and keep all employees up to date with the most important priorities.
DISCOVER
Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Process Management
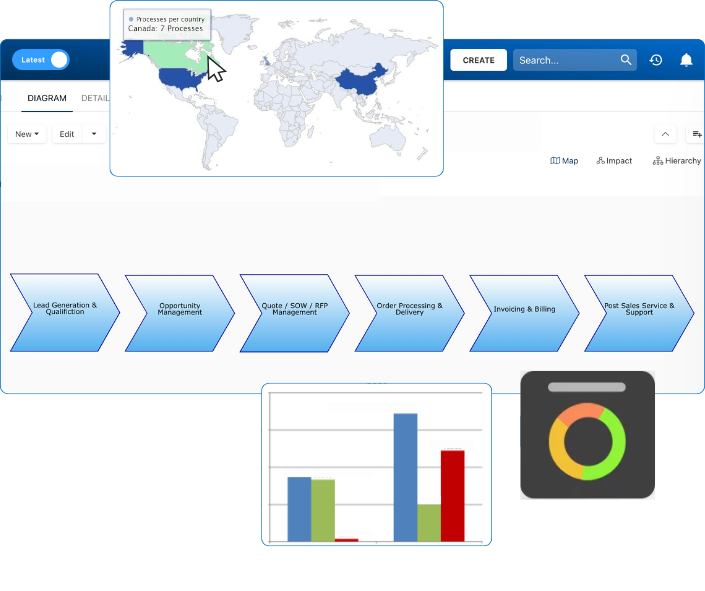
At the core of Enterprise Process Center® is a centralized repository that stores and manages processes and related information within a user-friendly and intuitive environment. EPC links together all complex artifacts of an enterprise: objectives, processes, procedures, employees, departments, customers, suppliers, systems, policies, documents, rules, risks, controls, capabilities and performance indicators and ties them all together as puzzle pieces forming a 360 degree blueprint of the organization’s architecture.


Role and Asset Management
Controlling the operation (e.g. acquisition, ongoing maintenance) as well as renewal and future disposal of organizational assets are all part of the role & asset management process. The benefit to any organization is in the improvement of delivery potential of all assets, while minimizing both costs and risks involved. Competent maintenance and efficient deployment of systems, personnel and processes, using the asset management process, will result in a positive capital overview of the asset lifecycle. By using the RASCI-VS matrix to assign responsibilities, individuals can better understand what is expected from them and see which assets have been made available to them. This will increase employee accountability.
- Recurrent Notifications
- Process Subscriptions
- Read Confirmations
- Automated revision cycles


Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is usually a core requirement for proactive business continuity planning (BCP), not only to understand the key risks and functions of your organization but also to set the priority of systems to bring back to full recovery in case of a disaster. EPCs BIA solution provides a comprehensive proactive multi-factor process impact analysis. The full scope of BIA covers much more than that and can be extended to include any of your own attributes. EPC supports User-defined attributes (UDAs) that can be used to extend any module.
Documenting processes and procedures are required to ensure the fully operational functioning of the organization in case of disaster.
Systems & Assets
This includes physical equipment such as laptops but also hardware such as servers.
Documents
Maintaining an archive of your most important documents in an easily retrievable and secure spot is a sure way to ensure business continuity.
Applications
Key applications may include your CRM, ERP, or other systems that are critical in the continuity of your operations.
Key Controls & Regulatory Requirements
Risk mitigation strategy can permeate through your policies and procedures.
Enterprise Risk Management
Risk policy, identification, assessment, treatment.
Direct Financial Impact
Business revenue losses.
Indirect Financial Impact
Reputation, market share.
Disaster Types
Natural (e.g., fire, flood, earthquake, tornado), financial, technology security, medical (e.g., pandemic).


Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
BCPs are a vital part of any organization. Disruptions and threat impact businesses with major losses in revenue and higher costs that will negatively impact profitability. Relying solely on insurance will not work as it will not cover all costs related to operations and customers who move to your competition. BCPs are created in advance for this purpose and involve key stakeholders and personnel. From minor to catastrophic, business are prone to a variety of potential disasters. Business continuity planning’s purpose involves assisting company’s to continue to operate in the event of major disasters (fire, flood, financial or system breach, pandemic etc.). BCPs are not the same as disaster recovery plans (DRPs). A DRP is focused on IT systems recovery after a crisis only, while a BCP involves addressing disaster loss mitigation and recovery for the entire organization.
Risks and potential business impact
Planning an effective response
Roles and responsibilities
- Communication plan in terms of continuity
- Identifying set of action items
- Prioritizing processes and assets


BCPs and Disaster Recovery Plans
Disaster simulations are an excellent way to validate disaster recovery procedures and resources in order to return to a successfully recovered state. This includes recovery sites and backup systems allocated for business continuity work and disaster recovery. These simulations will involve running a wide variety of disaster scenarios potentially possible in each location. The goal is to restart the technologies necessary to maintain business operations quickly and effectively. This process will also determine if staffing levels will meet the DR plan’s proper execution.
- Run simulation of your continuity and recovery plans
- Run multi-factor scenarios
- Activate relevant actions based on the scenarios, systems & stakeholders affected
- Filter your executable actions per Disaster type, Locations and /or Categories
- Notify relevant stakeholders of actions that will be taken during the execution (or simulation)
- Automatically collect all results for the simulation or execution


Action Item Management
In management, an action item is a documented event, task, activity, or action that needs to take place. Action items are discrete units that can be handled by a single person.
Action items are usually created during a discussion by a group of people who are meeting about one or more topics and during the discussion it is discovered that some kind of action is needed. The act required is then documented as an action item and usually assigned to someone, usually a member of the group. The person to whom the action is assigned is then obligated to perform the action and report back to the group on the results.
- Designate the set of actions necessary for your recovery and continuity plans
- Identify clear ownership to any actions to automatically notify the right owners in case of execution
- Assign relevant applicability for your actions per Disaster type, Locations and /or Categories
- For DR actions, you can track RTO, and RPO on your DR actions as well


Mass Notification Management
Notification Management helps you ensure accurate delivery of important information to the right person at the right time, without depending on employees to take action.
- Choose to Notify Groups, Users, Roles
- In-App Notification
- Email Notification
- SMS Notification


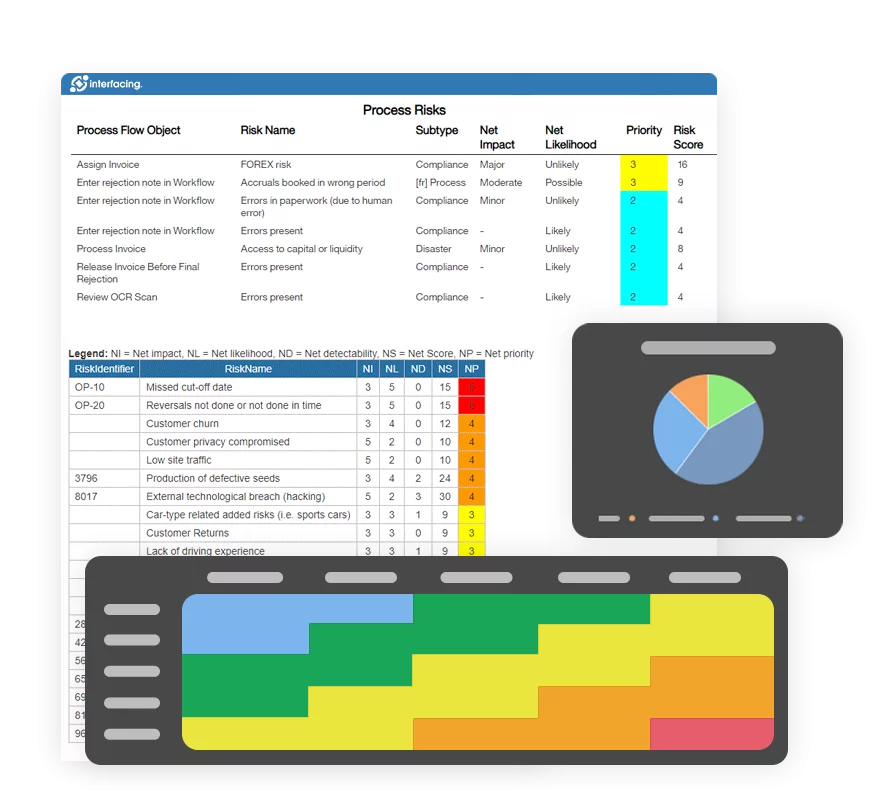
Risk Management
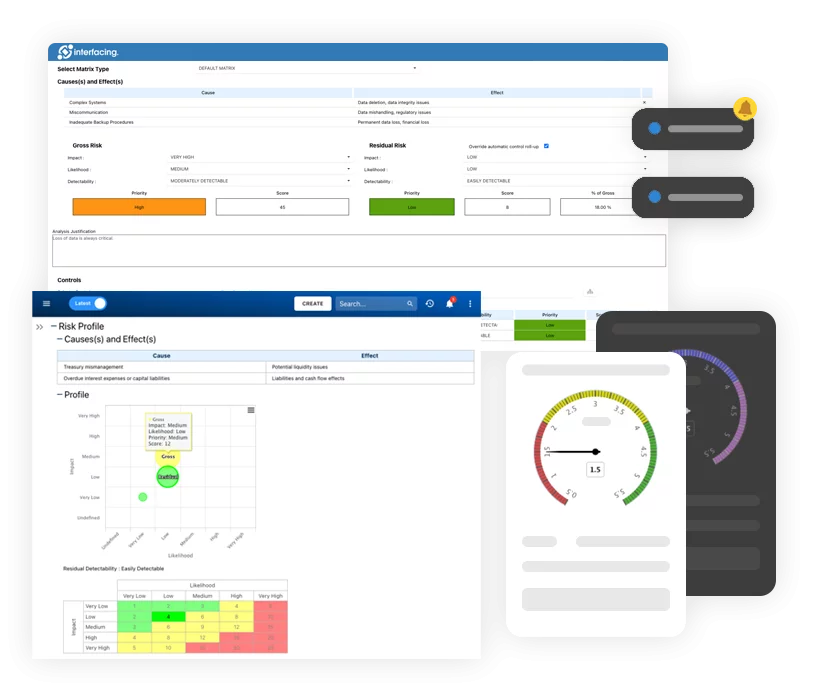
Enterprise Process Center® (EPC) facilitates organizations to be proactive vs. reactive when it comes to risk control and process risk management strategies. Not only is risk management important to protect against disaster striking, but by integrating controls into daily operations you can ensure that quality standards are met and customer satisfaction is maintained. Additionally, there is nothing greater than the cost of “non-compliance”, hence, comprehensive risk and process transparency is a necessity to comply with laws and regulatory requirements such as Sarbanes Oxley, Basel III, IMF, HIPAA, FDA, ISO 15000, among others.
- Detailed risk library including identifier, description, type, category, responsible resources (via RASCI-VS)
- Customizable risk matrices including risk likelihood, impact, score, percentage, color and priority
- Import/export risk details via Excel
- End-to end process visibility associated with risks
- Filter, search, & report risks by attributes
- Reusable risks & controls
- Trigger CAPA based on process & task risk analysis
- View the cause & effect of risks to track critical risk information; risk managers analyze and prioritize risk mitigation
- Extended risk editing (gross risk per process, net risk per control on process, specific controls per process, override roll-up calculation per process)
- Detect a risk’s occurrence; automated risk roll-up algorithm for risk scoring
- Residual risk provides realistic view of potential impact
- Risk matrix visualizes 5 different levels of risks residing in processes


Control Management:Strategies Risk
EPC offers within a single collaborative platform an area where analysts can identify, assess and prioritize risk mitigation plans, and auditors can schedule then execute control audits and implement corrective action plans based on test results. Furthermore, by identifying key risk and control indicators and quantifying threshold limits; management can monitor measures to ensure policies are enforced and standards are maintained.
- Monitor controls through audits
- Recurrent audit scheduling
- Implement CAPAs based on test results
- COSO Cube ERM framework
- General analysis, critical path analysis & high-risk path analysis generated in a dynamic manner
- General controls and risks report & custom report
- Reusable key risk & control indicators (KRIs, KCIs) for more than one source
- Target threshold setting for continuous improvement


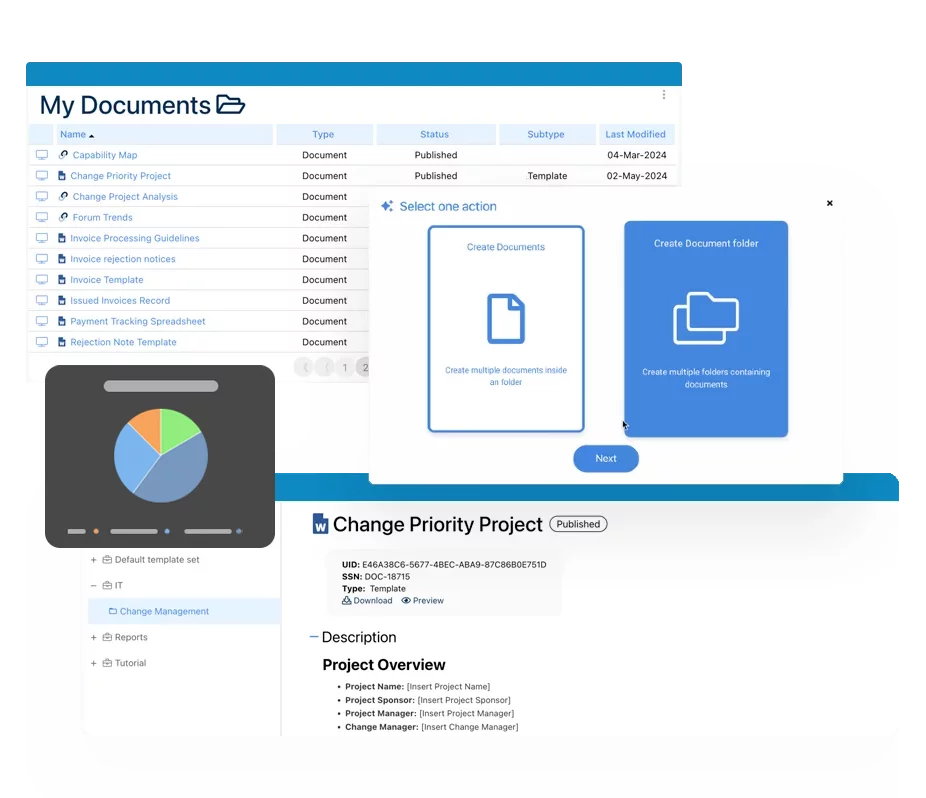
Documents & Records Management
It is nothing short of a challenge, if not near impossible, to maintain a paper-based ISO compliant document system today. Cumbersome, error prone and time-consuming would be the systems feature-set. Your productivity would increase significantly by automating all repetitive tasks associated with QMS document management. EPC’s BCM adds clear visibility into the document lifecycle and will proactively monitor your organizations workflow status while equally improving the quality system efficiency.
Teams dispersed geographically, are now able to connect, collaborate, co-author, proof-read, revise, comment and sign documents – all done electronically and securely within the system. Auto email notifications and read receipts support the systems expediting distribution process throughout the organization. Automatic document retention, printing, periodic reviews, and archiving are all in full compliance and controlled using USFDA 21 CFR part 11 encryption, making audits and quality inspections worry free.
Additionally, your BCM solution provides the secure storage, and management required to maintain accurate and up-to-date Business Continuity Plans that are electronically approved using eSignature; with all documents being downloadable as files.
- Adding new Documents
- Unique IDs and tags by document
- Version control by document
- Archive, move and delete existing documents
- Structure document in a hierarchy, folders
- Creates templates for Records and ability to reuse the workflow template
- Audit log / trail on changes to metadata
- Workflow for approvals, reviews
- Electronic signature on approvals
- Delegation on reviews, approvals
- Notifications, emails for workflows
- System check for publications and approvals
- Collaborate and raise change requests
- Multi-lingual support – UI, Metadata translation suggestions & Documents
- Document Name
- Document ID
- Organizational Unit
- Full Text
- Meta data (Type, Categories, Attributes)
- Filterable columns
- Last modified data
- Last modified by
- Any user-defined attributes (UDAs)


Business Continuity:
Management and Compliance
We understand that the requirements placed on organizations in terms of compliance are very high and that ISO9000, ISO13845, ISO17025, ISO27001, and SOC 2 for example, is an essential part of that program. By using our Integrated Management System BCM solutions, your company gains the preparedness, accountability and consistency that will give you a cutting edge over your competition.
Our tools ensure full visibility and tracking from end-to-end, all the way from the creation and amendment of a regulation to the approval and revision of the content through to the update and retraining of employees for standard operating procedures (SOPs). We see the full lifecycle management as moving parts of a complete ecosystem providing a unique approach that combines regulatory requirements, documents, processes, work instructions, and governance.

International standard that specifies requirements for a QMS. It is the most popular standard in the ISO 9000 series and the only standard in the series to which organizations can certify.
First published in 1987 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The current version of ISO 9001 was released in September 2015.
ISO/IEC 17025 defines the general requirements for competence in testing and calibration for all laboratories. For testing and calibration laboratories, this is the definitive ISO standard.
On many occasions, regulatory authorities and suppliers will not accept test or calibration results from a lab that runs independent of any accreditation oversight. This is where ISO/IEC 17025 (originally known as ISO/ISO/IEC 17025 Guide 25) comes into play.
Lesser known as the longer version, “Systems and Organizations Controls 2”, SOC 2 (or SOC II) is a framework used to assist companies demonstrate security controls that are in place to protect customer data in the cloud. These controls became known as the Trust Services Principles: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and lastly Privacy.
The US FDA QSR (also known as 21 CFR Part 820) was introduced prior to ISO 13485. All medical device companies in the US are required to meet this standard for national distribution but must comply with both regulations in order to distribute devices internationally. US FDA QSR must also be met by international companies wanting to do business with US customers.
Manage the individual pieces of information, assign owners, and ensure governance through approval cycles, and change requests.
Full visibility to understand where records are used and their applicability. You can also maintain digital content with clear accountability, including roles and responsibilities.
Generate complete customizable output of processes and related records such as regulations in a ready-to-print and exportable Word format. You no longer need to manage SOP on paper! The digital SOP is in-sync all the time.
By uniting goals and creating a common framework for your teams, they will be able to cooperate strategically, create change requests, and assign tasks to implementers.
In short, ISO 13485 is an internationally recognized standard that the following countries have adopted: Europe, Canada, Australia and other markets. Excluding Canada, the application of ISO 13485 is not a requirement but is the de facto standard in use today as a measurement of full QMS compliance set forth on medical device regulations.
ISO 27000 is a series of standards that were designed to safeguard organizations’ information assets. ISO 27000 also gives an overview of an Information Security Management System (ISMS), defining and describing the logically organized set of processes that guide organizations to align their business goals and objectives with their information security.
Other countries will have their own criteria to meet nuanced QMS requirements. For example while both Brazil and Japan have their own requirements, they are both based on existing US FDA QSR and ISO 13485 standards.
On a positive note, these standards achieve harmonized quality management requirements to meet US, Canadian, European and all other QMS standards in effect.
Our approach can help with all regulations and compliance's related to pharma production and medical devices (GxP, CFR, GCP, GLP, GMP, HIPAA, ISO9001, medical devices regulations, SOX, BITS, CSA, FDA, FedRAMP, FIPS, FISMA, MHRA, NISP DoD, PCI DSS, SOC 2, U.S. SEC 17a-4 among others).
We fully support digital signature to ensure that the audit trail of all content is secure, time-stamped, with accurate and complete copies of records available for inspection throughout the retention period.
Analyze your records for downstream impacts, and analyze the potential impacts on policies, SOPs, business units and related records.
Integrated and embedded approval workflows to ensure strict control over the change of your records, including validation of changes, evaluation of impacts and highlighting changes.
As part of our ongoing commitment to compliance and ensuring that our clients meet their regulatory requirements, we are always on the lookout for ways to help our clients attain and maintain full compliance. Interfacing is ISO 27001 certified and we are partnering with Amazon Web Services (AWS) for cloud-hosting since their commitment to compliance is proven, with global data centers compliance to SOC 1 Type II and ISO 27001. For more information on AWS compliance for ISO 18345, FDA QSR and GxP, please refer to their compliance program.
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Integration
Discover how we helped other Companies succeed