- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
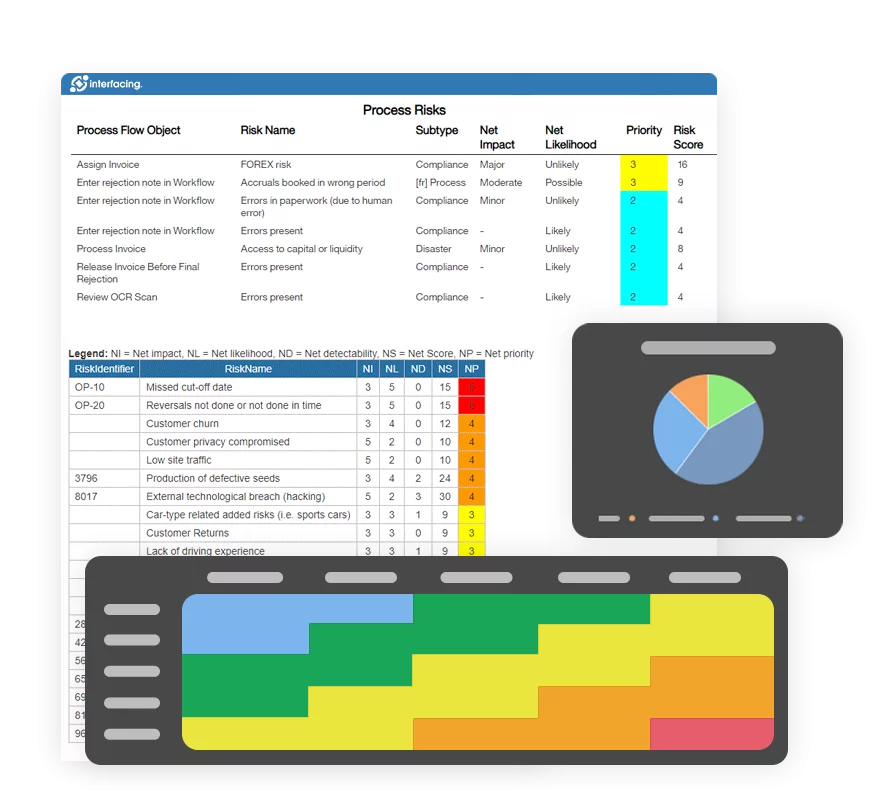 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


Wiki & Glossary
Please Select contact form.
Get familiar with Terminology and terms related to our products

General Industry Terms
Bill 198 is the ”Keeping the Promise for a Strong Economy Act” (Province of Ontario), which includes the Securities Act and Commodity Futures Act. It is part of the Canadian initiative to synchronize regulations with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. There are other provincial equivalents of this act for Quebec, British Columbia, and New Brunswick.
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systems approach to the management of processes, based on the management of process knowledge, control of process performance and conformance, continual improvement of processes, and customer satisfaction.
Business Process Management (BPM) Solution is a set of tools and services that support the creation, management, and optimization of business processes both on a human and application level.
Business Process Modeling (BPM) Software is computer software that lets users create business process management diagrams and integrate process content with critical business entities (departments, resources, etc.)
Business Process Management Systems is a systematic approach to BPM. Business Process Management Systems allow process users to create, store, and manage process information in a way that allows for the wide-scale deployment of business processes.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is the realignment of business process strategies through the use of an analytic tool and an intense consultation process. Business Process Reengineering is a facet of Business Process Management implementation that involves a great deal of risk due to change management.
Business Process Management Notation (BPMN) is a graphical system for the modeling of business processes using a standardized notation developed by the Object Management Group (OMG). BPMN serves as a communicative tool that enables the smooth transition between process design and implementation. Click here for more information: BPMN
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) is a process modeling/orchestration language that standardizes process descriptions in a markup language similar to XML, allowing for the integration of business processes and automated web service applications. BPEL allows business process users to define what business process activities interact with web services defined using web service description standards (WSDL). Click here for more information: BPEL
ISO 9000:2000 International standards that specify the requirements for a quality management system. ISO 9000:2000 provides the framework for any organization that needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide product that meets customer and applicable regulatory requirements and aims to enhance customer satisfaction. ISO 9000 puts strong focus on system approach to management, customer-related processes and continual improvement.
New Basel Capital Accord (Basel II) is a proposed international regulation that would require banks to tighten their integration of different back-office systems and use more sophisticated risk management tools.
Process Mapping (or Modeling) is an Illustrated description of business processes, usually created with flow diagrams. The model contains the relationship between activities, processes, sub-processes and information, as well as roles, the organization and resources.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act is a US legislation to ensure internal controls or rules to govern the creation and documentation of corporate information in financial statements. It establishes new standards for corporate accountability and penalties for corporate wrongdoing.
Service Oriented Architecture is the management of IT systems and applications for the invokation of loosely coupled software services in a process-centric environment. Service Oriented Architecture allows businesses to develop more agile supporting technologies for the execution of business processes management.
Six Sigma (1) is a management program aimed at maximizing business performance and customer satisfaction through continuous process improvement and design. (2) Methodology and tools that rely on statistical techniques to measure and analyze data, identify root causes of performance gaps, and control improved processes. (3) Generic performance metric based on the ability to minimize the process performance variation relative to targets.
Simulation is a way to make predictions about a system or process. A simulation of complex processes helps to discover problems and identify their root causes without directly impacting operations.
Swimlane Diagram is an expanded view of a process showing the flow of work partitioned either by organization unit, resource or role. Swimlane diagrams help clarify who is responsible for a given process or an activity and ease the identification of potential sources of delays in a process (handshakes).
XML (eXtended Markup Language) is a simple and flexible text format that facilitates the exchange of data on the web and between applications.
Product Specific Terms
Activities are the lowest-level process steps in modeling software where actual work is performed. Activities cannot be broken down into further steps. A series of activities may comprise a subprocess, several of which may constitute a process.
Authenticated User is any user added to the Enterprise Process Center who is recognized by the network domain controller. These users may be imported from Active Directory or added manually. Authenticated users automatically belong to both the Everyone and Authenticated Users groups.
Content Administrator can import models, create process sets and libraries, create tags for processes, activities and documents, and has full access to all objects in the system.
Delay a period of inactivity before execution can begin. Activity processing time includes duration and delay.
Description is information provided to help others understand the nature of the activity, process, organization unit, resource, role or material.
Documents are files (text files), file links or URLs (Internet addresses). You can associate documents to most objects.
Duration sets the length of time it takes to perform the activity. Activity processing time includes both duration and delay (if modeled). You cannot specify a Duration for a Trigger or Terminate activity.
Goal is a statement of the expected results. It can include a description of what is to be accomplished, measurable targets or results, and the time frame for the results.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are descriptive time, cost or quality indicators used to capture the performance of a process.
Process is a set of business tasks designed to deliver value to an internal or external client. A process may be comprised of any combination of subprocesses and activities.
Process Owner is the person (Resource) responsible for the process.
Role (Enterprise Role) represents specific skill sets, responsibilities or positions in a business environment. Roles allow the modeler to define criteria required for performing the activity, rather than the specific individuals who will perform the activity. These are also referred to as enterprise roles to differentiate them from security roles.
Scope describes the boundaries of a process and includes the start and end points, the context in which the process is performed and elements excluded from that context.
Sequence Numbers are modeler-defined identifiers for processes and activities. A process and its activities have the same sequence numbers in each process that references it.
Suppliers are the providers of the required input of a process. Represented as organization groups.
Viewer is a role assigned to a user for an object in a model such as a process, library, organization unit, or a document. This role allows the user to view the object or document and its attributes, and participate in discussions.
Get familiar with BPM Terminology and terms related to our products

Request Free Demo
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!